Spring Cloud Commons 源码分析
全部的组件实现以 Spring Cloud Tencent 举例说明
actuator 监控
提供了查看组件具体实现的功能,依赖 spring boot actuator。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
org.springframework.cloud.client.actuator 包如下:

HasFeatures 和 NamedFeature 用于描述组件的实现:
public class HasFeatures {
private final List<Class<?>> abstractFeatures = new ArrayList<>();
private final List<NamedFeature> namedFeatures = new ArrayList<>();
public HasFeatures(List<Class<?>> abstractFeatures, List<NamedFeature> namedFeatures) {
this.abstractFeatures.addAll(abstractFeatures);
this.namedFeatures.addAll(namedFeatures);
}
public static HasFeatures abstractFeatures(Class<?>... abstractFeatures) {
return new HasFeatures(Arrays.asList(abstractFeatures), Collections.emptyList());
}
public static HasFeatures namedFeatures(NamedFeature... namedFeatures) {
return new HasFeatures(Collections.emptyList(), Arrays.asList(namedFeatures));
}
public static HasFeatures namedFeature(String name, Class<?> type) {
return namedFeatures(new NamedFeature(name, type));
}
public static HasFeatures namedFeatures(String name1, Class<?> type1, String name2, Class<?> type2) {
return namedFeatures(new NamedFeature(name1, type1), new NamedFeature(name2, type2));
}
public List<Class<?>> getAbstractFeatures() {
return this.abstractFeatures;
}
public List<NamedFeature> getNamedFeatures() {
return this.namedFeatures;
}
}
public class NamedFeature {
private final String name;
private final Class<?> type;
public NamedFeature(String name, Class<?> type) {
this.name = name;
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public Class<?> getType() {
return this.type;
}
}
FeaturesEndpoint 使用 注册了一个端点,用于查看组件功能实现:
@Endpoint(id = "features")
public class FeaturesEndpoint implements ApplicationContextAware {
private final List<HasFeatures> hasFeaturesList;
private ApplicationContext context;
public FeaturesEndpoint(List<HasFeatures> hasFeaturesList) {
this.hasFeaturesList = hasFeaturesList;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
this.context = context;
}
@ReadOperation
public Features features() {
Features features = new Features();
for (HasFeatures hasFeatures : this.hasFeaturesList) {
List<Class<?>> abstractFeatures = hasFeatures.getAbstractFeatures();
if (abstractFeatures != null) {
for (Class<?> clazz : abstractFeatures) {
addAbstractFeature(features, clazz);
}
}
List<NamedFeature> namedFeatures = hasFeatures.getNamedFeatures();
if (namedFeatures != null) {
for (NamedFeature namedFeature : namedFeatures) {
addFeature(features, namedFeature);
}
}
}
return features;
}
private void addAbstractFeature(Features features, Class<?> type) {
String featureName = type.getSimpleName();
try {
Object bean = this.context.getBean(type);
Class<?> beanClass = bean.getClass();
addFeature(features, new NamedFeature(featureName, beanClass));
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException e) {
features.getDisabled().add(featureName);
}
}
private void addFeature(Features features, NamedFeature feature) {
Class<?> type = feature.getType();
features.getEnabled().add(new Feature(feature.getName(), type.getCanonicalName(),
type.getPackage().getImplementationVersion(), type.getPackage().getImplementationVendor()));
}
static class Features {
final List<Feature> enabled = new ArrayList<>();
final List<String> disabled = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Feature> getEnabled() {
return this.enabled;
}
public List<String> getDisabled() {
return this.disabled;
}
}
static class Feature {
final String type;
final String name;
final String version;
final String vendor;
Feature(String name, String type, String version, String vendor) {
this.type = type;
this.name = name;
this.version = version;
this.vendor = vendor;
}
public String getType() {
return this.type;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public String getVersion() {
return this.version;
}
public String getVendor() {
return this.vendor;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Feature{" + "type='" + this.type + '\'' + ", name='" + this.name + '\'' + ", version='"
+ this.version + '\'' + ", vendor='" + this.vendor + '\'' + '}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Feature feature = (Feature) o;
if (!Objects.equals(this.type, feature.type)) {
return false;
}
if (!Objects.equals(this.name, feature.name)) {
return false;
}
if (!Objects.equals(this.version, feature.version)) {
return false;
}
return Objects.equals(this.vendor, feature.vendor);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = this.type != null ? this.type.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + (this.name != null ? this.name.hashCode() : 0);
result = 31 * result + (this.version != null ? this.version.hashCode() : 0);
result = 31 * result + (this.vendor != null ? this.vendor.hashCode() : 0);
return result;
}
}
}
然后在一个 CommonsClientAutoConfiguration 中注册该类为一个 Bean:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class CommonsClientAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass(HealthIndicator.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DiscoveryClientHealthIndicatorProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(DiscoveryClient.class)
@ConditionalOnDiscoveryEnabled
@ConditionalOnBlockingDiscoveryEnabled
protected static class DiscoveryLoadBalancerConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnDiscoveryHealthIndicatorEnabled
public DiscoveryClientHealthIndicator discoveryClientHealthIndicator(
ObjectProvider<DiscoveryClient> discoveryClient, DiscoveryClientHealthIndicatorProperties properties) {
// 这个类用于本地服务注册向注册中心注册后的事件通知, 以此来展示监控信息
return new DiscoveryClientHealthIndicator(discoveryClient, properties);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.discovery.client.composite-indicator.enabled",
matchIfMissing = true)
@ConditionalOnBean({ DiscoveryHealthIndicator.class })
public DiscoveryCompositeHealthContributor discoveryCompositeHealthContributor(
List<DiscoveryHealthIndicator> indicators) {
// 可能注册了多个服务, 这个 indicators 就包含上面注册的 discoveryClientHealthIndicator
return new DiscoveryCompositeHealthContributor(indicators);
}
@Bean
public HasFeatures springCloudCommonsFeatures() {
// 添加两个组件抽象类, 用于端点在 applicationContext 查找具体的实现
return HasFeatures.abstractFeatures(DiscoveryClient.class, LoadBalancerClient.class);
}
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass(Endpoint.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.features.enabled", matchIfMissing = true) // 默认 spring.cloud.features.enabled 为 true, 也就是默认注册这个端点
protected static class ActuatorConfiguration {
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<HasFeatures> hasFeatures = new ArrayList<>();
@Bean
@ConditionalOnAvailableEndpoint
public FeaturesEndpoint featuresEndpoint() {
// 开启组件具体实现的查看端点
return new FeaturesEndpoint(this.hasFeatures);
}
}
}
circuitbreaker 断路器
想一下断路器需要哪些抽象:
- 断路器,提供抽象方法执行一个函数,短路状态由具体组件实现
- 配置建造者,为不同的断路器创建不同的配置,为什么是建造者而不是工厂?因为断路器的配置是一个固定的对象
- 断路器工厂,为断路器创建
下面是 Spring Cloud Commons 的定义:

CircuitBreaker 断路器
提供 run 方法,使用函数式来完成短路功能封装,并提供失败回调
public interface CircuitBreaker {
default <T> T run(Supplier<T> toRun) {
return run(toRun, throwable -> {
throw new NoFallbackAvailableException("No fallback available.", throwable);
});
}
<T> T run(Supplier<T> toRun, Function<Throwable, T> fallback);
}
ConfigBuilder 配置创建者
build 方法用于创建一个配置,且每一个 builder 对象都是有其属于自身的配置的,想一下其他对象的建造者模式就明白了,当然可以一个默认函数式实现
public interface ConfigBuilder<CONF> {
CONF build();
}
AbstractCircuitBreakerFactory 抽象断路器工厂
- ConcurrentHashMap<String, CONF> configuration 字段:用户缓存断路器配置
- configBuilder 方法:
// 不太重要的都省略了
public abstract class AbstractCircuitBreakerFactory<CONF, CONFB extends ConfigBuilder<CONF>> {
// 缓存断路器配置
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, CONF> configurations = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
protected ConcurrentHashMap<String, CONF> getConfigurations() {
return configurations;
}
// 由具体组件实现, 传入一个配置 id, 返回该配置 id 的 配置建造者
protected abstract CONFB configBuilder(String id);
// 由具体组件实现, 设置一个默认的配置建造者
public abstract void configureDefault(Function<String, CONF> defaultConfiguration);
}
CircuitBreakerFactory 短路器工厂
- create 方法:创建一个短路器
public abstract class CircuitBreakerFactory<CONF, CONFB extends ConfigBuilder<CONF>>
extends AbstractCircuitBreakerFactory<CONF, CONFB> {
public abstract CircuitBreaker create(String id);
}
Spring Cloud Tencent
至此,断路器具体的组件需要实现以下功能:
短路器工厂
以 PolarisCircuitBreakerFactory为例:
-
create 方法:通过 getConfigurations 方法 computeIfAbsent 从抽象短路器工厂的配置缓存中获取配置,然后新建一个组件自己实现的短路器 PolarisCircuitBreaker,注意这个 PolarisCircuitBreaker 不会被缓存,因此断路器具体的状态已经更改断路器状态所需的统计数据需要存放在其他地方,很明显这些数据放在 PolarisCircuitBreakerFactory 中再好不过,Polaris 的实现就是放在 CircuitBreakAPI 中了。
-
configureDefault 方法:用于通过配置 id 创建配置,参数是一个 lambda,前面提到过 ConfigBuilder 配置建造者,而配置 id 到 配置的创建过程需要由配置建造者辅助创建,因此可以看到默认的 defaultConfiguration 中有一个 PolarisCircuitBreakerConfigBuilder。
public class PolarisCircuitBreakerFactory
extends CircuitBreakerFactory<PolarisCircuitBreakerConfigBuilder.PolarisCircuitBreakerConfiguration, PolarisCircuitBreakerConfigBuilder> {
private Function<String, PolarisCircuitBreakerConfigBuilder.PolarisCircuitBreakerConfiguration> defaultConfiguration =
id -> {
String[] metadata = PolarisCircuitBreakerUtils.resolveCircuitBreakerId(id);
return new PolarisCircuitBreakerConfigBuilder()
.namespace(metadata[0])
.service(metadata[1])
.method(metadata[2])
.build();
};
private final CircuitBreakAPI circuitBreakAPI;
private final ConsumerAPI consumerAPI;
public PolarisCircuitBreakerFactory(CircuitBreakAPI circuitBreakAPI, ConsumerAPI consumerAPI) {
this.circuitBreakAPI = circuitBreakAPI;
this.consumerAPI = consumerAPI;
}
@Override
public CircuitBreaker create(String id) {
PolarisCircuitBreakerConfigBuilder.PolarisCircuitBreakerConfiguration conf = getConfigurations()
.computeIfAbsent(id, defaultConfiguration);
return new PolarisCircuitBreaker(conf, consumerAPI, circuitBreakAPI);
}
@Override
public void configureDefault(Function<String, PolarisCircuitBreakerConfigBuilder.PolarisCircuitBreakerConfiguration> defaultConfiguration) {
this.defaultConfiguration = defaultConfiguration;
}
}
断路器
以 PolarisCircuitBreaker为例,它的实现很简单,使用装饰、委托或代理的方法隐藏断路器的具体实现细节,只做调用以及错误回调处理。另外前面提到过 CircuitBreaker 只是一个函数,由 CircuitBreakerFactory#CircuitBreakerFactory(String) 方法创建,使用后就可以被 gc 回收,因此状态实际是放在 PolarisCircuitBreakerFactory 的 CircuitBreakAPI 中的,再看构造函数有一个 CircuitBreakAPI 参数,这样我们就明白了断路器是怎么更改状态的。
public class PolarisCircuitBreaker implements CircuitBreaker {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PolarisCircuitBreaker.class);
private final FunctionalDecorator decorator;
private final PolarisCircuitBreakerConfigBuilder.PolarisCircuitBreakerConfiguration conf;
private final ConsumerAPI consumerAPI;
public PolarisCircuitBreaker(PolarisCircuitBreakerConfigBuilder.PolarisCircuitBreakerConfiguration conf,
ConsumerAPI consumerAPI,
CircuitBreakAPI circuitBreakAPI) {
FunctionalDecoratorRequest makeDecoratorRequest = new FunctionalDecoratorRequest(new ServiceKey(conf.getNamespace(), conf.getService()), conf.getMethod());
makeDecoratorRequest.setSourceService(new ServiceKey(conf.getSourceNamespace(), conf.getSourceService()));
makeDecoratorRequest.setResultToErrorCode(new PolarisResultToErrorCode());
this.consumerAPI = consumerAPI;
this.conf = conf;
// 将短路器配置、短路器状态数据及实现组合到一起
this.decorator = circuitBreakAPI.makeFunctionalDecorator(makeDecoratorRequest);
}
@Override
public <T> T run(Supplier<T> toRun, Function<Throwable, T> fallback) {
Supplier<T> toRunDecorator = decorator.decorateSupplier(toRun);
try {
return toRunDecorator.get();
}
catch (CallAbortedException e) {
LOGGER.debug("PolarisCircuitBreaker CallAbortedException: {}", e.getMessage());
PolarisCircuitBreakerUtils.reportStatus(consumerAPI, conf, e);
return fallback.apply(e);
}
catch (Exception e) {
return fallback.apply(e);
}
}
}
discovery 服务发现
DiscoveryClient
服务发现需要从一个地方获取一些服务信息,这些服务信息包括地址、端口以及这个服务的一些元信息等等(比如服务的权重),可以简单归纳如下:
- DiscoveryClient:服务发现客户端,可以拿到一些服务信息
- ServiceInstance:服务示例,即服务信息,包含这个服务的地址、端口等等
下面是它们的定义,非常简单,首先是服务发现客户端:
public interface DiscoveryClient extends Ordered {
/**
* Default order of the discovery client.
*/
int DEFAULT_ORDER = 0;
/**
* A human-readable description of the implementation, used in HealthIndicator.
* @return The description.
*/
String description();
/**
* Gets all ServiceInstances associated with a particular serviceId.
* @param serviceId The serviceId to query.
* @return A List of ServiceInstance.
*/
List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId);
/**
* @return All known service IDs.
*/
List<String> getServices();
/**
* Can be used to verify the client is valid and able to make calls.
* <p>
* A successful invocation with no exception thrown implies the client is able to make
* calls.
* <p>
* The default implementation simply calls {@link #getServices()} - client
* implementations can override with a lighter weight operation if they choose to.
*/
default void probe() {// 健康监测功能,这里不会详细介绍
getServices();
}
/**
* Default implementation for getting order of discovery clients.
* @return order
*/
@Override
default int getOrder() {
return DEFAULT_ORDER;
}
}
然后是服务示例:
public interface ServiceInstance {
/**
* @return The unique instance ID as registered.
*/
default String getInstanceId() {
return null;
}
/**
* @return The service ID as registered.
*/
String getServiceId();
/**
* @return The hostname of the registered service instance.
*/
String getHost();
/**
* @return The port of the registered service instance.
*/
int getPort();
/**
* @return Whether the port of the registered service instance uses HTTPS.
*/
boolean isSecure();
/**
* @return The service URI address.
*/
URI getUri();
/**
* @return The key / value pair metadata associated with the service instance.
*/
Map<String, String> getMetadata();
/**
* @return The scheme of the service instance.
*/
default String getScheme() {
return null;
}
}
默认的 org.springframework.cloud.client.DefaultServiceInstance 提供了一个常用的 getUri 方法用来获取服务实例的网络 Uri:
public class DefaultServiceInstance implements ServiceInstance {
private String instanceId;
private String serviceId;
private String host;
private int port;
private boolean secure;
private Map<String, String> metadata = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private URI uri;
/**
* @param instanceId the id of the instance.
* @param serviceId the id of the service.
* @param host the host where the service instance can be found.
* @param port the port on which the service is running.
* @param secure indicates whether or not the connection needs to be secure.
* @param metadata a map containing metadata.
*/
public DefaultServiceInstance(String instanceId, String serviceId, String host, int port, boolean secure,
Map<String, String> metadata) {
this.instanceId = instanceId;
this.serviceId = serviceId;
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
this.secure = secure;
this.metadata = metadata;
}
/**
* @param instanceId the id of the instance.
* @param serviceId the id of the service.
* @param host the host where the service instance can be found.
* @param port the port on which the service is running.
* @param secure indicates whether or not the connection needs to be secure.
*/
public DefaultServiceInstance(String instanceId, String serviceId, String host, int port, boolean secure) {
this(instanceId, serviceId, host, port, secure, new LinkedHashMap<>());
}
public DefaultServiceInstance() {
}
/**
* Creates a URI from the given ServiceInstance's host:port.
* @param instance the ServiceInstance.
* @return URI of the form (secure)?https:http + "host:port". Scheme port default used
* if port not set.
*/
public static URI getUri(ServiceInstance instance) {
String scheme = (instance.isSecure()) ? "https" : "http";
int port = instance.getPort();
if (port <= 0) {
port = (instance.isSecure()) ? 443 : 80;
}
String uri = String.format("%s://%s:%s", scheme, instance.getHost(), port);
return URI.create(uri);
}
// 其他省略
}
自动服务注册
有一个 org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient 注解,它有一个 autoRegister 方法用于是否自动注册本地服务,另外也可以通过 spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled 属性设置,关于它们的优先级以及具体的使用可以看下面的分析:
这是 EnableDiscoveryClient 注解,他用 @Import 引入了一个 ImportSelector 类型 的 EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector 类,也就是说在 Bean 上存在这个注解,ConfigurationClassBeanPostProcessor 就会通过 ConfigurationClassParser 调用 EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector 的 selectImports(AnnotationMetadata) 方法
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableDiscoveryClient {
/**
* If true, the ServiceRegistry will automatically register the local server.
* @return - {@code true} if you want to automatically register.
*/
boolean autoRegister() default true;
}
然后看 EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector 类,它实现了 ImportSelector 接口,这个接口通常是通过被标注类上注解的元信息来确定手动注册哪些 bean 的,EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector 也是如此,它获取了被标注类的 EnableDiscoveryClient 注解,如果 autoRegister 为 true ,即需要自动注册本地服务,就注入一个 AutoServiceRegistrationConfiguration 类型的 bean,否则就向 Environment 中添加 spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled 属性为 false,注意这个 PropertySource 添加到了最后面,也就是说如果配置中已经存在了 spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled,那么读取该属性是以原本存在的配置优先的。经过上面的分析,就确定了一件事:如果手动配置了 spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled 属性,那么 EnableDiscoveryClient 注解是没用的,否则就以 EnableDiscoveryClient 的 autoRegister 为准。
@Order(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 100)
public class EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector extends SpringFactoryImportSelector<EnableDiscoveryClient> {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
String[] imports = super.selectImports(metadata);
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes
.fromMap(metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(getAnnotationClass().getName(), true));
boolean autoRegister = attributes.getBoolean("autoRegister");
if (autoRegister) {
List<String> importsList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(imports));
importsList.add("org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AutoServiceRegistrationConfiguration");
imports = importsList.toArray(new String[0]);
}
else {
Environment env = getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment configEnv) {
LinkedHashMap<String, Object> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put("spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", false);
MapPropertySource propertySource = new MapPropertySource("springCloudDiscoveryClient", map);
configEnv.getPropertySources().addLast(propertySource);
}
}
return imports;
}
@Override
protected boolean isEnabled() {
return getEnvironment().getProperty("spring.cloud.discovery.enabled", Boolean.class, Boolean.TRUE);
}
@Override
protected boolean hasDefaultFactory() {
return true;
}
}
此时还有一个问题,默认是否主动注册呢?如果配置和注解都没有(即没有产生任何自动注册的属性配置),那么看自动配置类 org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AutoServiceRegistrationConfiguration,这个类的 @ConditionalOnProperty 声明了没有 spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled 时条件结果为 true,也就是说默认是自动注册的,并且 EnableDiscoveryClient 和 AutoServiceRegistrationProperties 默认都是 true,语义是统一的,即默认自动注册。最后再说一点,可以看到如果开启了自动配置,那么就注入 AutoServiceRegistrationProperties,所以我们再自己实现服务注册时应该让组件的主动配置类在 AutoServiceRegistrationConfiguration 后执行,然后用 @ConditionalOnBean 判断是否存在 AutoServiceRegistrationProperties 来确定是否进行自动注册。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(AutoServiceRegistrationProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public class AutoServiceRegistrationConfiguration {
}
SimpleDiscoveryClient
从配置文件中作为服务实例来源的 DiscoveryClient
public class SimpleDiscoveryClient implements DiscoveryClient {
private SimpleDiscoveryProperties simpleDiscoveryProperties;
public SimpleDiscoveryClient(SimpleDiscoveryProperties simpleDiscoveryProperties) {
this.simpleDiscoveryProperties = simpleDiscoveryProperties;
}
@Override
public String description() {
return "Simple Discovery Client";
}
@Override
public List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId) {
List<ServiceInstance> serviceInstances = new ArrayList<>();
List<DefaultServiceInstance> serviceInstanceForService = this.simpleDiscoveryProperties.getInstances()
.get(serviceId);
if (serviceInstanceForService != null) {
serviceInstances.addAll(serviceInstanceForService);
}
return serviceInstances;
}
@Override
public List<String> getServices() {
return new ArrayList<>(this.simpleDiscoveryProperties.getInstances().keySet());
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return this.simpleDiscoveryProperties.getOrder();
}
}
配置属性中的 DefaultServiceInstance 前面提到过,配置属性如下:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.cloud.discovery.client.simple")
public class SimpleDiscoveryProperties implements InitializingBean {
private Map<String, List<DefaultServiceInstance>> instances = new HashMap<>();
/**
* The properties of the local instance (if it exists). Users should set these
* properties explicitly if they are exporting data (e.g. metrics) that need to be
* identified by the service instance.
*/
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private DefaultServiceInstance local = new DefaultServiceInstance(null, null, null, 0, false);
private int order = DiscoveryClient.DEFAULT_ORDER;
public Map<String, List<DefaultServiceInstance>> getInstances() {
return this.instances;
}
public void setInstances(Map<String, List<DefaultServiceInstance>> instances) {
this.instances = instances;
}
public DefaultServiceInstance getLocal() {
return this.local;
}
public int getOrder() {
return this.order;
}
public void setOrder(int order) {
this.order = order;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
for (String key : this.instances.keySet()) {
for (DefaultServiceInstance instance : this.instances.get(key)) {
instance.setServiceId(key);
}
}
}
public void setInstance(String serviceId, String host, int port) {
local = new DefaultServiceInstance(null, serviceId, host, port, false);
}
}
最后 Spring Cloud 将其注册到容器中,可以看到默认将自身添加到服务实例列表中了,也就是说使用服务 id 调用自己是可行的
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@AutoConfigureBefore({ CommonsClientAutoConfiguration.class })
public class SimpleDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration implements ApplicationListener<WebServerInitializedEvent> {
private ServerProperties server;
private InetUtils inet;
private int port = 0;
private final SimpleDiscoveryProperties simple = new SimpleDiscoveryProperties();
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setServer(ServerProperties server) {
this.server = server;
}
@Autowired
public void setInet(InetUtils inet) {
this.inet = inet;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SimpleDiscoveryProperties simpleDiscoveryProperties(
@Value("${spring.application.name:application}") String serviceId) {
simple.getLocal().setServiceId(serviceId);
simple.getLocal().setHost(inet.findFirstNonLoopbackHostInfo().getHostname());
simple.getLocal().setPort(findPort());
return simple;
}
@Bean
@Order
public DiscoveryClient simpleDiscoveryClient(SimpleDiscoveryProperties properties) {
return new SimpleDiscoveryClient(properties);
}
private int findPort() {
if (port > 0) {
return port;
}
if (server != null && server.getPort() != null && server.getPort() > 0) {
return server.getPort();
}
return 8080;
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(WebServerInitializedEvent webServerInitializedEvent) {
port = webServerInitializedEvent.getWebServer().getPort();
if (port > 0) {
simple.getLocal().setHost(inet.findFirstNonLoopbackHostInfo().getHostname());
simple.getLocal().setPort(port);
}
}
}
CompositeDiscoveryClient
除了默认的 SimpleDiscoveryClient 外还有一个 CompositeDiscoveryClient,这个类用于结合所有的服务发现客户端,查找时遍历客户端,直到有一个客户端返回了服务实例,其他 DiscoveryClient 的功能也是一样遍历,不同点就是 $$ 和 || 的区别。另外在构造函数中可以发现对 discoveryClients 做了 Order 排序,来完成服务发现客户端的优先级确定,默认的 DiscoveryClient 优先级是 0,SimpleDiscoveryClient 在其注册时修改了自身的优先级为最低(Integer.MAX_VALUE)
public class CompositeDiscoveryClient implements DiscoveryClient {
private final List<DiscoveryClient> discoveryClients;
public CompositeDiscoveryClient(List<DiscoveryClient> discoveryClients) {
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(discoveryClients);
this.discoveryClients = discoveryClients;
}
@Override
public String description() {
return "Composite Discovery Client";
}
@Override
public List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId) {
if (this.discoveryClients != null) {
for (DiscoveryClient discoveryClient : this.discoveryClients) {
List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances(serviceId);
if (instances != null && !instances.isEmpty()) {
return instances;
}
}
}
return Collections.emptyList();
}
@Override
public List<String> getServices() {
LinkedHashSet<String> services = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (this.discoveryClients != null) {
for (DiscoveryClient discoveryClient : this.discoveryClients) {
List<String> serviceForClient = discoveryClient.getServices();
if (serviceForClient != null) {
services.addAll(serviceForClient);
}
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(services);
}
@Override
public void probe() {
if (this.discoveryClients != null) {
for (DiscoveryClient discoveryClient : this.discoveryClients) {
discoveryClient.probe();
}
}
}
public List<DiscoveryClient> getDiscoveryClients() {
return this.discoveryClients;
}
}
接下来看它的主动配置类 CompositeDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration,这个类同样很简单,注册一个组合后的 DiscoveryClient,并声明为 Primary 保证依赖查找到的是它。另外它的类上有 @AutoConfigureBefore 注解,用来声明它在 SimpleDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration 前定义,我的理解是查找 BeanDefinition 时找到的是它而不是其他实现。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@AutoConfigureBefore(SimpleDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration.class)
public class CompositeDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@Primary
public CompositeDiscoveryClient compositeDiscoveryClient(List<DiscoveryClient> discoveryClients) {
return new CompositeDiscoveryClient(discoveryClients);
}
}
Spring Cloud Tencent
直接看 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports ,发现 PolarisDiscoveryAutoConfiguration:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnPolarisDiscoveryEnabled
@Import({PolarisDiscoveryClientConfiguration.class,
PolarisReactiveDiscoveryClientConfiguration.class, PolarisRefreshConfiguration.class})
public class PolarisDiscoveryAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public PolarisServiceDiscovery polarisServiceDiscovery(
@Nullable NacosContextProperties nacosContextProperties,
PolarisDiscoveryProperties polarisDiscoveryProperties,
PolarisDiscoveryHandler polarisDiscoveryHandler) {
return new PolarisServiceDiscovery(
nacosContextProperties,
polarisDiscoveryProperties,
polarisDiscoveryHandler);
}
}
可以看到这个类注入了服务发现的具体实现 PolarisServiceDiscovery,注意这个 Bean 不是 DiscoveryClient,很好理解,一个中间件不是为了专门给 Spring Cloud 设计的,因此需要将其实现与 Spring Cloud Commons 抽象出来的 DiscoveryClient 桥接后使用。
再看 @Import 注解,它引入了一个配置 PolarisDiscoveryClientConfiguration,这里我们就看到了桥接的 PolarisDiscoveryClient,也就是在此处完成了 DiscoveryClient 的具体实现注入。还可以看到 @AutoConfigureBefore({ SimpleDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration.class, CommonsClientAutoConfiguration.class }) 定义了当前配置要在这两个配置前完成,CommonsClientAutoConfiguration 前面讲到过,这个配置中会获取一个一个 DiscoveryClient 实现做健康检测,如果它获取到了 SimpleDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration 注册的 SimpleDiscoveryClient 就糟糕了,因此它需要在这两个类前完成配置定义。
类上还有两个 @Conditional 判断:@ConditionalOnBlockingDiscoveryEnabled 是 Spring Cloud Commons 提供的开启阻塞的服务发现,@ConditionalOnPolarisDiscoveryEnabled 是具体组件用来判断是否开启服务发现的,实现很简单,不看了。
最后说一个应该是错误的点,关于 @AutoConfigureBefore 的使用,这个注解是用来控制配置顺序的(不是 Bean 创建顺序哦),并且只能是在 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports 文件中读取的才生效,如果是被包扫描路径扫描到或 @Import 这种间接引入的等等方法都是不生效的,Eureka 和 Nacos 的 Spring Cloud Starter 实现没有这个问题,Polaris 目前有这个问题,详见:https://github.com/Tencent/spring-cloud-tencent/issues/1114#issue-1897914054。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnBlockingDiscoveryEnabled
@ConditionalOnPolarisDiscoveryEnabled
@AutoConfigureBefore({ SimpleDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration.class, CommonsClientAutoConfiguration.class })
public class PolarisDiscoveryClientConfiguration {
java
@Bean
public DiscoveryClient polarisDiscoveryClient(PolarisServiceDiscovery polarisServiceDiscovery) {
return new PolarisDiscoveryClient(polarisServiceDiscovery);
}
}
serviceregistry 服务注册
服务注册的抽象包括:
- ServiceRegistry<R extends Registration>:用于服务注册和注销
- Registration:ServiceInstance 的子类,仅用于标记其为服务注册示例
- AutoServiceRegistration:用于管理服务注册和注销的时机,即需要注册的服务实例的生命周期,具体实现通常继承自 AbstractAutoServiceRegistration<R extends Registration>
ServiceRegistry 和 Registration 都没什么可看的
public interface ServiceRegistry<R extends Registration> {
void register(R registration); // 注册
void deregister(R registration); // 注销
void close();
void setStatus(R registration, String status);
<T> T getStatus(R registration);
}
public interface Registration extends ServiceInstance {
}
AutoServiceRegistration 是用于管理服务注册生命周期的接口,里面什么都没有,我们直接看它的抽象实现(只看重点):
- 首先看构造函数,传入了 ServiceRegistry<R extends Registration> 对象,
- 实现了 ApplicationListener<WebServerInitializedEvent> 接口
- 使用了 @PreDestroy 注解
从上面三点可以看出,第一点是拿到 Registration 的管理者,第二点是在服务器准备就绪时注册本地服务,第三点是在 Spring 容器关闭的销毁 Bean 阶段注销本地服务
public interface AutoServiceRegistration {
}
// AutoServiceRegistration 的抽象实现,管理了服务注册的生命周期,因此通常我们都是继承它来实现具体的组建接入,下面的代码只截取了一部分
public abstract class AbstractAutoServiceRegistration<R extends Registration>
implements AutoServiceRegistration, ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<WebServerInitializedEvent> {
private final ServiceRegistry<R> serviceRegistry;
private final AtomicBoolean running = new AtomicBoolean(false);
private final AtomicInteger port = new AtomicInteger(0);
protected AbstractAutoServiceRegistration(ServiceRegistry<R> serviceRegistry,
AutoServiceRegistrationProperties properties) {
this.serviceRegistry = serviceRegistry;
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public void onApplicationEvent(WebServerInitializedEvent event) {
ApplicationContext context = event.getApplicationContext();
if (context instanceof ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext) {
if ("management".equals(((ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext) context).getServerNamespace())) {
return;
}
}
this.port.compareAndSet(0, event.getWebServer().getPort());
this.start();
}
public void start() {
if (!isEnabled()) {
return;
}
if (!this.running.get()) {
register();
this.context.publishEvent(new InstanceRegisteredEvent<>(this, getConfiguration()));
this.running.compareAndSet(false, true);
}
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
stop();
}
/**
* Register the local service with the {@link ServiceRegistry}.
*/
protected void register() {
this.serviceRegistry.register(getRegistration());
}
/**
* De-register the local service with the {@link ServiceRegistry}.
*/
protected void deregister() {
this.serviceRegistry.deregister(getRegistration());
}
public void stop() {
if (this.getRunning().compareAndSet(true, false) && isEnabled()) {
this.registrationLifecycles.forEach(
registrationLifecycle -> registrationLifecycle.postProcessBeforeStopRegister(getRegistration()));
deregister();
this.registrationLifecycles.forEach(
registrationLifecycle -> registrationLifecycle.postProcessAfterStopRegister(getRegistration()));
if (shouldRegisterManagement()) {
this.registrationManagementLifecycles
.forEach(registrationManagementLifecycle -> registrationManagementLifecycle
.postProcessBeforeStopRegisterManagement(getManagementRegistration()));
deregisterManagement();
this.registrationManagementLifecycles
.forEach(registrationManagementLifecycle -> registrationManagementLifecycle
.postProcessAfterStopRegisterManagement(getManagementRegistration()));
}
this.serviceRegistry.close();
}
}
}
其他生命周期和监控之类的就不介绍了
loadbalancer 负载均衡
总览
基本抽象
这个包啰几把嗦的,然后还有一个单独的 Spring Cloud Loadbalancer 包,真让人头大,直接看结果。
- ReactorLoadBalancer:负载均衡器,从 choose 方法可以看出它接收请求并返回结果,也就是说负载均衡策略是在这里完成的。ps:我们应该实现它的子接口 ReactorServiceInstanceLoadBalancer 来做具体实现,而不是用 ReactorLoadBalancer 接口。
public interface ReactorLoadBalancer<T> extends ReactiveLoadBalancer<T> {
/**
* Choose the next server based on the load balancing algorithm.
* @param request - an input request
* @return - mono of response
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Mono<Response<T>> choose(Request request);
}
public interface ReactorServiceInstanceLoadBalancer extends ReactorLoadBalancer<ServiceInstance> {
}
- ServiceInstanceListSupplier:服务实例列表提供者,用于获取 getServiceId 返回的服务 id 的示例列表,之前我们直到服务发现是由 DiscoveryClient 实现的,因此这里其实就是 DiscoveryClient 的封装,可以看到 builder 方法返回的 ServiceInstanceListSupplierBuilder 相当于装饰器建造者,通过一层层的构造来增强原来的 ServiceInstanceListSupplier,比如缓存、健康检测等等(但 Spring Cloud Tencent 好像是在 polaris 的 SDK 层面做的增强,而不是选择在 ServiceInstanceListSupplier 做增强,很明显在 SDK 增强是更合理的,因为 polaris SDK 可以脱离 Spring Cloud 使用,这样也方便其他云原生框架的适配)。
public interface ServiceInstanceListSupplier extends Supplier<Flux<List<ServiceInstance>>> {
String getServiceId();
default Flux<List<ServiceInstance>> get(Request request) {
return get();
}
static ServiceInstanceListSupplierBuilder builder() {
return new ServiceInstanceListSupplierBuilder();
}
}
public final class ServiceInstanceListSupplierBuilder {
public ServiceInstanceListSupplierBuilder withBlockingDiscoveryClient() {
// ...
}
public ServiceInstanceListSupplierBuilder withDiscoveryClient() {
if (baseCreator != null && LOG.isWarnEnabled()) {
LOG.warn("Overriding a previously set baseCreator with a ReactiveDiscoveryClient baseCreator.");
}
this.baseCreator = context -> {
ReactiveDiscoveryClient discoveryClient = context.getBean(ReactiveDiscoveryClient.class);
return new DiscoveryClientServiceInstanceListSupplier(discoveryClient, context.getEnvironment());
};
return this;
}
public ServiceInstanceListSupplierBuilder withCaching() {
//...
}
}
为每个服务单独配置
上面就完成了简单的负载均衡抽象,但还不够,比如如何为每个服务设置单独的负载均衡策略呢?最简单的实现就是一个 Map,Key 是 服务 ID,Value 是我们为其配置的负载均衡策略 ReactorLoadBalancer 实现,然后我们在执行请求时,拿到 URL 中的服务 ID,再去 map 中找到它的负载均衡策略实现 ReactorLoadBalancer 去找到一个服务实例去执行,这样每个服务都可以配置单独的负载均衡策略的功能就完成了,但实际的负载均衡中不仅仅可以是选择策略,还有如何获取服务列表等等,这是一组配置,简单的解决方式是 Map 中的 Value 变成了一个子 Map,子 Map 的 key 是功能名, value 是具体功能实现,但是如果我们的功能实现依赖了容器中的 Bean 怎么办?答案就是不使用子 Map 作为 Value,而是为这个服务 ID 创建一个 ApplicationContext 作为 Value, 并将主容器设置为这个 ApplicationContext 的 parent。当然还有一些细节,比如使用者如何为每个服务编写配置,也就是如何让配置添加到 Map 中?以 SpringBoot 来说上面说的配置就是以 Configuration 配置类的形式出现的,而负载均衡策略等功能实现是以 @Bean 出现在 Configuration 中,但这个 Configuration 不能注册到主容器中,因为被主容器扫描到就混乱了,那么如何注入呢?
万能的解决方案:再套一层抽象。我们可以用一个配置 Wrapper 去存储这个配置类的 className,然后注入这个 wrapper 类,然后用 List<ConfigurationWrapper> 添加到 Map 中,等到真正获取这个服务的配置时再初始化 ApplicationContext,这样就做到了每个服务的负载均衡都可以独自配置的。
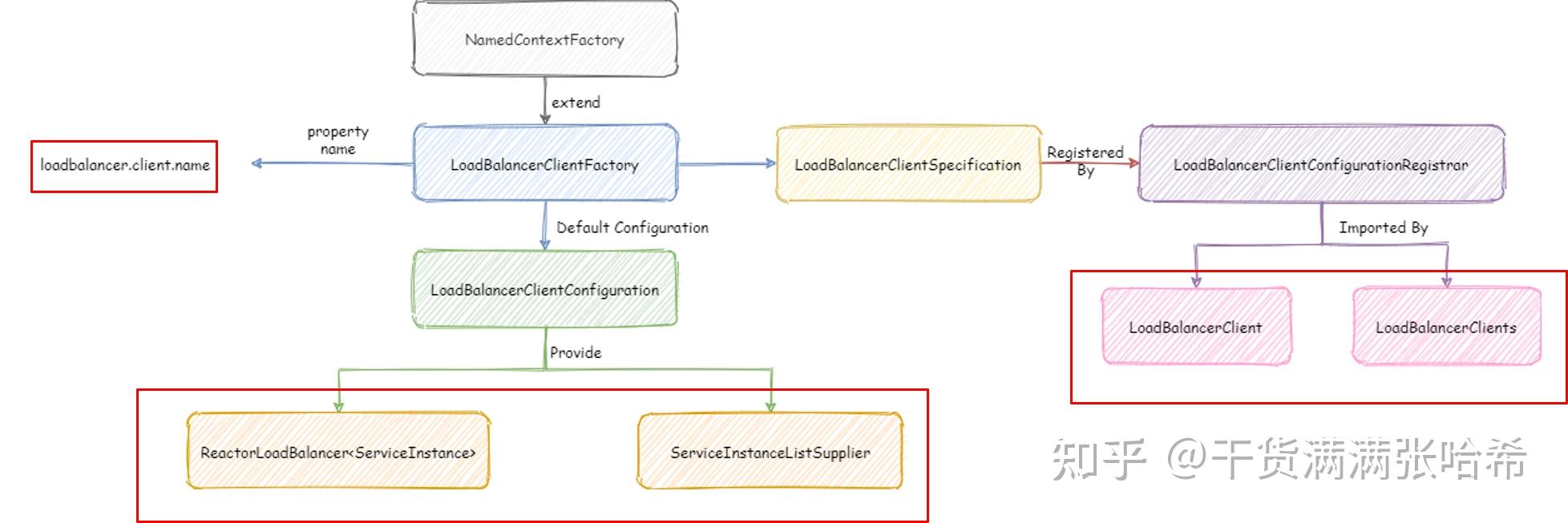
前面的两段话是我们自己的实现,Spring Cloud Commons 的实现是 NamedContextFactory,下面的代码以负载均衡的场景来描述:
public abstract class NamedContextFactory<C extends NamedContextFactory.Specification>
implements DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware {
private final Map<String, ApplicationContextInitializer<GenericApplicationContext>> applicationContextInitializers;
private final String propertySourceName; // 没用
private final String propertyName; // 先看各个属性上的注释,最后看 buildContext 方法中的注释,里面会说到为什么需要 propertyName
private final Map<String, GenericApplicationContext> contexts = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); // 存放的具体配置的,key 就是服务 ID,value 就是负载均衡定义所在的子 ApplicationContext 容器
private Map<String, C> configurations = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); // 存放每个服务的负载均衡定义,相当于前面说的 Configuration Wrapper,key 就是服务 ID,value 就是该服务独自的负载均衡定义
private ApplicationContext parent; // 主容器
private Class<?> defaultConfigType; // 默认配置
public NamedContextFactory(Class<?> defaultConfigType, String propertySourceName, String propertyName) {
this(defaultConfigType, propertySourceName, propertyName, new HashMap<>());
}
public NamedContextFactory(Class<?> defaultConfigType, String propertySourceName, String propertyName,
Map<String, ApplicationContextInitializer<GenericApplicationContext>> applicationContextInitializers) {
this.defaultConfigType = defaultConfigType;
this.propertySourceName = propertySourceName;
this.propertyName = propertyName;
this.applicationContextInitializers = applicationContextInitializers;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
this.parent = parent;
}
public void setConfigurations(List<C> configurations) {
// 转换一下,保存每个服务自己的负载均衡配置
for (C client : configurations) {
this.configurations.put(client.getName(), client);
}
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
Collection<GenericApplicationContext> values = this.contexts.values();
for (GenericApplicationContext context : values) {
// This can fail, but it never throws an exception (you see stack traces
// logged as WARN).
context.close();
}
this.contexts.clear();
}
protected GenericApplicationContext getContext(String name) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
synchronized (this.contexts) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
// 这个服务的配置所在的上下文没有就去创建
this.contexts.put(name, createContext(name));
}
}
}
return this.contexts.get(name);
}
public GenericApplicationContext createContext(String name) {
GenericApplicationContext context = buildContext(name);
// there's an AOT initializer for this context
if (applicationContextInitializers.get(name) != null) {
applicationContextInitializers.get(name).initialize(context);
context.refresh();
return context;
}
registerBeans(name, context);
context.refresh();
return context;
}
public void registerBeans(String name, GenericApplicationContext context) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(AnnotationConfigRegistry.class, context);
AnnotationConfigRegistry registry = (AnnotationConfigRegistry) context;
if (this.configurations.containsKey(name)) {
for (Class<?> configuration : this.configurations.get(name).getConfiguration()) {
registry.register(configuration);
}
}
for (Map.Entry<String, C> entry : this.configurations.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getKey().startsWith("default.")) {
for (Class<?> configuration : entry.getValue().getConfiguration()) {
registry.register(configuration);
}
}
}
// 最后把默认配置注册了
registry.register(PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration.class, this.defaultConfigType);
}
public GenericApplicationContext buildContext(String name) {
// https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-netflix/issues/3101
// https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-openfeign/issues/475
ClassLoader classLoader = getClass().getClassLoader();
GenericApplicationContext context;
if (this.parent != null) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
if (parent instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(
((ConfigurableApplicationContext) parent).getBeanFactory().getBeanClassLoader());
}
else {
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(classLoader);
}
context = AotDetector.useGeneratedArtifacts() ? new GenericApplicationContext(beanFactory)
: new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(beanFactory);
}
else {
context = AotDetector.useGeneratedArtifacts() ? new GenericApplicationContext()
: new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
}
context.setClassLoader(classLoader);
// 注意这里用到了 propertyName,并以 propertyName 为 key,服务名为 value 添加到 Environment 中的第一位
// 为什么要添加这个属性呢?某个服务 Configuration 类如果有想获取当前服务 ApplicationContext 中的 bean 的需求,即 NamedContextFactory#getInstance(String, Class<T>) ,需要用到用到服务 ID 值,而这个配置类可以是好几个服务的负载均衡配置,因此不能写死在 Configuration 中,而是动态获取
context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources().addFirst(
new MapPropertySource(this.propertySourceName, Collections.singletonMap(this.propertyName, name)));
if (this.parent != null) {
// Uses Environment from parent as well as beans
context.setParent(this.parent);
}
context.setDisplayName(generateDisplayName(name));
return context;
}
protected String generateDisplayName(String name) {
return this.getClass().getSimpleName() + "-" + name;
}
public <T> T getInstance(String name, Class<T> type) {
GenericApplicationContext context = getContext(name);
try {
return context.getBean(type);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException e) {
// ignore
}
return null;
}
public <T> ObjectProvider<T> getLazyProvider(String name, Class<T> type) {
// 注意负载均衡配置中 bean 的依赖应该使用延迟获取,因为我们的 bean 应该优先从子容器获取,
// 如果直接获取的话会错乱,因为主容器可能存在一个 bean,直接方法注入就获取不到该服务单独配置的 bean 了,而如果是延迟注入就能获取到最终的 bean
return new ClientFactoryObjectProvider<>(this, name, type);
}
public <T> ObjectProvider<T> getProvider(String name, Class<T> type) {
GenericApplicationContext context = getContext(name);
return context.getBeanProvider(type);
}
/**
* Specification with name and configuration.
*/
public interface Specification { // 这个就是我们前面提到的 Configuration Wrapper
String getName();
Class<?>[] getConfiguration();
}
}
关于 getLazyProvider 可以看下面 Spring Cloud Tencent 中的使用(注入 LoadBalancerClientFactory 的地方会在后面说):
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnPolarisEnabled
@ConditionalOnDiscoveryEnabled
public class PolarisLoadBalancerClientConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.polaris.loadbalancer.strategy", havingValue = "roundRobin", matchIfMissing = true)
public ReactorLoadBalancer<ServiceInstance> roundRobinLoadBalancer(Environment environment,
LoadBalancerClientFactory loadBalancerClientFactory) {
String name = environment.getProperty(LoadBalancerClientFactory.PROPERTY_NAME);
return new RoundRobinLoadBalancer(
loadBalancerClientFactory.getLazyProvider(name, ServiceInstanceListSupplier.class), name);
}
}
其他配置选项
- LoadBalancerRequestTransformer:重新构建 Http 请求,此时 URL 上的服务名等信息已经替换完,因此通常是用来处理请求头等信息的,比如处理请求头、Cookies:
@Bean
public LoadBalancerRequestTransformer transformer() {
return new LoadBalancerRequestTransformer() {
@Override
public HttpRequest transformRequest(HttpRequest request, ServiceInstance instance) {
return new HttpRequestWrapper(request) {
@Override
public HttpHeaders getHeaders() {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.putAll(super.getHeaders());
headers.add("X-InstanceId", instance.getInstanceId());
return headers;
}
};
}
};
}
其他的不介绍了。
自动配置
我们看 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports 文件中的负载均衡自动配置 LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration(注意这个是 Spring Cloud Loadblance 包下的,不要看错了),它注入了一个 LoadBalancerClientFactory,这个类就是前面介绍的 NamedContextFactory 实现类,注入后我们在就可以在配置类中使用了。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@LoadBalancerClients
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ LoadBalancerClientsProperties.class, LoadBalancerEagerLoadProperties.class })
@AutoConfigureBefore({ ReactorLoadBalancerClientAutoConfiguration.class,
LoadBalancerBeanPostProcessorAutoConfiguration.class })
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.loadbalancer.enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
public class LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration {
//...
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@Bean
public LoadBalancerClientFactory loadBalancerClientFactory(LoadBalancerClientsProperties properties,
ObjectProvider<List<LoadBalancerClientSpecification>> configurations) {
LoadBalancerClientFactory clientFactory = new LoadBalancerClientFactory(properties);
clientFactory.setConfigurations(configurations.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList));
return clientFactory;
}
//...
}
还有 Spring Cloud 是怎么加一个 @LoadBalanced 注解就能让 RestTemplate 或 WebClient 负载均衡生效呢?
@Configuration
@LoadBalancerClients({@LoadBalancerClient(value = "stores", configuration = StoresLoadBalancerClientConfiguration.class), @LoadBalancerClient(value = "customers", configuration = CustomersLoadBalancerClientConfiguration.class)})
public class MyConfiguration {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public WebClient.Builder loadBalancedWebClientBuilder() {
return WebClient.builder();
}
}
public class MyClass {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
public String doOtherStuff() {
String results = restTemplate.getForObject("http://stores/stores", String.class);
return results;
}
@Autowired
private WebClient.Builder webClientBuilder;
public Mono<String> doOtherStuff() {
return webClientBuilder.build().get().uri("http://stores/stores")
.retrieve().bodyToMono(String.class);
}
}
先以进入维护周期,不被推荐使用的 RestTemplate 来说,它存在一个 setInterceptors 方法用来做请求拦截,因此负载均衡就是这里做切入的。对于 WebClient 来说也类似,WebClient.Builder 存在一个 filter(ExchangeFilterFunction),用于做请求拦截:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ExchangeFilterFunction {
/**
* Apply this filter to the given request and exchange function.
* <p>The given {@link ExchangeFunction} represents the next entity in the
* chain, to be invoked via {@link ExchangeFunction#exchange} in order to
* proceed with the exchange, or not invoked to short-circuit the chain.
* <p><strong>Note:</strong> When a filter handles the response after the
* call to {@code ExchangeFunction.exchange(...)}, extra care must be taken
* to always consume its content or otherwise propagate it downstream for
* further handling, for example by the {@link WebClient}. Please see the
* reference documentation for more details on this.
* @param request the current request
* @param next the next exchange function in the chain
* @return the filtered response
*/
Mono<ClientResponse> filter(ClientRequest request, ExchangeFunction next);
// 其他方法省略...
}
参考
SpringCloud升级之路2020.0.x版-21.Spring Cloud LoadBalancer简介 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
SpringCloud升级之路2020.0.x版-8.理解 NamedContextFactory - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
Spring Cloud Context
上面的 Spring Cloud 基本都是 Spring Cloud Commons 模块下的,它涵盖了基本所有的云原生功能,但通常我们还需要一个配置中心,因此 Spring Cloud Context 为我们提供了 bootstrap context、加密、刷新 bean 和 environment 这些实用的功能
外部配置(配置中心)
先想我们如何使用 Spring Cloud 配置中心的:
-
引入 spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap 依赖
-
建一个 bootstrap.yml
-
在 bootstrap.yml 文件中写上配置中心的地址等信息
然后就可以使用了,从上面这个流程可以猜测:Spring Cloud 在 SpringBoot 容器 refresh 前从读取bootstrap.yml,并根据这个 bootstrap.yml 连接配置中心读取配置,下面按照这个思路来找。
读取 bootstrap.yml
注册一个 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 事件监听器 BootstrapApplicationListener 用于在 Environment 准备好后创建一个 Spring Cloud ApplicationContext,这个 ApplicationContext 创建的 Environment 中添加了一个 spring.config.name=bootstrap,然后启动这个 SpringCloud 容器去读取 bootstrap.yml,启动后将这个容器 Environment 中读取好的 propertySource 合并到 SpringBoot 容器中,这样就完成了 bootstrap.yml 的读取流程。下面说具体细节:
首先看 Spring Boot 程序启动的核心流程 org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#run(java.lang.String...) :
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// ...
}
// ...
return context;
}
可以看到 prepareEnvironment 方法,这个方法叫准备环境,并返回了一个 Environment:
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
EnvironmentConverter environmentConverter = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader());
environment = environmentConverter.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
这个方法中调用 environmentPrepared 发布 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 事件给所有订阅了此事件的 ApplicationListener,Spring Cloud Context 的外部配置就是在此处切入的,它实现了一个 BootstrapApplicationListener 订阅该事件:
public class BootstrapApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent>, Ordered {
/**
* Property source name for bootstrap.
*/
public static final String BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "bootstrap";
/**
* The default order for this listener.
*/
public static final int DEFAULT_ORDER = Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 5;
/**
* The name of the default properties.
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_PROPERTIES = "springCloudDefaultProperties";
private int order = DEFAULT_ORDER;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();
// 判断是否开启 bootstrap.yml 配置读取。
// 可以自己看下 bootstrapEnabled 方法,然后就懂为什么 bootstrap-starter 只有一个 Marker 类了
if (!bootstrapEnabled(environment) && !useLegacyProcessing(environment)) {
return;
}
// 为什么要这样判断?
// 下面的 bootstrapServiceContext 启动了一个新的 Spring Cloud ApplicationContext,
// 但这个容器同样也会扫描 spring.factories, 也就是说它的 SpringApplication.run 准备环境时
// 也会通知这个 BootstrapApplicationListener, 此时需要跳过.
// 而这个 ApplicationContext 里有一个名为 BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME 属性源,
// 那么这个属性源就可以作为判断条件
// don't listen to events in a bootstrap context
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) {
return;
}
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
String configName = environment.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.name:bootstrap}");
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<?> initializer : event.getSpringApplication().getInitializers()) {
if (initializer instanceof ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer) {
context = findBootstrapContext((ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer) initializer, configName);
}
}
if (context == null) {
// 创建 Spring Cloud ApplicationContext
context = bootstrapServiceContext(environment, event.getSpringApplication(), configName);
event.getSpringApplication().addListeners(new CloseContextOnFailureApplicationListener(context));
}
apply(context, event.getSpringApplication(), environment);
}
private ConfigurableApplicationContext bootstrapServiceContext(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
final SpringApplication application, String configName) {
ConfigurableEnvironment bootstrapEnvironment = new AbstractEnvironment() {
};
MutablePropertySources bootstrapProperties = bootstrapEnvironment.getPropertySources();
String configLocation = environment.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.location:}");
String configAdditionalLocation = environment
.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.additional-location:}");
Map<String, Object> bootstrapMap = new HashMap<>();
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.name", configName);
// if an app (or test) uses spring.main.web-application-type=reactive, bootstrap
// will fail
// force the environment to use none, because if though it is set below in the
// builder
// the environment overrides it
bootstrapMap.put("spring.main.web-application-type", "none");
if (StringUtils.hasText(configLocation)) {
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.location", configLocation);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(configAdditionalLocation)) {
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.additional-location", configAdditionalLocation);
}
bootstrapProperties.addFirst(new MapPropertySource(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, bootstrapMap));
for (PropertySource<?> source : environment.getPropertySources()) {
if (source instanceof StubPropertySource) {
continue;
}
bootstrapProperties.addLast(source);
}
// TODO: is it possible or sensible to share a ResourceLoader?
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder().profiles(environment.getActiveProfiles())
.bannerMode(Mode.OFF).environment(bootstrapEnvironment)
// Don't use the default properties in this builder
.registerShutdownHook(false).logStartupInfo(false).web(WebApplicationType.NONE);
final SpringApplication builderApplication = builder.application();
if (builderApplication.getMainApplicationClass() == null) {
// gh_425:
// SpringApplication cannot deduce the MainApplicationClass here
// if it is booted from SpringBootServletInitializer due to the
// absense of the "main" method in stackTraces.
// But luckily this method's second parameter "application" here
// carries the real MainApplicationClass which has been explicitly
// set by SpringBootServletInitializer itself already.
builder.main(application.getMainApplicationClass());
}
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains("refreshArgs")) {
// If we are doing a context refresh, really we only want to refresh the
// Environment, and there are some toxic listeners (like the
// LoggingApplicationListener) that affect global static state, so we need a
// way to switch those off.
builderApplication.setListeners(filterListeners(builderApplication.getListeners()));
}
builder.sources(BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration.class);
final ConfigurableApplicationContext context = builder.run();
// gh-214 using spring.application.name=bootstrap to set the context id via
// `ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer` prevents apps from getting the actual
// spring.application.name
// during the bootstrap phase.
context.setId("bootstrap");
// Make the bootstrap context a parent of the app context
addAncestorInitializer(application, context);
// It only has properties in it now that we don't want in the parent so remove
// it (and it will be added back later)
bootstrapProperties.remove(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
mergeDefaultProperties(environment.getPropertySources(), bootstrapProperties);
return context;
}
}
这个事件监听器会跳过 SpringCloud 容器触发的,只执行 SpringBoot 容器触发的事件,接着会创建了一个新的 ApplicationContext,具体的创建方法 bootstrapServiceContext 中可以看到引入了一个 BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration 配置:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(BootstrapImportSelector.class)
public class BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration {
}
然后接着看 BootstrapImportSelector:
public class BootstrapImportSelector implements EnvironmentAware, DeferredImportSelector {
private Environment environment;
private MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory();
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(BootstrapConfiguration.class, classLoader));
names.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils
.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(this.environment.getProperty("spring.cloud.bootstrap.sources", ""))));
List<OrderedAnnotatedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : names) {
try {
elements.add(new OrderedAnnotatedElement(this.metadataReaderFactory, name));
}
catch (IOException e) {
continue;
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(elements);
String[] classNames = elements.stream().map(e -> e.name).toArray(String[]::new);
return classNames;
}
//...
}
这里我们看到了 SpringCloud 导入了 spring.factories 中的 BootstrapConfiguration 为 key 的配置类。
我们知道实际的配置文件加载是 org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor 完成的,这个类的优先级是 Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10,而 BootstrapApplicationListener 的优先级是 Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 5,因此刚好满足先在 Environment 中添加 classpath:/bootstrap,再由 ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor 读取配置。
配置中心读取
完成 bootstrap 读取后也就表示 prepareEnvironment 完成,之后进入 prepareContext,这里会调用所有的 ApplicationContextInitializer 接口,其中就包括 org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config.PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(PropertySourceBootstrapProperties.class)
public class PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent>,
ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered {
/**
* Bootstrap property source name.
*/
public static final String BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = BootstrapApplicationListener.BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME
+ "Properties";
private static Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration.class);
private int order = Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10;
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<PropertySourceLocator> propertySourceLocators = new ArrayList<>();
@Autowired
private PropertySourceBootstrapProperties bootstrapProperties;
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return this.order;
}
public void setPropertySourceLocators(Collection<PropertySourceLocator> propertySourceLocators) {
this.propertySourceLocators = new ArrayList<>(propertySourceLocators);
}
/*
* The ApplicationListener is called when the main application context is initialized.
* This will be called after the ApplicationListener ContextRefreshedEvent is fired
* during the bootstrap phase. This method is also what added PropertySources prior to
* Spring Cloud 2021.0.7, this is why it will be called when
* spring.cloud.config.initialize-on-context-refresh is false. When
* spring.cloud.config.initialize-on-context-refresh is true this method provides a
* "second fetch" of configuration data to fetch any additional configuration data
* from profiles that have been activated.
*/
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
if (!bootstrapProperties.isInitializeOnContextRefresh() || !applicationContext.getEnvironment()
.getPropertySources().contains(BootstrapApplicationListener.BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) {
doInitialize(applicationContext);
}
}
private void doInitialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
List<PropertySource<?>> composite = new ArrayList<>();
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.propertySourceLocators);
boolean empty = true;
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment();
for (PropertySourceLocator locator : this.propertySourceLocators) {
Collection<PropertySource<?>> source = locator.locateCollection(environment);
if (source == null || source.size() == 0) {
continue;
}
List<PropertySource<?>> sourceList = new ArrayList<>();
for (PropertySource<?> p : source) {
if (p instanceof EnumerablePropertySource<?> enumerable) {
sourceList.add(new BootstrapPropertySource<>(enumerable));
}
else {
sourceList.add(new SimpleBootstrapPropertySource(p));
}
}
logger.info("Located property source: " + sourceList);
composite.addAll(sourceList);
empty = false;
}
if (!empty) {
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
String logConfig = environment.resolvePlaceholders("${logging.config:}");
LogFile logFile = LogFile.get(environment);
for (PropertySource<?> p : environment.getPropertySources()) {
if (p.getName().startsWith(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) {
propertySources.remove(p.getName());
}
}
insertPropertySources(propertySources, composite);
reinitializeLoggingSystem(environment);
setLogLevels(applicationContext, environment);
handleProfiles(environment);
}
}
//...
}
上面的 doInitialize 方法调用了 locator.locateCollection,最后会调用到 org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config.PropertySourceLocator#locate 来加载 PropertySource 属性源,配置中心就是在这里切入的,以 Spring Cloud Tencent 为例,即 com.tencent.cloud.polaris.config.adapter.PolarisConfigFileLocator(这个类在 Spring Cloud 容器中就加载了,所以是在哪里配置的呢?当然是前面说到的 Spring Factories 的 BootstrapConfiguration 啦):
@Order(0)
public class PolarisConfigFileLocator implements PropertySourceLocator {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PolarisConfigFileLocator.class);
private static final String POLARIS_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "polaris-config";
private final PolarisConfigProperties polarisConfigProperties;
private final PolarisContextProperties polarisContextProperties;
private final ConfigFileService configFileService;
private final PolarisPropertySourceManager polarisPropertySourceManager;
private final Environment environment;
// this class provides customized logic for some customers to configure special business group files
private final PolarisConfigCustomExtensionLayer polarisConfigCustomExtensionLayer = PolarisServiceLoaderUtil.getPolarisConfigCustomExtensionLayer();
public PolarisConfigFileLocator(PolarisConfigProperties polarisConfigProperties, PolarisContextProperties polarisContextProperties, ConfigFileService configFileService, PolarisPropertySourceManager polarisPropertySourceManager, Environment environment) {
this.polarisConfigProperties = polarisConfigProperties;
this.polarisContextProperties = polarisContextProperties;
this.configFileService = configFileService;
this.polarisPropertySourceManager = polarisPropertySourceManager;
this.environment = environment;
}
@Override
public PropertySource<?> locate(Environment environment) {
CompositePropertySource compositePropertySource = new CompositePropertySource(POLARIS_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
try {
// load custom config extension files
initCustomPolarisConfigExtensionFiles(compositePropertySource);
// load spring boot default config files
initInternalConfigFiles(compositePropertySource);
// load custom config files
List<ConfigFileGroup> configFileGroups = polarisConfigProperties.getGroups();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configFileGroups)) {
return compositePropertySource;
}
initCustomPolarisConfigFiles(compositePropertySource, configFileGroups);
return compositePropertySource;
}
finally {
afterLocatePolarisConfigExtension(compositePropertySource);
}
}
private void initCustomPolarisConfigExtensionFiles(CompositePropertySource compositePropertySource) {
if (polarisConfigCustomExtensionLayer == null) {
LOGGER.debug("[SCT Config] PolarisAdaptorTsfConfigExtensionLayer is not init, ignore the following execution steps");
return;
}
polarisConfigCustomExtensionLayer.initConfigFiles(environment, compositePropertySource, polarisPropertySourceManager, configFileService);
}
private void afterLocatePolarisConfigExtension(CompositePropertySource compositePropertySource) {
if (polarisConfigCustomExtensionLayer == null) {
LOGGER.debug("[SCT Config] PolarisAdaptorTsfConfigExtensionLayer is not init, ignore the following execution steps");
return;
}
polarisConfigCustomExtensionLayer.executeAfterLocateConfigReturning(compositePropertySource);
}
private void initInternalConfigFiles(CompositePropertySource compositePropertySource) {
List<ConfigFileMetadata> internalConfigFiles = getInternalConfigFiles();
for (ConfigFileMetadata configFile : internalConfigFiles) {
PolarisPropertySource polarisPropertySource = loadPolarisPropertySource(configFile.getNamespace(), configFile.getFileGroup(), configFile.getFileName());
compositePropertySource.addPropertySource(polarisPropertySource);
polarisPropertySourceManager.addPropertySource(polarisPropertySource);
LOGGER.info("[SCT Config] Load and inject polaris config file. file = {}", configFile);
}
}
private List<ConfigFileMetadata> getInternalConfigFiles() {
String namespace = polarisContextProperties.getNamespace();
String serviceName = polarisContextProperties.getService();
if (!StringUtils.hasText(serviceName)) {
serviceName = environment.getProperty("spring.application.name");
}
List<ConfigFileMetadata> internalConfigFiles = new LinkedList<>();
// priority: application-${profile} > application > boostrap-${profile} > boostrap
String[] activeProfiles = environment.getActiveProfiles();
String[] defaultProfiles = environment.getDefaultProfiles();
List<String> profileList = new ArrayList<>();
if (ArrayUtils.isNotEmpty(activeProfiles)) {
profileList.addAll(Arrays.asList(activeProfiles));
}
else if (ArrayUtils.isNotEmpty(defaultProfiles)) {
profileList.addAll(Arrays.asList(defaultProfiles));
}
// build application config files
buildInternalApplicationConfigFiles(internalConfigFiles, namespace, serviceName, profileList);
// build bootstrap config files
buildInternalBootstrapConfigFiles(internalConfigFiles, namespace, serviceName, profileList);
return internalConfigFiles;
}
private void buildInternalApplicationConfigFiles(List<ConfigFileMetadata> internalConfigFiles, String namespace, String serviceName, List<String> profileList) {
for (String profile : profileList) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(profile)) {
continue;
}
internalConfigFiles.add(new DefaultConfigFileMetadata(namespace, serviceName, "application-" + profile + ".properties"));
internalConfigFiles.add(new DefaultConfigFileMetadata(namespace, serviceName, "application-" + profile + ".yml"));
internalConfigFiles.add(new DefaultConfigFileMetadata(namespace, serviceName, "application-" + profile + ".yaml"));
}
// build default config properties files.
internalConfigFiles.add(new DefaultConfigFileMetadata(namespace, serviceName, "application.properties"));
internalConfigFiles.add(new DefaultConfigFileMetadata(namespace, serviceName, "application.yml"));
internalConfigFiles.add(new DefaultConfigFileMetadata(namespace, serviceName, "application.yaml"));
}
private void buildInternalBootstrapConfigFiles(List<ConfigFileMetadata> internalConfigFiles, String namespace, String serviceName, List<String> profileList) {
for (String profile : profileList) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(profile)) {
continue;
}
internalConfigFiles.add(new DefaultConfigFileMetadata(namespace, serviceName, "bootstrap-" + profile + ".properties"));
internalConfigFiles.add(new DefaultConfigFileMetadata(namespace, serviceName, "bootstrap-" + profile + ".yml"));
internalConfigFiles.add(new DefaultConfigFileMetadata(namespace, serviceName, "bootstrap-" + profile + ".yaml"));
}
// build default config properties files.
internalConfigFiles.add(new DefaultConfigFileMetadata(namespace, serviceName, "bootstrap.properties"));
internalConfigFiles.add(new DefaultConfigFileMetadata(namespace, serviceName, "bootstrap.yml"));
internalConfigFiles.add(new DefaultConfigFileMetadata(namespace, serviceName, "bootstrap.yaml"));
}
private void initCustomPolarisConfigFiles(CompositePropertySource compositePropertySource, List<ConfigFileGroup> configFileGroups) {
String namespace = polarisContextProperties.getNamespace();
for (ConfigFileGroup configFileGroup : configFileGroups) {
String group = configFileGroup.getName();
if (!StringUtils.hasText(group)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("polaris config group name cannot be empty.");
}
List<String> files = configFileGroup.getFiles();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(files)) {
return;
}
for (String fileName : files) {
PolarisPropertySource polarisPropertySource = loadPolarisPropertySource(namespace, group, fileName);
compositePropertySource.addPropertySource(polarisPropertySource);
polarisPropertySourceManager.addPropertySource(polarisPropertySource);
LOGGER.info("[SCT Config] Load and inject polaris config file success. namespace = {}, group = {}, fileName = {}", namespace, group, fileName);
}
}
}
private PolarisPropertySource loadPolarisPropertySource(String namespace, String group, String fileName) {
ConfigKVFile configKVFile;
// unknown extension is resolved as properties file
if (ConfigFileFormat.isPropertyFile(fileName) || ConfigFileFormat.isUnknownFile(fileName)) {
configKVFile = configFileService.getConfigPropertiesFile(namespace, group, fileName);
}
else if (ConfigFileFormat.isYamlFile(fileName)) {
configKVFile = configFileService.getConfigYamlFile(namespace, group, fileName);
}
else {
LOGGER.warn("[SCT Config] Unsupported config file. namespace = {}, group = {}, fileName = {}", namespace, group, fileName);
throw new IllegalStateException("Only configuration files in the format of properties / yaml / yaml" + " can be injected into the spring context");
}
Map<String, Object> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
for (String key : configKVFile.getPropertyNames()) {
map.put(key, configKVFile.getProperty(key, null));
}
return new PolarisPropertySource(namespace, group, fileName, configKVFile, map);
}
}
简单来说就是建立于配置中心的连接,根据 bootstrap 中配置的配置文件名从 Polaris 配置中心中获取对应的配置文件,并将这些配置文件中的配置转为 key value 的 MapPropertySource 返回,然后再添加到 Environment 中,当然,我们从配置中心获取到的配置肯定是优先级最高的,放入 Environment 的方式也就是 addFirst。
配置刷新
@ConfigurationProperties
可以看到默认的 org.springframework.cloud.context.properties.ConfigurationPropertiesRebinder 的 onApplicationEvent 方法条件有 event.getKeys().equals(event.getSource()),这个条件应该是为了兼容以前的代码,进而导致重建所有 @ConfigurationProperties Bean,这是没必要的
@Component
@ManagedResource
public class ConfigurationPropertiesRebinder
implements ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<EnvironmentChangeEvent> {
private ConfigurationPropertiesBeans beans;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private Map<String, Exception> errors = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public ConfigurationPropertiesRebinder(ConfigurationPropertiesBeans beans) {
this.beans = beans;
}
@ManagedOperation
public void rebind() {
this.errors.clear();
for (String name : this.beans.getBeanNames()) {
rebind(name);
}
}
@ManagedOperation
public boolean rebind(String name) {
if (!this.beans.getBeanNames().contains(name)) {
return false;
}
ApplicationContext appContext = this.applicationContext;
while (appContext != null) {
if (appContext.containsLocalBean(name)) {
return rebind(name, appContext);
}
else {
appContext = appContext.getParent();
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* WARNING: This method rebinds beans from any context in the hierarchy using the main
* application context.
* @param type bean type to rebind.
* @return true, if successful.
*/
public boolean rebind(Class type) {
String[] beanNamesForType = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this.applicationContext, type);
if (beanNamesForType.length > 0) {
String name = beanNamesForType[0];
if (ScopedProxyUtils.isScopedTarget(name)) {
name = ScopedProxyUtils.getOriginalBeanName(name);
}
return rebind(name, this.applicationContext);
}
return false;
}
private boolean rebind(String name, ApplicationContext appContext) {
try {
Object bean = appContext.getBean(name);
if (AopUtils.isAopProxy(bean)) {
bean = ProxyUtils.getTargetObject(bean);
}
if (bean != null) {
// TODO: determine a more general approach to fix this.
// see
// https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-commons/issues/571
if (getNeverRefreshable().contains(bean.getClass().getName())) {
return false; // ignore
}
appContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().destroyBean(bean);
appContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().initializeBean(bean, name);
return true;
}
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
this.errors.put(name, e);
throw e;
}
catch (Exception e) {
this.errors.put(name, e);
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot rebind to " + name, e);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(EnvironmentChangeEvent event) {
if (this.applicationContext.equals(event.getSource())
// Backwards compatible
|| event.getKeys().equals(event.getSource())) {
rebind();
}
}
}
因此 Spring Cloud Tencent 重新实现了一下,AffectedConfigurationPropertiesRebinder:
public class AffectedConfigurationPropertiesRebinder extends ConfigurationPropertiesRebinder {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AffectedConfigurationPropertiesRebinder.class);
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private Map<String, ConfigurationPropertiesBean> propertiesBeans = new HashMap<>();
private final Map<String, Map<String, Object>> propertiesBeanDefaultValues = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public AffectedConfigurationPropertiesRebinder(ConfigurationPropertiesBeans beans) {
super(beans);
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
super.setApplicationContext(applicationContext);
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
propertiesBeans = ConfigurationPropertiesBean.getAll(applicationContext);
initPropertiesBeanDefaultValues(propertiesBeans);
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(EnvironmentChangeEvent event) {
if (this.applicationContext.equals(event.getSource())) {
rebindAffectedBeans(event);
}
}
private void rebindAffectedBeans(EnvironmentChangeEvent event) {
Set<String> changedKeys = event.getKeys();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(changedKeys)) {
return;
}
propertiesBeans.forEach((name, bean) -> {
changedKeys.forEach(key -> {
String propertiesPrefix = Objects.requireNonNull(AnnotationUtils.getValue(bean.getAnnotation()))
.toString();
if (key.startsWith(propertiesPrefix)) {
rebind(name);
rebindDefaultValue(name, key);
}
});
});
}
private void rebindDefaultValue(String beanName, String key) {
String changeValue = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty(key);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(changeValue)) {
return;
}
Map<String, Object> defaultValues = propertiesBeanDefaultValues.get(beanName);
if (MapUtils.isEmpty(defaultValues)) {
return;
}
try {
String fieldName = key.substring(key.lastIndexOf(".") + 1);
Object bean = applicationContext.getBean(beanName);
Field field = ReflectionUtils.findField(bean.getClass(), fieldName);
if (field != null) {
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(bean, defaultValues.get(fieldName));
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("[SCT Config] rebind default value error, bean = {}, key = {}", beanName, key);
}
}
private void initPropertiesBeanDefaultValues(Map<String, ConfigurationPropertiesBean> propertiesBeans) {
if (MapUtils.isEmpty(propertiesBeans)) {
return;
}
for (ConfigurationPropertiesBean propertiesBean : propertiesBeans.values()) {
Map<String, Object> defaultValues = new HashMap<>();
try {
Object instance = propertiesBean.getInstance().getClass().getDeclaredConstructor((Class<?>[]) null).newInstance();
ReflectionUtils.doWithFields(instance.getClass(), field -> {
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
defaultValues.put(field.getName(), field.get(instance));
}
catch (Exception ignored) {
}
}, field -> {
int modifiers = field.getModifiers();
return !Modifier.isFinal(modifiers) && !Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && ReflectionUtils.writableBeanField(field);
});
}
catch (Exception ignored) {
}
propertiesBeanDefaultValues.put(propertiesBean.getName(), defaultValues);
}
}
}
这个类使用了 org.springframework.cloud.context.environment.EnvironmentChangeEvent#getKeys 返回的属性名,然后匹配到所属的 @ConfigurationProperties Bean,这样就可以只刷新一个 bean 了,另外还做了一个处理,即当这个属性被删除时还原为默认值。
@Value
SpringBoot 对 @Value 的处理是和 @Autowired 一起在 BeanPostProcessor 中处理的,因此如果通过 SpringBoot 的机制处理 @Value 属性的配置刷新只能重建 Bean,Spring Cloud Context 为其提供了 @RefreshScope 注解,将其标在 @Value 所在类上,然后在想刷新 @Value 配置时调用 org.springframework.cloud.context.refresh.ContextRefresher#refresh:
public synchronized Set<String> refresh() {
Set<String> keys = refreshEnvironment();
this.scope.refreshAll();
return keys;
}
public synchronized Set<String> refreshEnvironment() {
Map<String, Object> before = extract(this.context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources());
updateEnvironment();
Set<String> keys = changes(before, extract(this.context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources())).keySet();
this.context.publishEvent(new EnvironmentChangeEvent(this.context, keys));
return keys;
}
public void refreshAll() {
super.destroy();
this.context.publishEvent(new RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent());
}
可以看到他先调用了 refreshEnvironment 刷新配置,然后调用 refreshAll 销毁标记了 @RefreshScope 注解的 bean,具体原理就是自定义 bean 的 scope,然后用 cglib 生成存在 @RefreshScope 注解的 bean,使用这个 bean 时如果代理类发现 bean 没创建会创建,总之就是代理类延迟创建 bean 那一套。
当然通常我们不想重新创建 bean,因此像 Apollo 和 Spring Cloud Tencent 都是使用反射来修改 @Value 配置,以 Spring Cloud Tencent 为例,PolarisConfigPropertyAutoRefresher 监听 ApplicationReadyEvent 事件,在 SpringApplication 初始化完成后为 Polaris 添加配置修改回调完成配置修改。
因为只想刷新部分 @Value,所以我们需要记录下 @Value 所在的 bean,Spring Cloud Tencent 是在 BeanPostProcessor(SpringValueProcessor)做的扩展,它的生命周期大家都明白就不多说了,记下所有 @Value 后就可以在 Polaris 触发配置更改回调时从记录中拿到那个 Bean 作反射更改配置了。
总结
Spring Cloud Context 定义了两种配置的刷新方式,第一种是针对 @ConfigurationProperties 的 Rebinder,第二种是针对 @Value 的 @RefreshScope,两种方式都有一些不尽如人意的地方,因此像 Spring Cloud Tencent 等具体实现都做了一定修改,针对第一种修改为只刷新涉及更新配置的 XxxProperties 类,而不是所有配置类,针对第二种修改为反射字段或方法更改配置属性,而不是重建所有 @RefreshScope bean,另外 SpringBoot @Value 是在 BeanPostProcessor 阶段处理的,反射修改 @Value 不符合 SpringBoot 对这个注解的定义,因此 Spring Cloud Tencent 也保留提供了 Spring Cloud Context 重建 bean 来完成 @Value 配置更改的方式。
关于 Spring Cloud Tencent 的配置中心相关代码可以看它的自动配置类 com.tencent.cloud.polaris.config.PolarisConfigAutoConfiguration
PS:PolarisConfigAutoConfiguration 类有 @AutoConfigureBefore 的不正确用法,@AutoConfigureBefore 只能用于 spring.factories 文件,另外配置类如果有嵌套配置类,那么嵌套配置类一定是优先处理的(详见 ConfigurationClassParser,里面有注释说首先递归处理嵌套类)
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnPolarisConfigEnabled
public class PolarisConfigAutoConfiguration {
//...
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnReflectRefreshType
@AutoConfigureBefore(PolarisConfigAutoConfiguration.class)
public static class PolarisReflectRefresherAutoConfiguration {
//...
}
}
Spring Cloud Gateway
Spring Cloud Gateway 通常需要动态配置,否则重启的影响太大,以 Spring Cloud Tencent 为例,它的配置是一分钟刷新一次的,先看入口 com.tencent.cloud.polaris.discovery.refresh.PolarisRefreshApplicationReadyEventListener:
public class PolarisRefreshApplicationReadyEventListener
implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationReadyEvent>, ApplicationEventPublisherAware, DisposableBean {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PolarisRefreshApplicationReadyEventListener.class);
private static final int DELAY = 60;
private final PolarisSDKContextManager polarisSDKContextManager;
private final PolarisServiceStatusChangeListener polarisServiceStatusChangeListener;
private final ScheduledExecutorService refreshExecutor;
private ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;
public PolarisRefreshApplicationReadyEventListener(PolarisSDKContextManager polarisSDKContextManager,
PolarisServiceStatusChangeListener polarisServiceStatusChangeListener) {
this.polarisSDKContextManager = polarisSDKContextManager;
this.polarisServiceStatusChangeListener = polarisServiceStatusChangeListener;
this.refreshExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(
new NamedThreadFactory("polaris-service-refresh"));
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationReadyEvent event) {
// Register service change listener.
polarisSDKContextManager.getSDKContext().getExtensions().getLocalRegistry()
.registerResourceListener(polarisServiceStatusChangeListener);
// Begin scheduled refresh thread.
refresh();
}
/**
* Start the refresh thread.
*/
public void refresh() {
refreshExecutor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> {
try {
// Trigger reload of gateway route cache.
this.publisher.publishEvent(new HeartbeatEvent(this, INDEX.getAndIncrement()));
}
catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error("refresh polaris service error.", e);
}
}, DELAY, DELAY, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
@Override
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) {
this.publisher = applicationEventPublisher;
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
refreshExecutor.shutdown();
}
}
可以看到触发 ApplicationReadyEvent 事件即 SpringBoot 应用启动完成时,启动一个 1 分钟执行一次的定时任务,延迟 1 分钟后执行,任务内容是发布一个 HeartbeatEvent 事件,然后 Spring Cloud Gateway 的 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteRefreshListener 监听到该事件:
public class RouteRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
private final ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;
private HeartbeatMonitor monitor = new HeartbeatMonitor();
public RouteRefreshListener(ApplicationEventPublisher publisher) {
Assert.notNull(publisher, "publisher may not be null");
this.publisher = publisher;
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) {
ContextRefreshedEvent refreshedEvent = (ContextRefreshedEvent) event;
if (!WebServerApplicationContext.hasServerNamespace(refreshedEvent.getApplicationContext(), "management")) {
reset();
}
}
else if (event instanceof RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent || event instanceof InstanceRegisteredEvent) {
reset();
}
else if (event instanceof ParentHeartbeatEvent) {
ParentHeartbeatEvent e = (ParentHeartbeatEvent) event;
resetIfNeeded(e.getValue());
}
else if (event instanceof HeartbeatEvent) {
HeartbeatEvent e = (HeartbeatEvent) event;
resetIfNeeded(e.getValue());
}
}
private void resetIfNeeded(Object value) {
if (this.monitor.update(value)) {
reset();
}
}
private void reset() {
this.publisher.publishEvent(new RefreshRoutesEvent(this));
}
}
resetIfNeeded 的 monitor.update(value) 一定成功,因为这个 value 是递增的心跳号,接着发送了一个 RefreshRoutesEvent 事件,org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.CachingRouteLocator 监听到了该事件:
public class CachingRouteLocator
implements Ordered, RouteLocator, ApplicationListener<RefreshRoutesEvent>, ApplicationEventPublisherAware {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(CachingRouteLocator.class);
private static final String CACHE_KEY = "routes";
private final RouteLocator delegate;
private final Flux<Route> routes;
private final Map<String, List> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher;
public CachingRouteLocator(RouteLocator delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
routes = CacheFlux.lookup(cache, CACHE_KEY, Route.class).onCacheMissResume(this::fetch);
}
private Flux<Route> fetch() {
return this.delegate.getRoutes().sort(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
private Flux<Route> fetch(Map<String, Object> metadata) {
return this.delegate.getRoutesByMetadata(metadata).sort(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
@Override
public Flux<Route> getRoutes() {
return this.routes;
}
/**
* Clears the routes cache.
* @return routes flux
*/
public Flux<Route> refresh() {
this.cache.remove(CACHE_KEY);
return this.routes;
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(RefreshRoutesEvent event) {
try {
if (this.cache.containsKey(CACHE_KEY) && event.isScoped()) {
final Mono<List<Route>> scopedRoutes = fetch(event.getMetadata()).collect(Collectors.toList())
.onErrorResume(s -> Mono.just(List.of()));
scopedRoutes.subscribe(scopedRoutesList -> {
Flux.concat(Flux.fromIterable(scopedRoutesList), getNonScopedRoutes(event)).materialize()
.collect(Collectors.toList()).subscribe(signals -> {
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new RefreshRoutesResultEvent(this));
cache.put(CACHE_KEY, signals);
}, this::handleRefreshError);
}, this::handleRefreshError);
}
else {
final Mono<List<Route>> allRoutes = fetch().collect(Collectors.toList());
allRoutes.subscribe(list -> Flux.fromIterable(list).materialize().collect(Collectors.toList())
.subscribe(signals -> {
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new RefreshRoutesResultEvent(this));
cache.put(CACHE_KEY, signals);
}, this::handleRefreshError), this::handleRefreshError);
}
}
catch (Throwable e) {
handleRefreshError(e);
}
}
private Flux<Route> getNonScopedRoutes(RefreshRoutesEvent scopedEvent) {
return this.getRoutes()
.filter(route -> !RouteLocator.matchMetadata(route.getMetadata(), scopedEvent.getMetadata()));
}
private void handleRefreshError(Throwable throwable) {
if (log.isErrorEnabled()) {
log.error("Refresh routes error !!!", throwable);
}
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new RefreshRoutesResultEvent(this, throwable));
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) {
this.applicationEventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher;
}
}
CachingRouteLocator 是一个组合所有 RouteLocator 的类,并具有缓存功能,可以看到这个 cache 没有失效时间,前面说到触发了 onApplicationEvent 方法,这个方法里进行了 cache 的更新,我们想要从配置中心获取的路由规则就在在这里通过 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocator 获取的(响应式编程 debug 太复杂了,不会,看调用栈发现的):
public class PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocator implements RouteDefinitionLocator {
private final GatewayProperties properties;
public PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocator(GatewayProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public Flux<RouteDefinition> getRouteDefinitions() {
return Flux.fromIterable(this.properties.getRoutes());
}
}
从 PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocator 类中可以看到构造函数中的 GatewayProperties,这个类就是一个 @ConfigurationProperties 配置类,这样就完成了路由规则刷新。
简单总结下:程序启动后,启动刷新路由规则的定时任务,1 分钟一次,任务执行最终会触发 CachingRouteLocator 的 onApplicationEvent 方法,然后通过 PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocator 加载到最新的 GatewayProperties 路由规则(GatewayProperties 被配置中心修改了,所以是最新的),需要注意:路由规则不是在配置中心发布后立即生效的,而是发布后的下一个定时任务执行后才会生效。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?