结构体
一 结构体定义
struct 结构名 {
成员类型 成员名;
成员类型 成员名;
}; // 注意这里要有分号
//例:
struct student {
char name[16];
int age;
char tel[12];
};
二 结构体初始化
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct _student
{
char name[12];
int age;
char tel[12];
};
int main()
{
/* 结构体初始化 */
// 方式一:定义的时候初始化所有属性
struct _student s1 = { "zhangsan", 18, "88888888" };
// 方式二:定义的时候指定初始化的属性,vs不支持,gcc支持
//struct _student s2 = { .name = "xiaohong", .age = 17 };
// 方式三:单独初始化每一个属性
struct _student s3;
strcpy_s(s3.name, sizeof(s3.name), "wangwu");
s3.age = 18;
s3.tel[0] = '\0';
// 结构体变量之间可以直接赋值
struct _student s4;
s4 = s1;
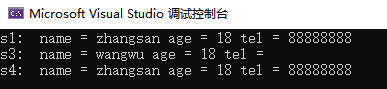
cout << "s1: name = " << s1.name << " age = " << s1.age << " tel = " << s1.tel << endl;
cout << "s3: name = " << s3.name << " age = " << s3.age << " tel = " << s3.tel << endl;
cout << "s4: name = " << s4.name << " age = " << s4.age << " tel = " << s4.tel << endl;
return 0;
}
三 结构体数组
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct _student
{
char name[12];
int age;
char tel[12];
};
int main()
{
struct _student s[3] = {
{"张三",18,""},
{"李四",19,"13333333333"},
{"王五",20,""}
};
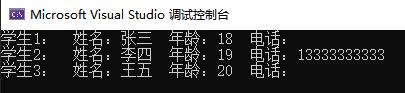
cout << "学生1: 姓名:" << s[0].name << " 年龄:" << s[0].age << " 电话:" << s[0].tel << endl;
cout << "学生2: 姓名:" << s[1].name << " 年龄:" << s[1].age << " 电话:" << s[1].tel << endl;
cout << "学生3: 姓名:" << s[2].name << " 年龄:" << s[2].age << " 电话:" << s[2].tel << endl;
return 0;
}
四 指向结构体的指针
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct _student
{
char name[12];
int age;
char tel[12];
};
int main()
{
struct _student s = { "张三",18,"888888" };
struct _student* p = &s;
//指针访问结构体变量的成员,有两种方式
// 方式一:直接解引
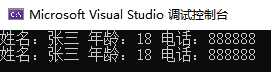
cout << "姓名:" << (*p).name << " 年龄:" << (*p).age << " 电话:" << (*p).tel << endl;
// 方式二:直接使用指针访问 ->
cout << "姓名:" << p->name << " 年龄:" << p->age << " 电话:" << p->tel << endl;
return 0;
}
五 使用结构体传递值
注意:
一般不建议把结构体直接作为函数参数。 因为结构体的 size 比较大,直接传递,消耗性能!
解决方案:(使用指针和引用,优先使用引用)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct _student
{
char name[12];
int age;
int score;
};
//1.形参是结构体变量,值传递
void addScore1(struct _student s, int addScore)
{
s.score += addScore;
}
//2.形参是结构体指针, 址传递
void addScore2(struct _student* s, int addScore)
{
s->score += addScore;
}
//3.形参是结构体引用,址传递
void addScore3(struct _student& s, int addScore)
{
s.score += addScore;
}
//4.形参是结构体变量,返回值引用
struct _student& addScore4(struct _student s, int addScore)
{
s.age = 19;
s.score += addScore;
return s;
}
int main()
{
//1.形参是结构体变量,值传递
struct _student s1;
s1.score = 60;
addScore1(s1, 10);
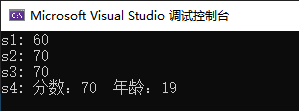
cout << "s1: " << s1.score << endl;
//2.形参是结构体指针, 址传递
struct _student s2;
s2.score = 60;
addScore2(&s2, 10);
cout << "s2: " << s2.score << endl;
//3.形参是结构体引用,址传递
struct _student s3;
s3.score = 60;
addScore3(s3, 10);
cout << "s3: " << s3.score << endl;
//4.形参是结构体变量,返回值引用
struct _student s4;
s4.score = 60;
s4.age = 18;
s4 = addScore4(s4, 10);
cout << "s4: 分数:" << s4.score << " 年龄:" << s4.age << endl;
return 0;
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现