顺序表
一 顺序表原理
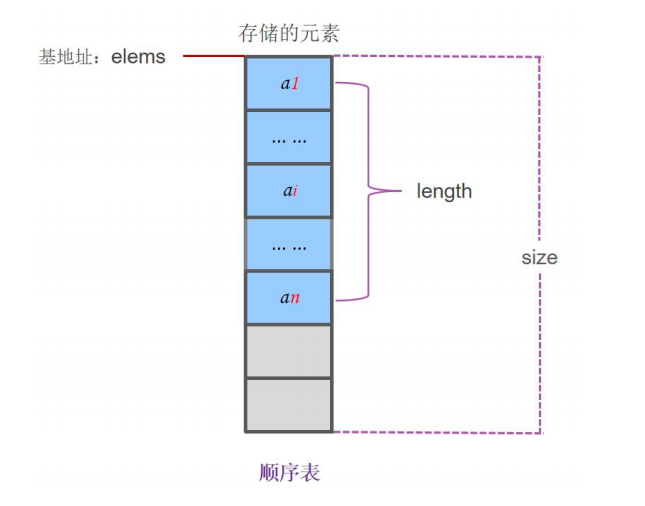
顺序表是简单的一种线性结构,逻辑上相邻的数据在计算机内的存储位置也是相邻的,可以快速定位第几个元素,中间不允许有空值,插入、删除时需要移动大量元素。
顺序表的三个要素:
1.用 elems 记录存储位置的基地址
2.分配一段连续的存储空间 size
3.用 length 记录实际的元素个数,即顺序表的长度
结构体定义
#define MAX_SIZE 100
struct _SqList
{
ElemType *elems; // 顺序表的基地址
int length; // 顺序表的长度
int size; // 顺序表总的空间大小
}
二 顺序表算法实现
2.1 顺序表的初始化
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct _SqList
{
int* elems; // 顺序表的基地址
int length; // 顺序表的长度
int size; // 顺序表总的空间大小
}SqList;
bool initList(SqList& L)
{
L.elems = new int[MAX_SIZE];
if (!L.elems)
{
return false;
}
L.length = 0;
L.size = MAX_SIZE;
}
void listPrint(SqList& L)
{
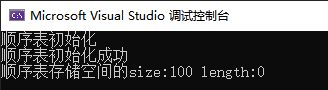
cout << "顺序表存储空间的size:" << L.size << " length:" << L.length << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < L.length; i++)
{
cout << L.elems[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
SqList list;
cout << "顺序表初始化" << endl;
if (initList(list))
{
cout << "顺序表初始化成功" << endl;
}
listPrint(list);
return 0;
}
2.2 顺序表增加元素
bool listAppend(SqList& list, int elem)
{
if (list.length == MAX_SIZE) // 存储空间已经满了
{
return false;
}
list.elems[list.length] = elem;
list.length++;
return true;
}
2.3 顺序表插入元素
bool listInsert(SqList& list, int subscript, int elem)
{
// 插入的位置不合法
if (subscript < 0 || subscript >= list.length)
{
return false;
}
// 存储空间已经满了
if (list.length == list.size)
{
return false;
}
// 循环把元素往后移
for (int i = list.length - 1; i >= subscript; i--)
{
list.elems[i + 1] = list.elems[i];
}
// 插入新元素
list.elems[subscript] = elem;
list.length++;
return true;
}
2.4 顺序表删除元素
bool listDelete(SqList& list, int subscript)
{
if (subscript < 0 || subscript >= list.length)
{
return false;
}
// 删除最后一个元素
if (subscript == list.length - 1)
{
list.length--;
return true;
}
// 循环把元素往前移
for (int i = subscript; i < list.length-1; i++)
{
list.elems[i] = list.elems[i + 1];
}
list.length--;
return true;
}
2.5 顺序表的销毁
void destoryList(SqList& list)
{
if (list.elems)
{
delete[] list.elems;
}
list.length = 0;
list.size = 0;
}
三 顺序表的企业级应用案例
高并发 WEB 服务器中顺序表的应用:
高性能的 web 服务器 Squid 每秒可处理上万并发的请求,从网络连接到服务器的客 户端与服务器端在交互时会保持一种会话(和电话通话的场景类似)。服务器端为了管 理好所有的客户端连接,给每个连接都编了一个唯一的整数编号,叫做文件句柄,简称 fd
为了防止某些恶意连接消耗系统资源,当某个客户端连接超时(在设定的一定时间内没有发送数据)时,服务器就需要关闭这些客户端的连接
具体实现方案:
1.当有新的请求连到服务器时,如果经过服务器频率限制模块判断,貌似恶意连接,则使用顺序表来保存此连接的超时数据,超时值使用时间戳来表示,时间戳是指格林威治时间 1970 年 01 月 01 日 00 时 00 分 00 秒(相当于北京时间 1970 年 01 月 01 日 08 时 00 分 00 秒)起至现在的总秒数,其结构体定义如下:
typedef struct {
int fd;
time_t timeout; // 使用超时时刻的时间戳表示
}ConnTimeout;
2.服务器程序每隔一秒钟扫描一次所有的连接,检查是否超时,如果存在超时的连接,就关闭连接,结束服务,同时将顺序表中的记录清除!
代码实现:
//---------------- timeoutSqList.h ------------------
#ifndef _TIMEOUT_SQLIST_H_
#define _TIMEOUT_SQLIST_H_
#include "webServe.h"
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct
{
ConnTimeout* elems; // 顺序表的基地址
int length; // 顺序表的长度
int size; // 顺序表的空间
}TimeoutSqList;
// 顺序表的接口
bool initList(TimeoutSqList& L);
bool listAppend(TimeoutSqList& list, ConnTimeout elem);
bool listDelete(TimeoutSqList& list, int subscript);
void destoryList(TimeoutSqList& list);
void listPrint(TimeoutSqList& L);
#endif // !_TIMEOUT_SQLIST_H_
//---------------- timeoutSqList.cpp ------------------
#include <iostream>
#include "webServe.h"
#include "timeoutSqList.h"
using namespace std;
bool initList(TimeoutSqList& L)
{
L.elems = new ConnTimeout[MAX_SIZE];
if (!L.elems)
{
return false;
}
L.length = 0;
L.size = MAX_SIZE;
return true;
}
bool listAppend(TimeoutSqList& list, ConnTimeout elem)
{
if (list.length == MAX_SIZE) // 存储空间已经满了
{
return false;
}
list.elems[list.length] = elem;
list.length++;
return true;
}
bool listDelete(TimeoutSqList& list, int subscript)
{
if (subscript < 0 || subscript >= list.length)
{
return false;
}
// 删除最后一个元素
if (subscript == list.length - 1)
{
list.length--;
return true;
}
// 循环把元素往前移
for (int i = subscript; i < list.length - 1; i++)
{
list.elems[i] = list.elems[i + 1];
}
list.length--;
return true;
}
void destoryList(TimeoutSqList& list)
{
if (list.elems)
{
delete[] list.elems;
}
list.length = 0;
list.size = 0;
}
void listPrint(TimeoutSqList& L)
{
cout << "顺序表存储空间的size:" << L.size << " length:" << L.length << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < L.length; i++)
{
cout << "句柄:" << L.elems[i].fd << " 时间戳:" << L.elems[i].timeout << endl;
}
}
//---------------- webServe.h ------------------
#ifndef _WEB_SERVE_H_
#define _WEB_SERVE_H_
#include <time.h>
typedef struct
{
int fd;
time_t timeout; // 使用超时时刻的时间戳表示
}ConnTimeout;
#endif // !_WEB_SERVE_H_
//---------------- main.cpp ------------------
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
#include <Windows.h>
#include "webServe.h"
#include "timeoutSqList.h"
using namespace std;
// 加static: 此函数只能在本文件中调用
// 每一秒中检查一次,看有没有超时的
static void checkTimeouts(TimeoutSqList& list, time_t now)
{
int fd, i;
cout << "检查超时fd..." << endl;
for (i = 0; i < list.length; i++)
{
if (list.elems[i].timeout > now)
{
continue;
}
// 超时,清理连接
fd = list.elems[i].fd;
// 关闭连接
cout << "连接fd=" << fd << "已经超时,关闭连接" << endl;
// 删除顺序表中的元素
listDelete(list, i);
i--;
}
}
int main()
{
time_t now; // 开始的时间
time_t end; // 结束的时间
time_t last_timeout; // 上一次处理timeout的时间
TimeoutSqList list;
initList(list);
time(&now);
end = now + 60;
last_timeout = now;
// 1.模拟频率限制模块通过判断分析,增加恶意连接到顺序表中
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
ConnTimeout e;
e.fd = i;
e.timeout = now+5+2*i;
listAppend(list, e);
}
listPrint(list);
while (now < end)
{
// 用Sleep(1000)的话,服务器在休眠,做不了其它事情,所以不可取
//Sleep(1000);
if (last_timeout + 0.99 < now) // 已经过了1秒钟了
{
checkTimeouts(list, now); // 检测超市连接
last_timeout = now;
}
Sleep(10); // 防止cpu一直在不断的空转
time(&now);
}
return 0;
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现