建模常用手段:组合与聚合
一 组合
具体组合方式:
1)被组合的对象直接使用成员对象。(常用)
2)使用指针表示被组合的对象,在构造函数中,创建被组合的对象;在析构函数中,释放 被组合的对象。
1.1 被组合的对象直接使用成员对象
需求:
构建一个计算机类,一台计算机,由 CPU 芯片,硬盘,内存等组成。
CPU 芯片也使用类来表示。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Cpu
{
public:
Cpu(string brand = "intel", string version = "i5");
~Cpu();
private:
string brand; //品牌
string version; //型号
};
Cpu::Cpu(string brand, string version)
{
this->brand = brand;
this->version = version;
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
}
Cpu::~Cpu()
{
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
}
class Computer
{
public:
Computer(const char* brand, const char* version, int hardDisk, int memory);
~Computer();
private:
Cpu cpu; //Computer与Cpu之间就是“组合”
int hardDisk; //硬盘 单位:G
int memory; //内存 单位:G
};
Computer::Computer(const char* brand, const char* version, int hardDisk, int memory) :cpu(brand, version)
{
//this->cpu = Cpu(brand, version); //不用初始化列表的话,也可以这样初始化,不常用
this->hardDisk = hardDisk;
this->memory = memory;
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
}
Computer::~Computer()
{
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
}
int main()
{
Computer c("intel", "i9", 500, 16);
return 0;
}
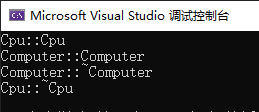
1.2 使用指针表示被组合的对象,在构造函数中,创建被组合的对象;在析构函数中,释放 被组合的对象。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Cpu
{
public:
Cpu(string brand = "intel", string version = "i5");
~Cpu();
private:
string brand; //品牌
string version; //型号
};
Cpu::Cpu(string brand, string version)
{
this->brand = brand;
this->version = version;
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
}
Cpu::~Cpu()
{
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
}
class Computer
{
public:
Computer(const char* brand, const char* version, int hardDisk, int memory);
~Computer();
private:
Cpu *cpu; //使用指针表示被组合的对象
int hardDisk; //硬盘 单位:G
int memory; //内存 单位:G
};
Computer::Computer(const char* brand, const char* version, int hardDisk, int memory)
{
this->cpu = new Cpu(brand, version); // 如果用指针,这里要new一个对象
this->hardDisk = hardDisk;
this->memory = memory;
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
}
Computer::~Computer()
{
delete cpu; // 这里要释放
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
}
int main()
{
Computer c("intel", "i9", 500, 16);
return 0;
}
1.3 UML中的组合表示
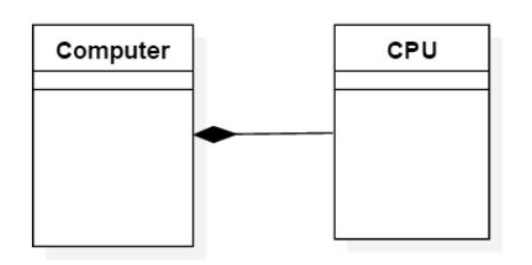
注意包含者使用实心菱形
【补充】UML 画图工具:starUML
二 聚合
需求: 给计算机配一台音响。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class VoiceBox
{
public:
VoiceBox()
{
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
}
~VoiceBox()
{
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
}
};
class Computer
{
public:
Computer(int hardDisk, int memory);
~Computer();
void addVoiceBox(VoiceBox* voicebox);
private:
VoiceBox* voicebox; //音响,和计算机是聚合关系
int hardDisk; //硬盘 单位:G
int memory; //内存 单位:G
};
Computer::Computer(int hardDisk, int memory)
{
this->hardDisk = hardDisk;
this->memory = memory;
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
}
Computer::~Computer()
{
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
}
void Computer::addVoiceBox(VoiceBox* voicebox)
{
this->voicebox = voicebox;
}
void test(VoiceBox &box)
{
Computer c(500,16);
c.addVoiceBox(&box);
}
int main()
{
VoiceBox box;
test(box);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
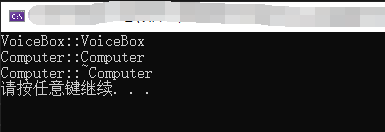
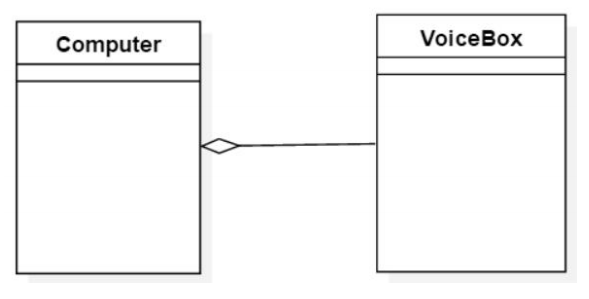
聚合不是组成关系,被包含的对象,也可能被其他对象包含。
拥有者,不需要对被拥有的对象的生命周期负责。
UML 中的组合表示:





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现