异步调用--@Async使用方法说明
使用场景
Spring Boot中@Async和Future的使用场景适合于以下场景:
- 当前运行的任务可以分为N步分解时,例如一个统计需要统计三项数据,分别来源于三个表,那么我们可以把统计分为三个接口,在控制层使用Future调用任务。这种情况在控制层还是处于阻塞状态。
- 当前运行的任务不关心另外一个任务的运行结果,我们可以直接使用@Async实现异步调用。
- 其它需要异步调用的方法。
下面我们使用一个Spring Boot工程说明这1、2两种情况:
代码详解
- pom.xml引入spring-boot-starter-web。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.新建一个接口:PiceaService,里面包含三个方法
public interface PiceaService {
//无返回参数方法
void asyncTask() throws Exception;
//有返回参数方法
Future<String> asyncTaskFuture() throws Exception;
//有返回参数方法2
Future<String> asyncTaskFuture2() throws Exception;
}
3.新建接口实现类 PiceaServiceImpl。
要点:
1)注意每个方法上面的注解@Async,这个一定要写,否则就不是异步任务
@Service
public class PiceaServiceImpl implements PiceaService {
@Async
@Override
public void asyncTask() throws Exception {
System.out.println("无返回异步线程,线程名:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("无返回异步处理方法-----start-------");
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("无返回异步处理方法------end--------");
}
@Async
@Override
public Future<String> asyncTaskFuture() throws Exception {
System.out.println("有返回睡眠异步线程,线程名:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("有返回睡眠异步处理方法-----start-------1---");
int k = 1;
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("有返回睡眠异步处理方法-----end----------1--");
return new AsyncResult<String>(String.valueOf(k));
}
@Async
@Override
public Future<String> asyncTaskFuture2() throws Exception {
System.out.println("有返回异步线程,线程名:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("有返回异步处理方法-----start------------2---");
int k = 2;
System.out.println("有返回异步处理方法-----end--------------2---");
return new AsyncResult<String> (String.valueOf(k));
}
}
4.然后我们建立一个控制类 PiceaContoller。
@RestController
public class PiceaContoller {
@Autowired
private PiceaService piceaService;
@RequestMapping("/asyncTask")
public void asyncTask() throws Exception {
piceaService.asyncTask();
}
@RequestMapping("/asyncTaskFuture")
public String asyncTaskFuture() throws Exception {
String ret = null;
//异步先执行任务1
Future<String> future = piceaService.asyncTaskFuture();
//异步执行任务2
Future<String> future2 = piceaService.asyncTaskFuture2();
String ret1 = null;
String ret2 = null;
//获取任务1执行结果
while (true) {
if (future.isDone()){
ret1 = future.get();
break;
}
}
//获取任务2执行结果
while (true) {
if (future2.isDone()) {
ret2 = future2.get();
break;
}
}
//任务1结果+任务2结果
ret = ret1 + "+" + ret2;
//最终返回任何合集
return ret;
}
}
5.最后一步,不要忘记在启动类加异步服务开启的注解@EnableAsync。
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootAsync1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootAsync1Application.class, args);
}
}
大功告成!赶紧回家找妈妈!
-
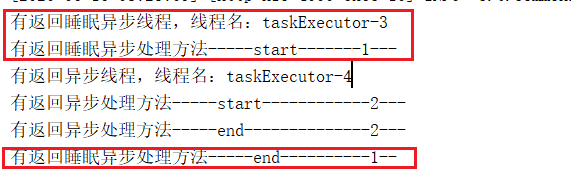
查看结果
从结果上,可以明显看出两个异步执行的任务,因为我在代码中,让任务1休眠了1秒。
总结:
通过异步的方式可以间接提高程序的运行能力,异步适用于逻辑没有关联的工作,比如原题说的统计。
其次也可以创建异步线程池来进行异步控制
线程池使用如下:
- 新建一个线程配置类:ThreadPoolTaskConfig
要点:
1)增加@Configuration注解,确定是配置类。
2)增加@EnableAsync,把异步服务开启转移到线程配置类。
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class ThreadPoolTaskConfig {
private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() *2;
private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE = CORE_POOL_SIZE *4 <256 ? 256 : CORE_POOL_SIZE * 4;
private static final int KEEP_ALIVE_TIME = 10; //允许线程空闲时间(单位为秒)
private static final int QUEUE_CAPACITY = 200; // 缓冲队列数
private static final int AWAIT_TERMINATION = 60;//线程池中任务的等待时间,如果超过这个时候还没有销毁就强制销毁
private static final Boolean WAIT_FOR_TASKS_TO_COMPLETE_ON_SHUTDOWN = true;//用来设置线程池关闭的时候等待所有任务都完成再继续销毁其他的Bean
private static final String THREAD_NAME_PREFIX = "PiceaAsync-Service-"; // 线程池名前缀
/**
* <p>"@Bean("piceaTaskExecutor"),Bean后面的()内容可以省略
* 如果省略则使用方法名<p>
* @author jiangbing.yang
* @date 2019/3/27 11:07
* @params
* @return
* @throws
*/
@Bean("piceaTaskExecutor")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor piceaTaskExecutor () {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(CORE_POOL_SIZE);
taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(MAX_POOL_SIZE);
taskExecutor.setKeepAliveSeconds(KEEP_ALIVE_TIME);
taskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(QUEUE_CAPACITY);
taskExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix(THREAD_NAME_PREFIX);
taskExecutor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(WAIT_FOR_TASKS_TO_COMPLETE_ON_SHUTDOWN);
taskExecutor.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(AWAIT_TERMINATION);
// 线程池对拒绝任务的处理策略
taskExecutor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
// 初始化
taskExecutor.initialize();
return taskExecutor;
}
}
制定异步方法使用线程池执行
@Service
public class PiceaServiceImpl implements PiceaService {
@Async("piceaTaskExecutor")
@Override
public void asyncTask() throws Exception {
System.out.println("异步线程,线程名:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("异步处理方法-----start-------");
System.out.println("------------------------在看貂蝉,不要打扰--------------");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("异步处理方法------end--------");
}
@Async("piceaTaskExecutor")
@Override
public Future<String> asyncTaskFuture() throws Exception {
System.out.println("异步线程,线程名:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("异步处理方法-----start-------asyncTaskFuture---");
int k = 1;
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("异步处理方法-----end---------asyncTaskFuture---");
return new AsyncResult<String> (String.valueOf(k));
}
@Async("piceaTaskExecutor")
@Override
public Future<String> asyncTaskFuture2() throws Exception {
System.out.println("异步线程,线程名:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("异步处理方法-----start-------asyncTaskFuture-----2---");
int k = 2;
System.out.println("异步处理方法-----end---------asyncTaskFuture-----2---");
return new AsyncResult<String> (String.valueOf(k));
}
}


