异常
一 异常处理基本语法
// 异常发生第一现场,抛出异常
void fun()
{
//...
throw 表达式;
//....
}
// 在需要关注异常的地方,捕捉异常
try
{
//...
fun();
//...
}
catch(异常类型 形参)
{
// 异常处理代码...
}
catch(异常类型 形参)
{
// 异常处理代码...
}
catch(...) // 其它异常类型
{
// 异常处理代码
}
注意事项:
- 通过 throw 操作创建一个异常对象并抛弃
- 在需要捕捉异常的地方,将可能抛出异常的程序段嵌在 try 块之中
- 按正常的程序顺序执行到达 try 语句,然后执行 try 块{}内的保护段
- 如果在保护段执行期间没有引起异常,那么跟在 try 块后的 catch 子句就不执 行,程序从 try 块后跟随的最后一个 catch 子句后面的语句继续执行下去
- catch 子句按其在 try 块后出现的顺序被检查,匹配的 catch 子句将捕获并按 catch 子句中的代码处理异常(或继续抛掷异常)
- 如果没有找到匹配,则缺省功能是调用 abort 终止程序
提示:处理不了的异常,我们可以在 catch 的最后一个分支,使用 throw 语法, 继续向调用者 throw。
// 示例
void test(int value) throw(string*, int, float)
{
switch (value)
{
case 1:
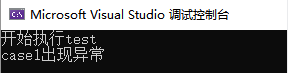
throw new string("case1出现异常"); // 这里new了一个string对象
break;
case 2:
throw 0;
break;
case 3:
throw 0.03f;
break;
}
}
int main()
{
//按正常的程序顺序执行到达 try 语句,然后执行 try 块{}内的保护段
//如果在保护段执行期间没有引起异常,那么跟在 try 块后的 catch 子句就不执行,程序从 try 块后跟随的最后一个 catch 子句后面的语句继续执行下去
try // 保护段
{
cout << "开始执行test" << endl;
test(1);
cout << "test执行结束" << endl; // 发生异常后就不会执行这句
}
//catch 子句按其在 try 块后出现的顺序被检查,匹配的 catch 子句将 捕获并按 catch 子句中的代码处理异常(或继续抛掷异常)
catch (string* str) // 这里是string指针
{
cout << str->c_str() << endl;
delete str;
}
catch (int ret)
{
cout << ret << endl;
}
catch (...) // 处理其他类型的异常
{
cout << "catch...." << endl;
}
//如果没有找到匹配,则缺省功能是调用 abort 终止程序。
return 0;
}
二 异常接口声明
可以在函数声明中列出可能抛出的所有类型异常,加强程序的可读性
void test(int value) throw(string*, int, float);
- 对于异常接口的声明,在函数声明中列出可能抛出的所有异常类型
- 如果没有包含异常接口声明,此函数可以抛出任何类型的异常
- 如果函数声明中列出可能抛出的所有异常类型,那么抛出其它类型的异常将可能导致程序终止
- 如果一个函数不想抛出任何异常,可以使用 throw() 声明
三 异常类型
3.1 throw基本类型
// 第1种情况:throw普通类型
void test(int value) throw(int, float)
{
switch (value)
{
case 1:
throw 1;
break;
case 2:
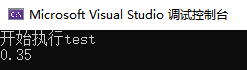
throw 0.35f;
break;
}
}
int main()
{
try
{
cout << "开始执行test" << endl;
test(2);
cout << "test执行结束" << endl;
}
catch (int ret)
{
cout << ret << endl;
}
catch (float ret)
{
cout << ret << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3.2 throw字符串类型
// 第2种情况,throw字符串类型,实际抛出指针
void test(int value)
{
switch (value)
{
case 1:
{
const char* ret1 = "case1异常";
throw ret1;
break;
}
case 2:
{
string ret2("case2异常");
throw ret2;
break;
}
case 3:
{
throw new string("case3异常");
break;
}
}
}
void fun(int value)
{
try
{
test(value);
}
catch(const char* ret)
{
cout << "const char* " << ret << endl;
}
catch (string ret)
{
cout << "string " << ret << endl;
}
catch (string* ret)
{
cout << "string* " << *ret << endl;
delete ret;
}
}
int main()
{
fun(1);
fun(2);
fun(3);
return 0;
}

3.3 throw类对象类型
第3种情况 throw 类类型,最佳的方式是使用引用类型捕捉,抛出匿名对象
当然,如果是动态分配的对象,直接抛出其指针
注意:引用和普通的形参传值不能共存
// 第3种情况 throw 类类型,最佳的方式是使用引用类型捕捉,抛出匿名对象
// 当然,如果是动态分配的对象,直接抛出其指针
// 注意:引用和普通的形参传值不能共存
class Student
{
public:
Student()
{
m_id = 1;
cout << "调用构造函数,id=1" << endl;
}
Student(const Student& other)
{
m_id = 2;
cout << "调用拷贝构造函数,id=2" << endl;
}
~Student()
{
cout << "调用析构函数,id=" << m_id << endl;
}
int m_id;
};
void test()
{
throw Student();
//throw new Student(); // 如果这里是动态分配的对象,直接抛出其指针
}
int main()
{
try
{
test();
}
// 我们这里可以用引用 Student& error,这样就不用调用拷贝构造函数了,引用和普通的形参传值不能共存
catch(Student error) // 最佳方式是用引用进行捕捉 Student& error
{
cout << "Student 异常,id:" << error.m_id << endl;
}
catch(Student* error)
{
cout << "Student* 异常,id:" << error->m_id << endl;
delete error; // 注意这里要进行释放
}
catch (...)
{
cout << "没有捉到具体的异常类型" << endl;
}
return 0;
}

四 继承与异常
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
案例:
设计一个数组类容器 Vector,重载[]操作,数组初始化时,对数组的个数进行有效检查
1) index<0 抛出异常 errNegativeException
2) index = 0 抛出异常 errZeroException
3)index>1000 抛出异常 errTooBigException
4)index<10 抛出异常 errTooSmallException
5)errSizeException 类是以上类的父类,实现有参数构造、并定义 virtual void printError() 输出错误。
*/
// 父类
class errSizeException
{
public:
errSizeException(int size) { m_size = size; }
virtual void printError()
{
cout << "size:" << m_size << endl;
}
protected:
int m_size;
};
class errNegativeException : public errSizeException//index<0
{
public:
errNegativeException(int size):errSizeException(size) { }
virtual void printError()
{
cout << "errNegativeException size:" << m_size << endl;
}
};
class errZeroException : public errSizeException //index = 0
{
public:
errZeroException(int size) :errSizeException(size) { }
virtual void printError()
{
cout << "errZeroException size:" << m_size << endl;
}
};
class errTooBigException : public errSizeException //index>1000
{
public:
errTooBigException(int size) :errSizeException(size) { }
virtual void printError()
{
cout << "errTooBigException size:" << m_size << endl;
}
};
class errTooSmallException : public errSizeException//index < 10
{
public:
errTooSmallException(int size) :errSizeException(size) { }
virtual void printError()
{
cout << "errTooSmallException size:" << m_size << endl;
}
};
class Vector
{
public:
Vector(int len);
Vector(const Vector& other);
~Vector();
int getLength() const;
int& operator[](int index) const; // 要注意访问越界问题
private:
int* m_base;
int m_len;
};
Vector::Vector(int len)
{
if (len < 0)
{
throw errNegativeException(len);
}
else if (len == 0)
{
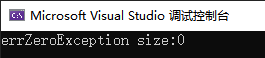
throw errZeroException(len);
}
else if (len > 1000)
{
throw errTooBigException(len);
}
else if (len < 10)
{
throw errTooSmallException(len);
}
m_len = len;
m_base = new int[len];
}
Vector::Vector(const Vector& other)
{
this->m_len = other.m_len;
this->m_base = new int[m_len];
// 拷贝数据
for (int i = 0; i < m_len; i++)
{
m_base[i] = other.m_base[i];
}
}
Vector::~Vector()
{
if (m_base)
{
delete[] m_base;
m_base = NULL;
}
m_len = 0;
}
int Vector::getLength() const
{
return m_len;
}
int& Vector::operator[](int index) const
{
return m_base[index];
}
int main()
{
try
{
Vector v1(0);
for (int i = 0; i < v1.getLength(); i++)
{
v1[i] = 10 + i;
cout << v1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
catch (errSizeException& error) // 这里我们直接用多态,父类的引用指向子类的对象
{
error.printError();
}
return 0;
}
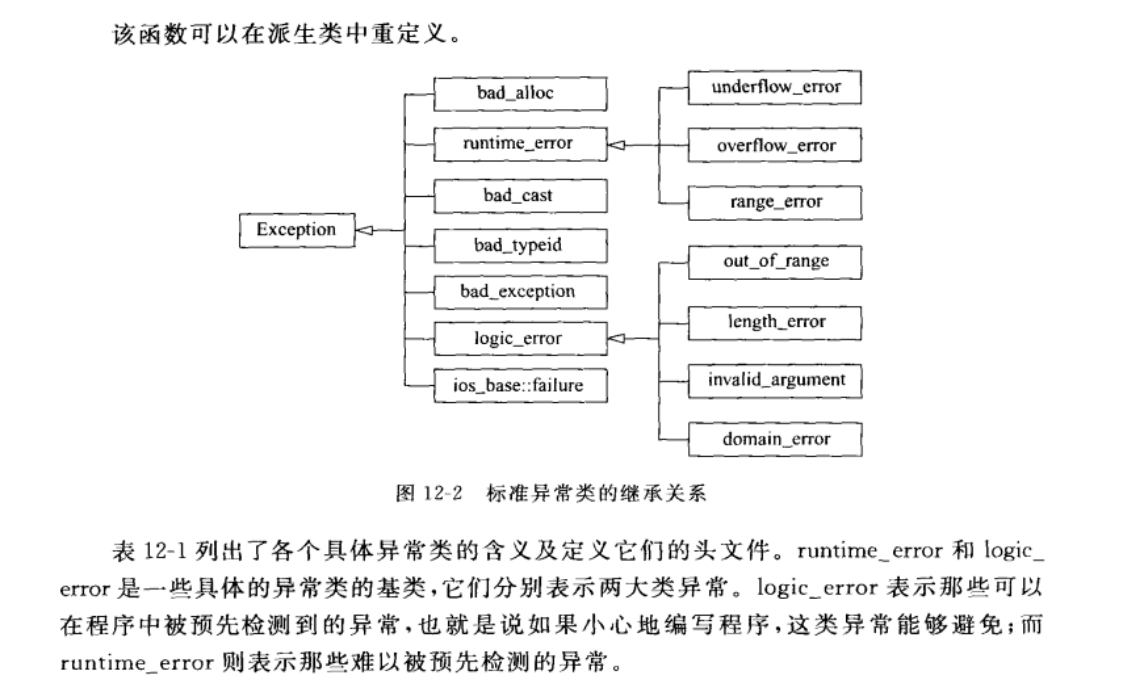
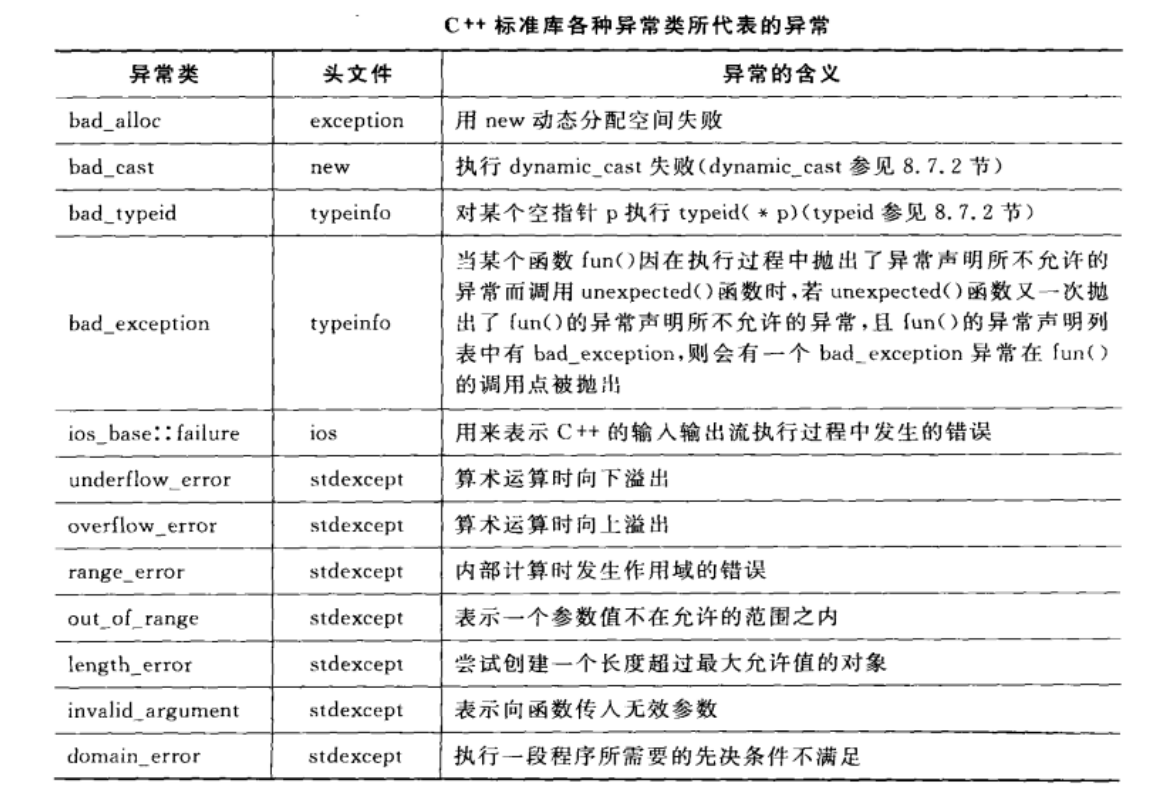
五 标准库里的异常类


#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
Student(int age)
{
if (age > 249)
{
throw out_of_range("年龄太大,你是外星人吗");
}
m_age = age;
}
private:
int m_age;
};
int main()
{
try
{
Student s1(300);
}
catch (out_of_range& error)
{
cout << "捉到异常 " << error.what() << endl;
}
return 0;
}

六 noexcept关键字
noexcept关键字是c++11之后新增的。该关键字会告诉编译器,被修饰的函数不会发生异常,这有利于编译器对程序做更多的优化。
1)noexcept
2)noexcept(expression)
noexcept(true) 表示被修饰的函数不抛出异常,noexcept(false) 表示被修饰的函数会抛出异常。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号