多线程的同步机制
一、通过synchronized执行一半同步,一半异步
1.新建一个Task.java
public class Task { public void doLongTimeTask(){ for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ System.out.println("nosynchronized threadName="+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" i="+(i+1)); } System.out.println(""); synchronized(this){ for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ System.out.println("synchronized threadName="+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" i="+(i+1)); } } } }
2.新建Mythread1.java
public class Mythread1 extends Thread{ private Task task; public Mythread1(Task task){ super(); this.task=task; } public void run(){ super.run(); task.doLongTimeTask(); } }
3.新建Mythread2.java
public class Mythread2 extends Thread{ private Task task; public Mythread2(Task task){ super(); this.task=task; } public void run(){ super.run(); task.doLongTimeTask(); } }
4.新建run.java
public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Task task=new Task(); Mythread1 t1=new Mythread1(task); t1.setName("线程1"); t1.start(); Mythread2 t2=new Mythread2(task); t2.setName("线程2"); t2.start(); } }
5.输出结果:
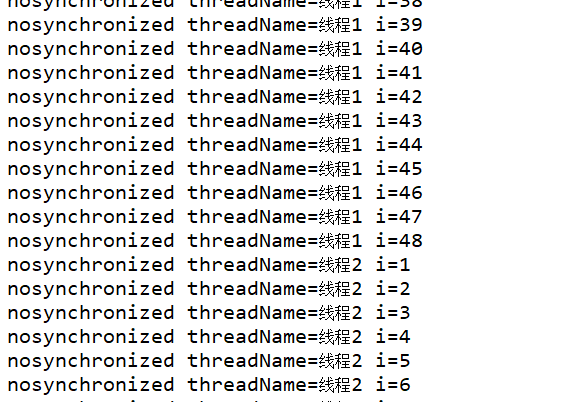
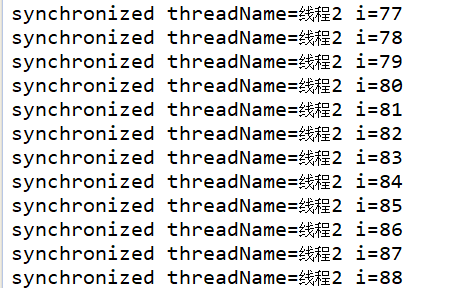
我们可看到,程序运行时,同步代码块只能允许一个线程运行,而不能存在多个线程交替运行,必须等待另外一个线程结束才能运行本线程,
在非同步代码块中,线程可以交替运行
二、验证synchronized(锁定当前对象)
1.创建Task.java
public class Task { public synchronized void otherMethod(){ System.out.println("===============run-otherMethod"); } public void doLongTimeTask(){ synchronized(this){ for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ System.out.println("synchronized threadName="+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" i="+(i+1)); } } } }
2.创建Mythread1.java
public class Mythread1 extends Thread{ private Task task; public Mythread1(Task task){ super(); this.task=task; } public void run(){ super.run(); task.doLongTimeTask(); } }
3.创建Mythread.java
public class Mythread2 extends Thread{ private Task task; public Mythread2(Task task){ super(); this.task=task; } public void run(){ super.run(); task.otherMethod(); } }
4.创建Run.java
public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Task task=new Task(); Mythread1 t1=new Mythread1(task); t1.setName("线程1"); t1.start(); Mythread2 t2=new Mythread2(task); t2.setName("线程2"); t2.start(); } }
5.结果
由于创建synchronized(this)是针对对象锁,虽然是不同的对象,但是只拥有一把锁,因此执行同步
没有停止的脚步,只有倒下去的脚步




