JAVA IO框架
目录
1. 流
- 概念:
内存与存储设备之间传输数据的通道。
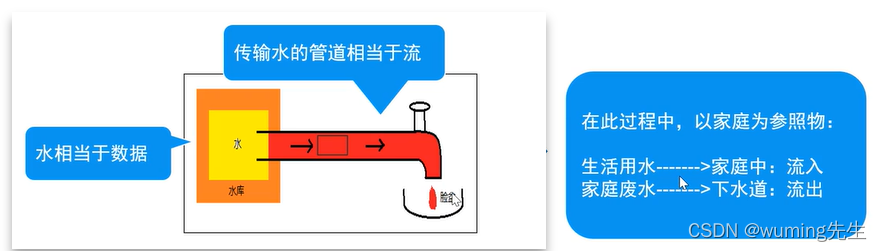
- 分类
- 按方向【重点】:
输入流:将<存储设备>中的内容读入到<内存>中。
输出流:将<内存>中的内容写入到<存储设备>中。

- 按单位:
字节流:以字节为单位,可以读写所有数据。
字符流:以字符为单位,只能读写文本数据。 - 按功能:
节点流:具有实际传输数据的读写功能。
过滤流:在节点流的基础之上增强功能。
- 按方向【重点】:
字节流
抽象父类
//InputStream 字节输入流 public int read(){} public int read(byte[] b){} public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len){} // OutputStream 字节输出流 public void write(int n){} public void write(byte[] b){} public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len){}
文件字节流
文件输入流
psvm(String[] args) throws Exception{ // 1 创建FileInputStream 并指定文件路径 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:\\abc.txt"); // 2 读取文件 // fis.read(); // 2.1单字节读取 int data = 0; while((data = fis.read()) != -1){ sout((char)data); } // 2.2 一次读取多个字节 byte[] buf = new byte[3]; // 大小为3的缓存区 int count = fis.read(buf); // 一次读3个 sout(new String(buf)); sout(count); int count2 = fis.read(buf); // 再读3个 sout(new String(buf)); sout(count2); // 上述优化后 int count = 0; while((count = fis.read(buf)) != -1){ sout(new String(buf, 0, count)); } // 3 关闭 fis.close(); }
文件输出流
psvm(String[] args) throws Exception{ // 1 创建文件字节输出流 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("路径", true);// true表示不覆盖 接着写 // 2 写入文件 fos.write(97); fos.write('a'); // String string = "hello world"; fos.write(string.getByte()); // 3 关闭 fos.close(); }
文件字节流的案例
复制图片
// 1 创建流 // 1.1 文件字节输入流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("输入图片路径"); // 1.2 文件字节输出流 FileInputStream fos = new FileOutpuStream("输出图片路径"); // 2 边读边写 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; int count = 0; while((count = fis.read(buf)) != -1){ fos.write(buf, 0, count); } // 3 关闭 fis.close(); fos.close();
字节缓冲流
缓冲流:BufferedInputStream/ BufferedOutputStream
- 提高IO效率,减少访问磁盘次数
- 数据存储在缓冲区中,flush是将缓冲区的内容写入文件中,也可以直接close
输入
// 使用字节缓冲流 读取 文件 psvm(String[] args) throws Exception{ // 1 创建BufferedInputStream FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("路径"); BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); // 2 读取 int data = 0; while((data = bis.read()) != -1){ sout((char)data); } // 用自己创建的缓冲流 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; int count = 0; while((count = bis.read(buf)) != -1){ sout(new String(buf, 0, count)); } // 3 关闭 bis.close(); }
输出
// 使用字节缓冲流 写入 文件 psvm(String[] args) throws Exception{ // 1 创建BufferedInputStream FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("路径"); BufferedOutputStream bis = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); // 2 写入文件 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++){ bos.write("hello".getBytes());// 写入8k缓冲区 bos.flush(); // 刷新到硬盘 } // 3 关闭 bos.close(); }
对象流
ObjectOutputStream / ObjectInputStream
- 增强了缓冲区功能
- 增强了读写8种基本数据类型和字符串的功能
- 增强了读写对象的功能
- readObject() 从流中读取一个对象
- writeObject(Object obj) 向流中写入一个对象
- 使用流传输对象的过程称为序列化、反序列化
序列化
序列化就是把对象以文件的形式保存在磁盘中
// 使用objectoutputStream实现序列化 psvm(String[] args){ // 1. 创建对象流 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\\st.bin"); ObjectOutputSream oos = new objectOutputSream(fos); // 2. 序列化(写入操作) Student zhangsan = new Student("zs", 20); oos.WriteObject(zhangsan); // 3. 关闭 oos.close(); sout("序列化完毕"); }
反序列化
把对象从磁盘中读到内存中
// 使用ObjectInputSteam实现反序列化(读取重构对象) psvm(String[] args){ // 1. 创建对象流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:\\stu.bin"); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis); // 2. 读取文件(反序列化) Student s = (Student)ois.readObject(); // 3. 关闭 ois.close(); sout("执行完毕"); sout(s.toString()); }
注意事项
- 某个类要想序列化必须实现Serializable接口
- 序列化类中对象属性要求实现Serializable接口
- 序列化版本号ID,保证序列化的类和反序列化的类是同一个类
- 使用transient修饰属性,这个属性就不能序列化
- 静态属性不能序列化
- 序列化多个对象,可以借助集合来实现
字符流
字符流中的函数有默认的编码方式
字节流是二进制读取,而字符流是安装字符个数进行读取
reader 字符输入流 public int read(){} public int read(char[] c){} public int read(char[] b, int off, int len){} Writer 字符输出流 public void write(int n){} public void write(String str){} public void write(char[] c){}
文件字符输入流
// 1. 创建FileReader 文件字符输入流 FileReader fr = new FileReader(".."); // 2. 读取 // 2.1 单个字符读取(读取到文件末尾返回-1.否则返回文件中的字符) int data = 0; while((data = fr.read()) != -1){ sout((char)data);// 读取一个字符 } char[] buf = new char[2];// 字符缓冲区读取 int count = 0; while((count = fr.read(buf) != -1)){ sout(new String(buf, 0, count)); } // 3. 关闭 fr.close();
文件字符输出流
// 1. 创建FileWriter对象 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(".."); // 2. 写入 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++){ fw.write("写入的内容"); fw.flush(); } // 3. 关闭 fw.close(); sout("执行完毕");
字符流实现文本文件的复制
不能复制图片,因为字符流以某种编码方式解析数据,而图片没有数据
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(new File("hello.txt")); FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(new File("copy.txt")); int len = 0; char[] buffer = new char[100]; while ((len = fileReader.read(buffer))!= -1){ System.out.println(new String(buffer,0,len)); fileWriter.write(buffer,0,len); fileWriter.flush(); } fileReader.close(); fileWriter.close(); } }
字符缓冲流
BufferedReader / BufferedWriter
高效读写、支持输入换行符、可一次写一行读一行
输入流
psvm(String[] args) throws Exception{ // 创建缓冲流 FileReader fr = new FileReader(".."); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr); // 读取 // 1. 第一种方式 char[] buf = new char[1024]; int count = 0; while((count = br.read(buf)) != -1){ sout(new String(buf, 0, count)); } // 2. 第二种方式 一行一行读取 String line = null; while((line = br.readLine()) != null){ sout(line); } // 关闭 br.close(); }
输出流
psvm(String[] args){ // 1. 创建BufferedWriter对象 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(".."); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw); // 2. 写入 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++){ bw.write("写入的内容"); vw.newLine(); // 写入一个换行符 bw.flush(); } // 3. 关闭 bw.close(); // 此时会自动关闭fw }
转换流
桥转换流 InputStreamReader / OutputStreamWriter
可将字节流转换为字符流
可设置字符的编码方式
输入流
psvm(String[] args) throws Exception{ // 1 创建InputStreamReader对象 FileInputStream fis = new FisInputStream(".."); InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "utf-8"); // 2 读取文件 int data = 0; while((data = isr.read()) != -1){ sout((char)data); } // 3 关闭 isr.close(); }
输出流
psvm(String[] args) throws Exception{ // 1 创建OutputStreamReader对象 FileOutputStream fos = new FisOutputStream(".."); OutputStreamWRITER osw = new OutputStreamReader(fos, "utf-8"); // 2 写入 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++){ osw.write("写入内容"); osw.flush(); } // 3 关闭 osw.close(); }
File类
概念:代表物理盘符中的一个文件或者文件夹
/* File类的使用 1. 分隔符 2. 文件操作 3. 文件夹操作 */ public class Demo{ psvm(String[] args){ separator(); } // 1. 分隔符 public static void separator(){ sout("路径分隔符" + File.pathSeparator); sout("名称分隔符" + File.separator); } // 2. 文件操作 public static void fileOpen(){ // 1. 创建文件 if(!file.exists()){ // 是否存在 File file = new File("..."); boolean b = file.creatNewFile(); } // 2. 删除文件 // 2.1 直接删除 file.delete(); // 成功true // 2.2 使用jvm退出时删除 file.deleteOnExit(); // 3. 获取文件信息 sout("获取绝对路径" + file.getAbsolutePaht()); sout("获取路径" + file.getPath()); sout("获取文件名称" + file.getName()); sout("获取夫目录" + file.getParent()); sout("获取文件长度" + file.length()); sout("文件创建时间" + new Date(file.lashModified()).toLocalString()); // 4. 判断 sout("是否可写" + file.canWrite()); sout("是否是文件" + file.isFile()); sout("是否隐藏" + file.isHidden()); } // 文件夹操作 public static void directoryOpe() throws Exception{ // 1. 创建文件夹 File dir = new File("..."); sout(dir.toString()); if(!dir.exists()){ //dir.mkdir(); // 只能创建单级目录 dir.mkdirs(); // 创建多级目录 } // 2. 删除文件夹 // 2.1 直接删除 dir.delete(); // 只能删除最底层空目录 // 2.2 使用jvm删除 dir.deleteOnExit(); // 3. 获取文件夹信息 sout("获取绝对路径" + dir.getAbsolutePaht()); sout("获取路径" + dir.getPath()); sout("获取文件名称" + dir.getName()); sout("获取夫目录" + dir.getParent()); sout("获取文件长度" + dir.length()); sout("文件夹创建时间" + new Date(dir.lashModified()).toLocalString()); // 4. 判断 sout("是否是文件夹" + dir.isFile()); sout("是否隐藏" + dir.isHidden()); // 5. 遍历文件夹 File dir2 = new File("..."); String[] files = dir2.list(); for(String string : files){ sout(string); } // FileFilter接口的使用 File[] files2 = dir2.listFiles(new FileFilter(){ @Override public boolean accept(File pathname){ if(pathname.getName().endsWith(".jpg")){ return true; } return false; } }); for(File file : files2){ sout(file.getName()); } } }
例子:遍历文件夹
psvm(String[] args){ listDir(new File("d:\\myfiles")); } public static void listDir(File dir){ File[] files = dir.listFiles(); sout(dir.getAbsolutePath()); if(files != null && files.length > 0){ for(File file : files){ if(file.isDirectory()){ listDir(file); // 递归 }else { sout(file.getAbsolutePath()); } } } }
删除文件夹
public static void deleteDir(File dir){ File[] files = dir.listFiles(); if(files != null && files.length > 0){ for(File file : files){ if(file.idDirectory()){ deleteDir(file); // 递归 }else{ // 删除文件 sout(file.getAbsolutePath() + "删除" + file.delete()); } } } }
本文来自博客园,作者:墨镜一戴谁也不爱,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hnuzmh/p/16204244.html




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律