c++文件读写
目录
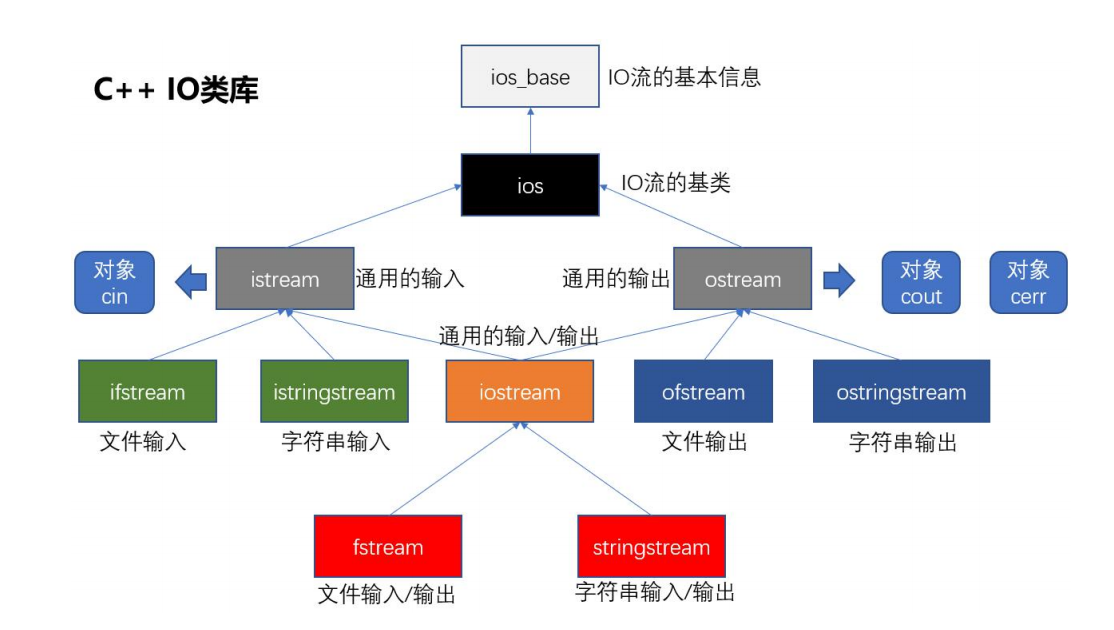
一 c++的 IO 流
c++的io流:

设备:
- 文件
- 控制台
- 特定的数据类型(stringstream)
c++中,必须通过特定的已经定义好的类, 来处理 IO(输入输出)
二 读写文件:文件流
文件流: 对文件进行读写操作
头文件:<fstream>
类库:
- ifstream 对文件输入(读文件)
- ofstream 对文件输出(写文件)
- fstream 对文件输入或输出
三 对文本文件流读写
文件打开方式:
| 模式标志 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ios::in | (对文件的输入)读方式打开文件 |
| ios::out | (对文件的输出)写方式打开文件 |
| ios::trunc | 如果此文件已经存在,就会打开文件之前把文件长度截断为0 |
| ios::app | 尾部追加方式(在尾部写入) |
| ios::ate | 文件打开后,定位到文件尾 |
| ios::binary | 二进制方式(默认是文本方式) |
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string name = "";
int age = 0;
// 写文件
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("user.txt");
if (!outfile.is_open())
{
cout << "outfile 文件打开失败" << endl;
}
// 也可以定义fstream,但是要注意fstream的默认打开方式
// ofstream的默认打开方式是,截断式写入 ios::out | ios::trunc
// fstream的默认打开方式不是截断式写入 ios::out
//fstream outfile;
//outfile.open("user.txt", ios::out | ios::trunc);
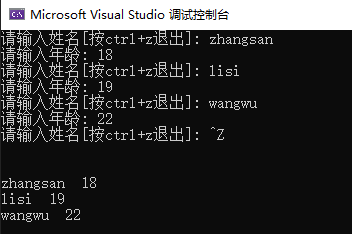
while (1)
{
cout << "请输入姓名[按ctrl+z退出]: ";
cin >> name;
if (cin.eof()) // 检测用户是否输入文件结束符 ctrl+z
{
break;
}
outfile << name << "\t";
cout << "请输入年龄: ";
cin >> age;
outfile << age << endl;
}
outfile.close();
cout << endl << endl;
// 读文件
ifstream infile;
infile.open("user.txt");
while (1)
{
infile >> name;
if (infile.eof()) //判断读取的是否是文件结束符
{
break;
}
cout << name << " ";
infile >> age;
cout << age << endl;
}
infile.close();
return 0;
}
这里我们如果在写文件的时候用fstream写文件
fstream outfile;
outfile.open("user.txt");
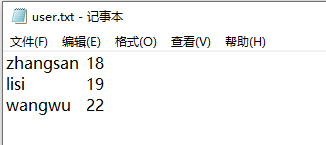
文件中本身有zhangsan lisi wangwu 三条数据,这里我们写入一行数据
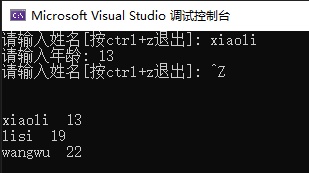
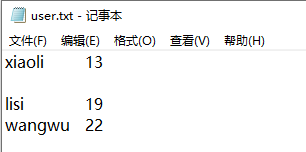
xiaoli这条数据把zhangsan这条数据覆盖了,但后面lisi和wangwu的数据还在,所以我们用fstream在写文件的时候要注意文件打开方式
四 对二进制文件流读写
使用文件流对象的write方法写入二进制数据
以read方法读取的时候不会自动跳过空格
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string name;
int age;
// 写文件
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("user.dat", ios::out | ios::binary | ios::trunc);
while (1)
{
cout << "请输入姓名[按ctrl+z退出]:";
cin >> name;
if (cin.eof())
{
break;
}
outfile << name << " ";
cout << "请输入年龄: ";
cin >> age;
//outfile << age << endl; // 会自动转成文本方式写入
outfile.write((char*)&age, sizeof(age));
}
outfile.close();
cout << endl;
// 读文件
cout << "读文件" << endl;
ifstream infile;
infile.open("user.dat", ios::in | ios::binary);
while (1)
{
infile >> name;
if (infile.eof())
{
break;
}
cout << name << " ";
// 以read方法读取的时候不会自动跳过空格
char temp = 0;
infile.read(&temp, sizeof(char)); // 读取空格
infile.read((char*)&age, sizeof(age));
cout << age << endl;
}
infile.close();
return 0;
}
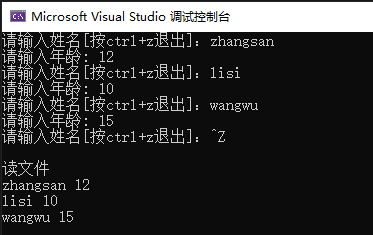
这里我们用EditPlus打开文件,用十六进制查看器查看
五 对文件流按指定格式读写数据
使用stringstream和c语言的sscanf
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string name;
int age;
// 写文件
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("user.txt");
if (!outfile.is_open())
{
cout << "文件打开失败" << endl;
return 0;
}
while (1)
{
cout << "请输入姓名[按ctrl+z退出]:";
cin >> name;
if (cin.eof())
{
break;
}
cout << "请输入年龄:";
cin >> age;
stringstream s;
s << "姓名:" << name << " 年龄:" << age << endl;
outfile << s.str();
}
outfile.close();
cout << endl;
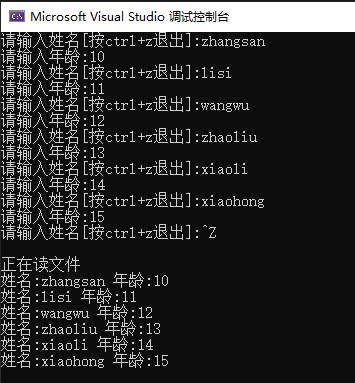
// 读文件
cout << "正在读文件" << endl;
ifstream infile;
string line;
char cname[32];
infile.open("user.txt");
if (!infile.is_open())
{
cout << "文件打开失败" << endl;
return 0;
}
while (1)
{
getline(infile, line);
if (infile.eof())
{
break;
}
//这里是%s,所以需要用char*类型。 char cname[32];
sscanf_s(line.c_str(), "姓名:%s 年龄:%d", cname, sizeof(cname), &age);
cout << "姓名:" << cname << " 年龄:" << age << endl;
}
infile.close();
return 0;
}

六 文件流的状态检查
fstream s;
- s.is_open()
文件流是否打开成功 - s.eof()
流 s 是否结束 - s.fail()
流 s 的 failbit 或者 badbit 被置位时, 返回 true
failbit: 出现非致命错误,可挽回, 一般是软件错误
badbit 置位, 出现致命错误, 一般是硬件错误或系统底层错误, 不可挽回 - s.bad()
流 s 的 badbit 置位时, 返回 true - s.good()
流 s 处于有效状态时, 返回 true - s.clear()
流 s 的所有状态都被复位
七 文件流的定位
7.1 seekg 设置输入流的位置
seekg( off_type offset, //偏移量
ios::seekdir origin ); //起始位置
作用:设置输入流的位置
- 参数 1: 偏移量
- 参数 2: 相对位置
- beg 相对于开始位置
- cur 相对于当前位置
- end 相对于结束位置
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/*
读取当前程序的最后 50 个字符
seekg 设置输入流的位置
*/
int main()
{
// 读取文件最后50个字符
ifstream infile;
string line;
infile.open("main.cpp");
if (!infile.is_open())
{
cout << "文件打开失败" << endl;
return 0;
}
infile.seekg(-50, infile.end); //设置输入流的位置
while (1)
{
getline(infile, line);
if (infile.eof())
{
break;
}
cout << line << endl;
}
infile.close();
return 0;
}
7.2 tellg 返回该输入流的当前位置
tellg返回该输入流的当前位置(距离文件的起始位置的偏移量)
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/*
获取当前文件的长度
*/
int main()
{
// 读取文件
ifstream infile;
infile.open("main.cpp");
if (!infile.is_open())
{
cout << "文件打开失败" << endl;
return 0;
}
infile.seekg(0, infile.end); // 设置输入流的位置
//cout << "main.cpp文件的大小是:" << infile.tellg() << "个字节" << endl; // 这种写法错误,输出不出来
int len = infile.tellg();
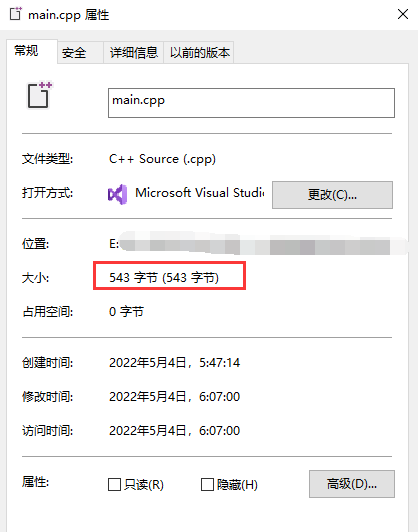
cout << "main.cpp文件的大小是:" << len << "个字节" << endl;
infile.close();
return 0;
}

7.3 seekp 设置输出流的位置
seekp 设置输出流的位置
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
/*
先向新文件写入:“123456789”
然后再在第 4 个字符位置写入“ABC”
*/
int main()
{
// 写文件
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("test.txt");
if (!outfile.is_open())
{
cout << "文件打开失败" << endl;
return 0;
}
outfile << "123456789";
outfile.seekp(4, outfile.beg); // 设置输出流的位置
outfile << "ABC";
outfile.close();
return 0;
}

八 常见错误总结
- 文件没有关闭
文件没有关闭, close(),可能导致写文件失败 - 文件打开方式不合适
- 在 VS2015 的部分版本中,当 sscanf 和 sscanf_s 的格式字符串中含有中文时,可能会读 取失败。 在 vs2019 中未发现该类问题。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现