GPT之路(六) Plugins & Function Calling
1. Plugins 是什么
1.1 Plugins 的工作原理
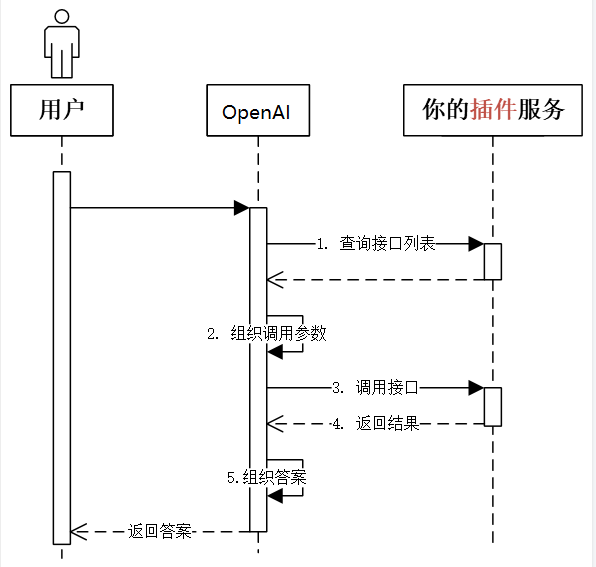
1.2 Plugin开发
可能是史上最容易开发的 plugin。只需要定义两个文件:
1. `yourdomain.com/.well-known/ai-plugin.json`,描述插件的基本信息
2. `openai.yaml`,描述插件的 API(Swagger生成的文档)
而 OpenAI 那边,更简单,没有任何人和你对接。是 AI 和你对接!AI 阅读上面两个文件,就知道该怎么调用你了。
下面是官方的例子
ai-plugin.json
{ "schema_version": "v1", //配置文件版本 "name_for_human": "Sport Stats", //插件名字,给用户看的名字 "name_for_model": "sportStats", //插件名字,给ChatGPT模型看的名字,需要唯一 "description_for_human": "Get current and historical stats for sport players and games.", //描述插件的功能,这个字段是在插件市场展示给用户看的 "description_for_model": "Get current and historical stats for sport players and games. Always display results using markdown tables.", //描述插件的功能,ChatGPT会分析这个字段,确定什么时候调用你的插件 "auth": { "type": "none" //这个是API认证方式,none 代表不需要认证 }, "api": { "type": "openapi", "url": "PLUGIN_HOSTNAME/openapi.yaml" //这个是Swagger API文档地址,ChatGPT通过这个地址访问我们的api文档 }, "logo_url": "PLUGIN_HOSTNAME/logo.png", //插件logo地址 "contact_email": "support@example.com", //插件官方联系邮件 "legal_info_url": "https://example.com/legal" //与该插件相关的legal information }
openapi.yaml
openapi: 3.0.1 info: title: Sport Stats description: Get current and historical stats for sport players and games. version: "v1" servers: - url: PLUGIN_HOSTNAME paths: /players: get: operationId: getPlayers summary: Retrieves all players from all seasons whose names match the query string. parameters: - in: query name: query schema: type: string description: Used to filter players based on their name. For example, ?query=davis will return players that have 'davis' in their first or last name. responses: "200": description: OK /teams: get: operationId: getTeams summary: Retrieves all teams for the current season. responses: "200": description: OK /games: get: operationId: getGames summary: Retrieves all games that match the filters specified by the args. Display results using markdown tables. parameters: - in: query name: limit schema: type: string description: The max number of results to return. - in: query name: seasons schema: type: array items: type: string description: Filter by seasons. Seasons are represented by the year they began. For example, 2018 represents season 2018-2019. - in: query name: team_ids schema: type: array items: type: string description: Filter by team ids. Team ids can be determined using the getTeams function. - in: query name: start_date schema: type: string description: A single date in 'YYYY-MM-DD' format. This is used to select games that occur on or after this date. - in: query name: end_date schema: type: string description: A single date in 'YYYY-MM-DD' format. This is used to select games that occur on or before this date. responses: "200": description: OK /stats: get: operationId: getStats summary: Retrieves stats that match the filters specified by the args. Display results using markdown tables. parameters: - in: query name: limit schema: type: string description: The max number of results to return. - in: query name: player_ids schema: type: array items: type: string description: Filter by player ids. Player ids can be determined using the getPlayers function. - in: query name: game_ids schema: type: array items: type: string description: Filter by game ids. Game ids can be determined using the getGames function. - in: query name: start_date schema: type: string description: A single date in 'YYYY-MM-DD' format. This is used to select games that occur on or after this date. - in: query name: end_date schema: type: string description: A single date in 'YYYY-MM-DD' format. This is used to select games that occur on or before this date. responses: "200": description: OK /season_averages: get: operationId: getSeasonAverages summary: Retrieves regular season averages for the given players. Display results using markdown tables. parameters: - in: query name: season schema: type: string description: Defaults to the current season. A season is represented by the year it began. For example, 2018 represents season 2018-2019. - in: query name: player_ids schema: type: array items: type: string description: Filter by player ids. Player ids can be determined using the getPlayers function. responses: "200": description: OK
description的内容非常重要,决定了ChatGPT会不会调用你的插件,调用得是否正确。
1.3 Plugins的市场表现
1. 时间线: 1. 3月24日发布, 提供11个插件,可以申请加入waitlist获得使用权 2. 5月15日开始向Plus用户全量开放插件和Browsing, 插件数70多个 3. 7月5日因安全原因,关闭Browsing(用户可通过此功能访问付费页面) 4. 7月11日开始全量开放Code Interpreter。插件数已超400
2. 媒体将其类比为App Store,获得鼓吹
3. 6月7日(全面放开后三星期)一篇应OpenAI要求而[被删除的帖子](https://humanloop.com/blog/openai-plans)中透露,Sam Altman 在一个闭门会中说:「插件的实际使用情况表明,除了Browsing以外,还没有达到理想的产品市场契合点。他表示,很多人认为他们希望自己的应用程序位于ChatGPT中,但他们真正想要的是应用程序中的ChatGPT。」
(被删内容这里可以看到:https://web.archive.org/web/20230531203946/https://humanloop.com/blog/openai-plans)
1.4 Plugins到目前还没做起来的原因分析
它暂时歇菜了,主要原因:
1. 缺少强 Agent调度,只能手工选三个 plugin,使用成本太高。(解决此问题,相当于 App Store + Siri,可挑战手机操作系统地位)
2. 不在场景中,不能提供端到端一揽子服务。(解决此问题,就是全能私人助理了,人类唯一需要的软件)
3. 开销大。(至少两次 GPT-4 生成,和一次 Web API 调用)
这是我们做智能应用也要面对的问题。OpenAI 很快推出了大杀器 Function Calling 功能,来帮助我们开发更好的智能应用
2. Function Calling
2.1 Function Calling 的机制
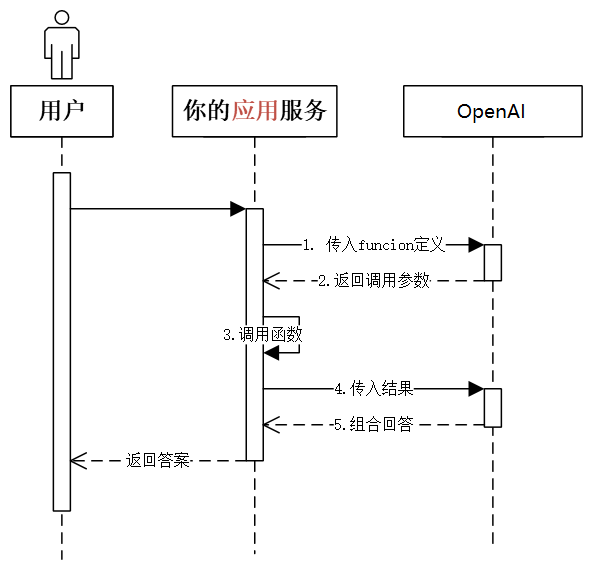
Function Calling完整的官方接口文档:https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/gpt/function-calling
Function Calling详细的参数说明: https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/azure/ai-services/openai/how-to/function-calling
2.2 Function Calling 示例 1:加法计算器
需求:用户输入任意可以用加法解决的问题,都能得到计算结果。
# 加载环境变量 import openai import os import json from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv _ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv()) # 读取本地 .env 文件,里面定义了 OPENAI_API_KEY openai.api_key = os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY')
def get_completion(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo"): response = openai.ChatCompletion.create( model=model, messages=messages, temperature=0, # 模型输出的随机性,0 表示随机性最小 functions=[{ # 用 JSON 描述函数。可以定义多个,但是只有一个会被调用,也可能都不会被调用 "name": "sum", "description": "计算一组数的求和", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "numbers": { "type": "array", "items": { "type": "number" } } } }, }], ) return response.choices[0].message
from math import * # prompt = "Tell me the sum of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10." prompt = "桌上有 2 个苹果,四个桃子和 3 本书,一共有几个水果?" # prompt = "1+2+3...+99+100" messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "你是一个小学数学老师,你要教学生加法"}, {"role": "user", "content": prompt} ] response = get_completion(messages) messages.append(response) # 把大模型的回复加入到对话中 print("=====GPT回复=====") print(response) # 如果返回的是函数调用结果,则打印出来 if (response.get("function_call")): # 是否要调用 sum if (response["function_call"]["name"] == "sum"): args = json.loads(response["function_call"]["arguments"]) result = sum(args["numbers"]) print("=====自定义的函数返回=====") print(result) messages.append( {"role": "function", "name": "pythonRunner", "content": str(result)} # 数值result 必须转成字符串 ) print("=====最终回复=====") print(get_completion(messages).content)
运行结果:

2.3 Function Calling 示例2:计算数学表达式
def get_completion(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo"): response = openai.ChatCompletion.create( model=model, messages=messages, temperature=0, # 模型输出的随机性,0 表示随机性最小 functions=[{ # 用 JSON 描述函数。可以定义多个,但是只有一个会被调用,也可能都不会被调用 "name": "calculate", "description": "计算一个数学表达式的值", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "expression": { "type": "string", "description": "a mathematical expression in python grammar.", } } }, }], ) return response.choices[0].message
from math import * # prompt = "从1加到20" prompt = "3的平方根乘以2再开平方" messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "你是一个数学家,你可以计算任何算式。"}, {"role": "user", "content": prompt} ] response = get_completion(messages) messages.append(response) # 把大模型的回复加入到对话中 print("=====GPT回复=====") print(response) # 如果返回的是函数调用结果,则打印出来 if (response.get("function_call")): if (response["function_call"]["name"] == "calculate"): args = json.loads(response["function_call"]["arguments"]) result = eval(args["expression"]) print("=====函数返回=====") print(result) messages.append( {"role": "function", "name": "calculate", "content": str(result)} # 数值result 必须转成字符串 ) print("=====最终回复=====") print(get_completion(messages).content)
运行结果:
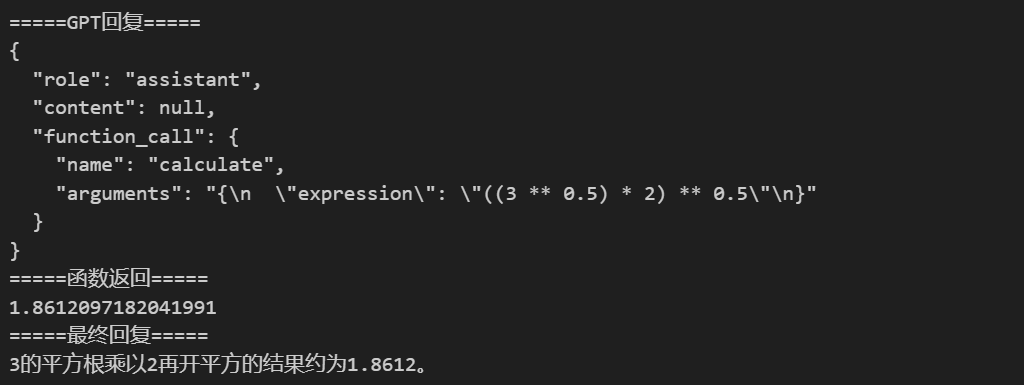
Function Calling中的函数与参数的描述也是一种Prompt. 这种Prompt也需要调优,否则会影响函数的召回、参数的准确性,甚至让GPT产生幻觉
2.3 Function Calling 示例3:计算数学表达式的一个反面教材
def get_completion(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo"): response = openai.ChatCompletion.create( model=model, messages=messages, temperature=0, # 模型输出的随机性,0 表示随机性最小 functions=[{ # 用 JSON 描述函数。可以定义多个,但是只有一个会被调用,也可能都不会被调用 "name": "calculate", "description": "计算一个以Python形式表示的数学表达式的值", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "expression": { "type": "string", "description": "a mathematical expression in python format. it must be evaluatable by Python's eval()", } } }, }], ) return response.choices[0].message prompt = "从1加到20" messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "你是一个数学家,你可以计算任何算式。"}, {"role": "user", "content": prompt} ] response = get_completion(messages) messages.append(response) # 把大模型的回复加入到对话中 print("=====GPT回复=====") print(response) # 如果返回的是函数调用结果,则打印出来 if (response.get("function_call")): if (response["function_call"]["name"] == "calculate"): args = json.loads(response["function_call"]["arguments"]) result = eval(args["expression"]) print("=====函数返回=====") print(result) messages.append( {"role": "function", "name": "calculate", "content": str(result)} # 数值result 必须转成字符串 ) print("=====最终回复=====") print(get_completion(messages).content)
运行结果:

上面的例子是做数学表达式的function call, 我的目标是计算数学表达,但是由于在function的description和parameters的description描述中过于强调python,导致GPT返回了错误的funcation name
2.4 Function Calling 示例4:多Function调用
def get_completion(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo"): response = openai.ChatCompletion.create( model=model, messages=messages, temperature=0, # 模型输出的随机性,0 表示随机性最小 function_call="auto", # 默认值,由系统自动决定,返回function call还是返回文字回复 functions=[{ # 用 JSON 描述函数。可以定义多个,但是最多只有一个会被调用,也可能不被调用 "name": "get_location_coordinate", "description": "根据POI名称,获得POI的经纬度坐标", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "location": { "type": "string", "description": "POI名称,必须是中文", }, "city": { "type": "string", "description": "搜索城市名,必须是中文", } }, "required": ["location"], }, }, { "name": "search_nearby_pois", "description": "搜索给定坐标附近的poi", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "longitude": { "type": "string", "description": "中心点的经度", }, "latitude": { "type": "string", "description": "中心点的纬度", }, "keyword": { "type": "string", "description": "目标poi的关键字", } }, "required": ["longitude","latitude","keyword"], }, }], ) return response.choices[0].message
import requests amap_key="baidu_map_key" def get_location_coordinate(location,city): url = f"https://restapi.amap.com/v5/place/text?key={amap_key}&keywords={location}®ion={city}" print(url) r = requests.get(url) result = r.json() if "pois" in result and result["pois"]: return result["pois"][0] return None def search_nearby_pois(longitude,latitude,keyword): url = f"https://restapi.amap.com/v5/place/around?key={amap_key}&keywords={keyword}&location={longitude},{latitude}" print(url) r = requests.get(url) result = r.json() ans = "" if "pois" in result and result["pois"]: for i in range(min(3,len(result["pois"]))): name = result["pois"][i]["name"] address = result["pois"][i]["address"] distance = result["pois"][i]["distance"] ans += f"{name}\n{address}\n距离:{distance}米\n\n" return ans
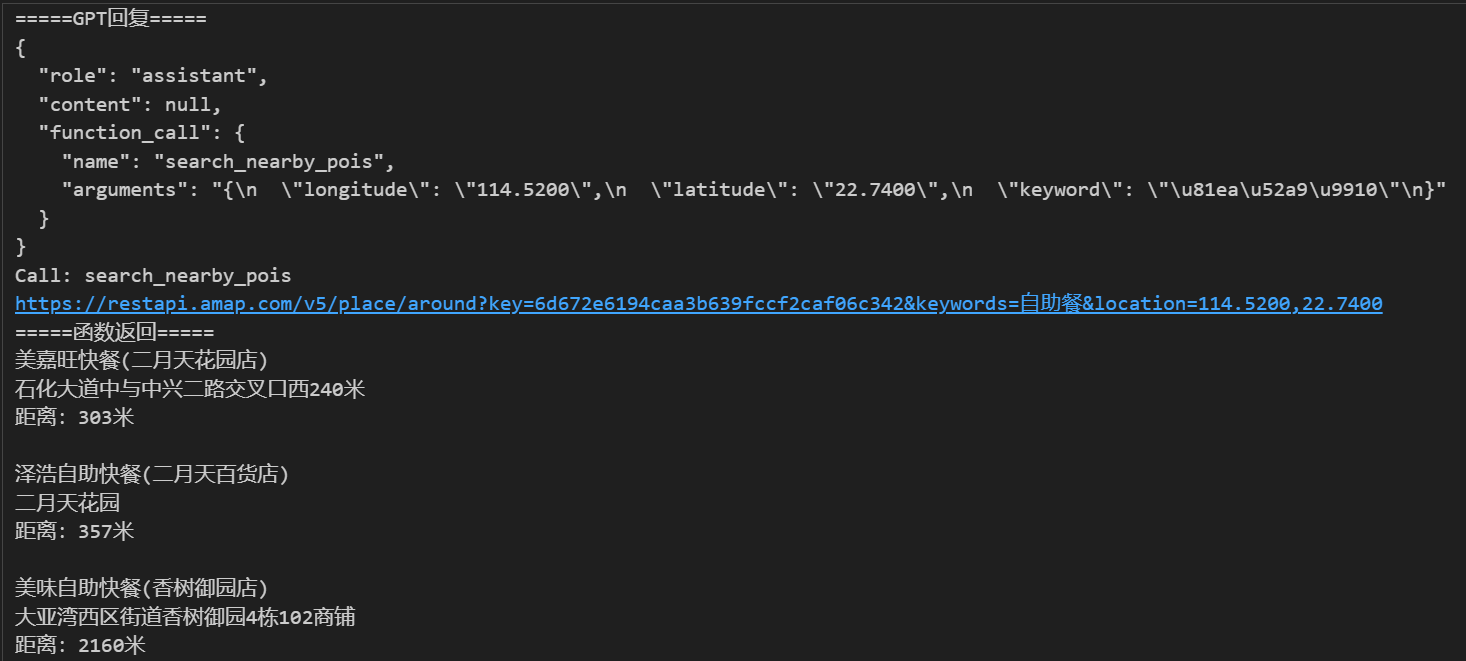
prompt = "惠州市大亚湾石化大道西39号附近的自助餐" messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "你是一个地图通,你可以找到任何地址。"}, {"role": "user", "content": prompt} ] response = get_completion(messages) messages.append(response) # 把大模型的回复加入到对话中 print("=====GPT回复=====") print(response) # 如果返回的是函数调用结果,则打印出来 while (response.get("function_call")): if (response["function_call"]["name"] == "get_location_coordinate"): args = json.loads(response["function_call"]["arguments"]) print("Call: get_location_coordinate") result = get_location_coordinate(**args) elif (response["function_call"]["name"] == "search_nearby_pois"): args = json.loads(response["function_call"]["arguments"]) print("Call: search_nearby_pois") result = search_nearby_pois(**args) print("=====函数返回=====") print(result) messages.append( {"role": "function", "name": response["function_call"]["name"], "content": str(result)} # 数值result 必须转成字符串 ) response = get_completion(messages) print("=====最终回复=====") print(get_completion(messages).content)
运行结果:
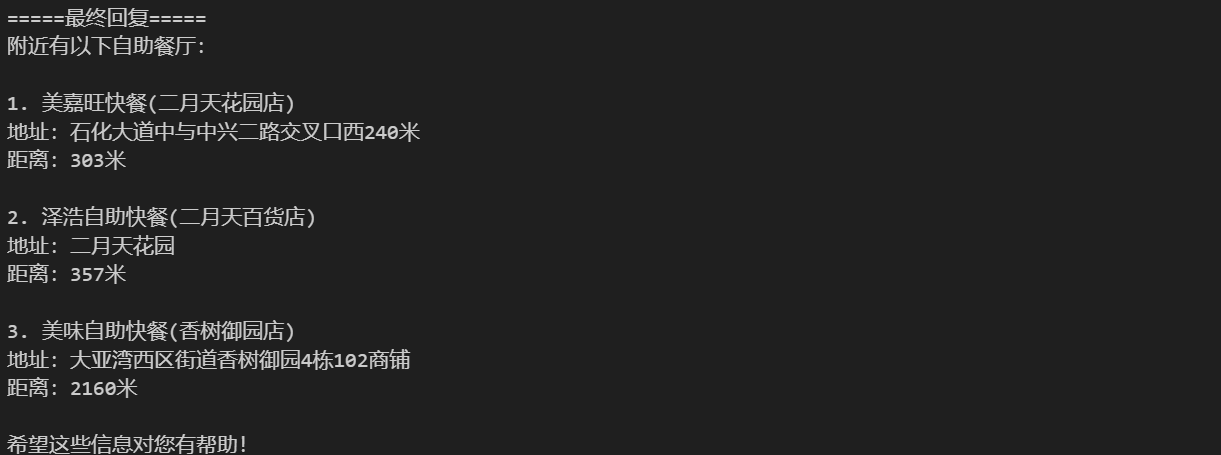
2.5 Function Calling 示例5:用Function Calling实现信息抽取
def get_completion(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo"): response = openai.ChatCompletion.create( model=model, messages=messages, temperature=0, # 模型输出的随机性,0 表示随机性最小 function_call="auto", functions=[{ "name": "add_contact", "description": "添加联系人", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "name": { "type": "string", "description": "联系人姓名" }, "address": { "type": "string", "description": "联系人地址" }, "tel": { "type": "string", "description": "联系人电话" }, } }, }], ) return response.choices[0].message prompt = "中秋礼品A,收货人是Brian,收货地址是深圳市宝安区西乡街道,电话190xxxx123。" messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "你是一个联系人录入员。"}, {"role": "user", "content": prompt} ] response = get_completion(messages) print("====GPT回复====") print(json.dumps(response,ensure_ascii=False,indent=2)) args = json.loads(response["function_call"]["arguments"]) print("====函数参数====") print(args)
运行结果:
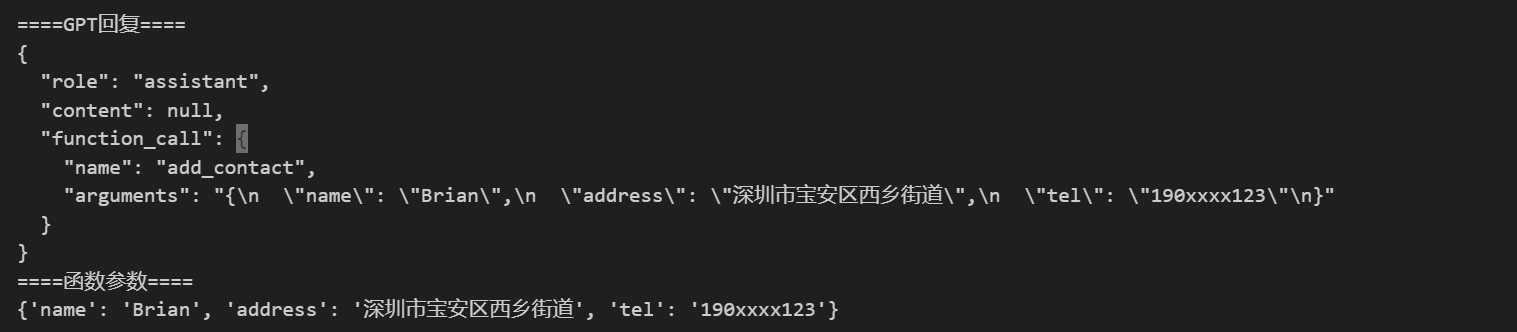
如果只想要个JSON格式数据,那么Prompt和Function Calling哪个更好?因为Function Calling能力是特别fine-tune在模型内的,所以输出更稳定,用来获取JSON更可靠。搞个假函数声明,就能拿到JSON了。
2.6 Function Calling 示例 6:通过Function Calling查询数据库
需求:从订单表中查询各种信息,比如某个用户的订单数量、某个商品的销量、某个用户的消费总额等等。
import openai import os import json from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv _ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv()) # 读取本地 .env 文件,里面定义了 OPENAI_API_KEY openai.api_key = os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY') def get_sql_completion(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo"): response = openai.ChatCompletion.create( model=model, messages=messages, temperature=0, # 模型输出的随机性,0 表示随机性最小 function_call="auto", functions=[{ # 摘自 OpenAI 官方示例 https://github.com/openai/openai-cookbook/blob/main/examples/How_to_call_functions_with_chat_models.ipynb "name": "ask_database", "description": "Use this function to answer user questions about business. \ Output should be a fully formed SQL query.", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "query": { "type": "string", "description": f""" SQL query extracting info to answer the user's question. SQL should be written using this database schema: {database_schema_string} The query should be returned in plain text, not in JSON. The query should only contain grammars supported by SQLite. """, } }, "required": ["query"], }, }], ) return response.choices[0].message
import openai import os import json from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv _ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv()) # 读取本地 .env 文件,里面定义了 OPENAI_API_KEY openai.api_key = os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY') def get_sql_completion(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo"): response = openai.ChatCompletion.create( model=model, messages=messages, temperature=0, # 模型输出的随机性,0 表示随机性最小 function_call="auto", functions=[{ # 摘自 OpenAI 官方示例 https://github.com/openai/openai-cookbook/blob/main/examples/How_to_call_functions_with_chat_models.ipynb "name": "ask_database", "description": "Use this function to answer user questions about business. \ Output should be a fully formed SQL query.", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "query": { "type": "string", "description": f""" SQL query extracting info to answer the user's question. SQL should be written using this database schema: {database_schema_string} The query should be returned in plain text, not in JSON. The query should only contain grammars supported by SQLite. """, } }, "required": ["query"], }, }], ) return response.choices[0].message
# 描述数据库表结构 database_schema_string = """ CREATE TABLE orders ( id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, -- 主键,不允许为空 customer_id INT NOT NULL, -- 客户ID,不允许为空 product_id STR NOT NULL, -- 产品ID,不允许为空 price DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL, -- 价格,不允许为空 status INT NOT NULL, -- 订单状态,整数类型,不允许为空。0代表待支付,1代表已支付,2代表已退款 create_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, -- 创建时间,默认为当前时间 pay_time TIMESTAMP -- 支付时间,可以为空 ); """
import sqlite3 # 创建数据库连接 conn = sqlite3.connect(':memory:') cursor = conn.cursor() # 创建orders表 cursor.execute(database_schema_string) # 插入5条明确的模拟记录 mock_data = [ (1, 1001, 'TSHIRT_1', 50.00, 0, '2023-08-12 10:00:00', None), (2, 1001, 'TSHIRT_2', 75.50, 1, '2023-08-16 11:00:00', '2023-08-16 12:00:00'), (3, 1002, 'SHOES_X2', 25.25, 2, '2023-08-17 12:30:00', '2023-08-17 13:00:00'), (4, 1003, 'HAT_Z112', 60.75, 1, '2023-08-20 14:00:00', '2023-08-20 15:00:00'), (5, 1002, 'WATCH_X001', 90.00, 0, '2023-08-28 16:00:00', None) ] for record in mock_data: cursor.execute(''' INSERT INTO orders (id, customer_id, product_id, price, status, create_time, pay_time) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?) ''', record) # 提交事务 conn.commit()
def ask_database(query): cursor.execute(query) records = cursor.fetchall() return records # prompt = "上个月的销售额" # prompt = "统计每月每件商品的销售额" prompt = "哪个用户消费最高?消费多少?" messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "基于 order 表回答用户问题"}, {"role": "user", "content": prompt} ] response = get_sql_completion(messages) print("====Function Calling====") print(response) if "function_call" in response: if response["function_call"]["name"] == "ask_database": arguments = response["function_call"]["arguments"] args = json.loads(arguments) print("====SQL====") print(args["query"]) result = ask_database(args["query"]) print("====DB Records====") print(result) messages.append({ "role": "user", "content": f"用户问:{prompt}\n系统通过以下SQL查询后,返回:"+str(result)+"\n据此请回答:" }) response = get_sql_completion(messages) print("====最终回复====") print(get_completion(messages).content)
运行结果:
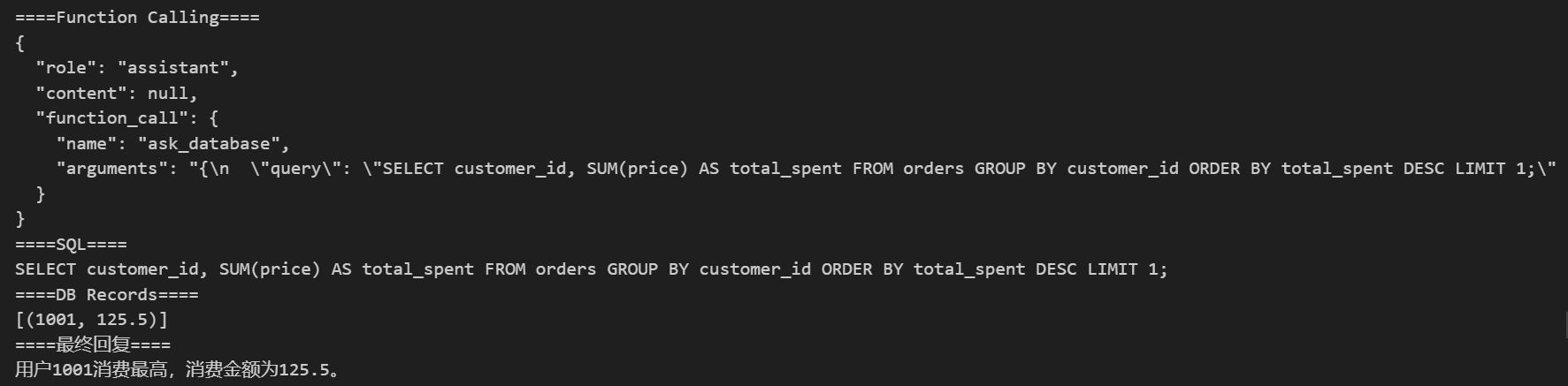
2.7 Function Calling 示例 7:用Function Calling实现多表查询
# 描述数据库表结构 database_schema_string = """ CREATE TABLE customers ( id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, -- 主键,不允许为空 customer_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, -- 客户名,不允许为空 email VARCHAR(255) UNIQUE, -- 邮箱,唯一 register_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP -- 注册时间,默认为当前时间 ); CREATE TABLE products ( id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, -- 主键,不允许为空 product_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, -- 产品名称,不允许为空 price DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL -- 价格,不允许为空 ); CREATE TABLE orders ( id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, -- 主键,不允许为空 customer_id INT NOT NULL, -- 客户ID,不允许为空 product_id INT NOT NULL, -- 产品ID,不允许为空 price DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL, -- 价格,不允许为空 status INT NOT NULL, -- 订单状态,整数类型,不允许为空。0代表待支付,1代表已支付,2代表已退款 create_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, -- 创建时间,默认为当前时间 pay_time TIMESTAMP -- 支付时间,可以为空 ); """ #prompt = "统计每月每件商品的销售额" prompt = "这星期消费最高的用户是谁?他买了哪些商品? 每件商品买了几件?花费多少?" messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "基于 order 表回答用户问题"}, {"role": "user", "content": prompt} ] response = get_sql_completion(messages) print(response)
运行结果:
{ "role": "assistant", "content": null, "function_call": { "name": "ask_database", "arguments": "{\n \"query\": \"SELECT c.customer_name, p.product_name, COUNT(o.id) AS quantity, SUM(o.price) AS total_cost FROM customers c JOIN orders o ON c.id = o.customer_id JOIN products p ON o.product_id = p.id WHERE o.create_time >= DATE_SUB(CURDATE(), INTERVAL WEEKDAY(CURDATE()) DAY) AND o.create_time < DATE_ADD(CURDATE(), INTERVAL 1 DAY) GROUP BY c.customer_name, p.product_name ORDER BY total_cost DESC LIMIT 1\"\n}" } }
2.8 Function Calling 的注意事项
1. 截至到目前只有 `gpt-3.5-turbo-0613` 和 `gpt-4-0613` 可用。它俩针对Function Calling做了fine-tuning,以尽可能保证正确率。
2. 但不保证不出错,包括不保证json格式正确。所以官方强烈建议(原文:strongly recommend)如果有写操作,一定插入人工流程做确认。但比纯靠 prompt控制,可靠性是大了很多的
3. 函数声明是消耗token的。要在功能覆盖、省钱、节约上下文窗口之间找到最佳平衡
4. 实战经验:把自己的函数调用结果用自然语言给到OpenAI,效果有时更好。调优时可以试试
分类:
AI & Tool
标签:
function calling




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本