liunx驱动----构造和运行模块
以hello world模块为例
#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> //在执行 insmod hlello 的时候会被调用 static int hello_init(void) { printk(KERN_ALERT"hello_init\n"); return 0; } //在执行 rmmod hlello 的时候会被调用 static void hello_exit(void) { printk(KERN_ALERT"hello_exit\n"); } MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");//添加自由许可证 module_init(hello_init); module_exit(hello_exit);
KERN_ALERT:是用来定义这条消息的优先级的。声明在:kernel.h include\linux\kernel.h中声明
#define KERN_EMERG "<0>" /* system is unusable (紧急情况,系统可能会崩溃) */ #define KERN_ALERT "<1>" /* action must be taken immediately(必须立即响应) */ #define KERN_CRIT "<2>" /* critical conditions (临界情况) */ #define KERN_ERR "<3>" /* error conditions (错误信息) */ #define KERN_WARNING "<4>" /* warning conditions (警告信息) */ #define KERN_NOTICE "<5>" /* normal but significant condition( 普通的但可能需要注意的信息) */ #define KERN_INFO "<6>" /* informational (提示性信息) */ #define KERN_DEBUG "<7>" /* debug-level messages (调试信息) */
Makfile:
KERN_DIR = /work/system/linux-2.6.22.6 //内核路径 all: make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean: make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean rm -rf modules.order obj-m += helloworld.o //编译成helloworld.o
make输出信息:
make -C /work/system/linux-2.6.22.6 M=`pwd` modules make[1]: Entering directory `/work/system/linux-2.6.22.6' CC [M] /home/book/work/nfs_root/first_fs/work/helloworld/helloworld.o Building modules, stage 2. MODPOST 1 modules CC /home/book/work/nfs_root/first_fs/work/helloworld/helloworld.mod.o LD [M] /home/book/work/nfs_root/first_fs/work/helloworld/helloworld.ko make[1]: Leaving directory `/work/system/linux-2.6.22.6'
从输出信息中可以看出 ,最终的目的是生成了 helloworld.ko 这个文件
运行结果:

为什么需要使用printk 函数来打印了?
在模块运行过程中,不能依赖于c库,模块能够调用printk是因为在 insmod函数装入模块后,模块就链接到了内核中。所以就能访问公用的符号(printk)
为什么模块需要初始化?
模块初始化的目的就是为了以后调用模块中的函数做准备。
设备驱动程序如何引用当前进程?
在设备驱动程序中只需要包含<linux/sched.h>头文件即可引用当前进程。例如 通过访问 Staruc task_staruct 成员变量答应当前的命令名称。和进程ID
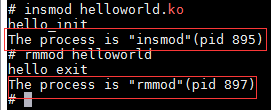
分别在装载和卸载调用中添加两条打印语句:printk(KERN_INFO"The process is \"%s\"(pid %i)\n",current->comm,current->pid)
打印出当前命令名称与进程ID
//在执行 insmod hlello 的时候会被调用 static int hello_init(void) { printk(KERN_ALERT"hello_init\n"); printk(KERN_INFO"The process is \"%s\"(pid %i)\n",current->comm,current->pid); return 0; } //在执行 rmmod hlello 的时候会被调用 static void hello_exit(void) { printk(KERN_ALERT"hello_exit\n"); printk(KERN_INFO"The process is \"%s\"(pid %i)\n",current->comm,current->pid); }
运行状态如下:
模块参数:
由于系统不同,所以驱动程序需要的参数也会发生变化,其中包括设备编号以及其他一些用来控制驱动程序操作方式的参数。
为了满足这个需求,内核允许对驱动程序指定参数,而这些参数可在装载驱动模块是发生改变。
在insmod改变模块参数之前,模块必须让这些参数对insmod命令可见(可操作)。必须使用module_param 宏来声明,在moduleparm.h中定义
module_param 需要三个参数: 变量名称 类型 用于sysfs入口项的访问许可掩码。
代码如下:
static char *param_string = "hello";//一个名字为param_string 的指针变量 static int print_cont =1; //int 型变量 module_param(param_string, charp, S_IRUGO);//使用module_param宏来让param_string变量对insmod 命令可见 module_param(print_cont, int, S_IRUGO);//同上 //在执行 insmod hlello 的时候会被调用 static int hello_init(void) { int i; printk(KERN_ALERT"hello_init\n"); printk(KERN_INFO"The process is \"%s\"(pid %i)\n",current->comm,current->pid); for(i= 0 ;i < print_cont; i++) //根据变量打印对应的次数 printk(KERN_ALERT"%s\n",param_string); //打印 return 0; } //在执行 rmmod hlello 的时候会被调用 static void hello_exit(void) { printk(KERN_ALERT"hello_exit\n"); printk(KERN_INFO"The process is \"%s\"(pid %i)\n",current->comm,current->pid); } MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");//添加自由许可证 module_init(hello_init); module_exit(hello_exit);
运行结果:

内核模块支持参数类型:
bool
invbool(反转其值,true变为false false 变为true)
charp 字符指针值,内核会给字符串分配内存,并相应设置指针。
int
long
short
uint
ulong
ushort


