实验2 类和对象_基础编程1
实验一
t.h源码:
#pragma once #include <string> // 类T: 声明 class T { // 对象属性、方法 public: T(int x = 0, int y = 0); // 普通构造函数 T(const T& t); // 复制构造函数 T(T&& t); // 移动构造函数 ~T(); // 析构函数 void adjust(int ratio); // 按系数成倍调整数据 void display() const; // 以(m1, m2)形式显示T类对象信息 private: int m1, m2; // 类属性、方法 public: static int get_cnt(); // 显示当前T类对象总数 public: static const std::string doc; // 类T的描述信息 static const int max_cnt; // 类T对象上限 private: static int cnt; // 当前T类对象数目 // 类T友元函数声明 friend void func(); }; // 普通函数声明 void func();
t.cpp源码:
// 类T: 实现 // 普通函数实现 #include "t.h" #include <iostream> #include <string> using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::string; // static成员数据类外初始化 const std::string T::doc{"a simple class sample"}; const int T::max_cnt = 999; int T::cnt = 0; // 对象方法 T::T(int x, int y): m1{x}, m2{y} { ++cnt; cout << "T constructor called.\n"; } T::T(const T &t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} { ++cnt; cout << "T copy constructor called.\n"; } T::T(T &&t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} { ++cnt; cout << "T move constructor called.\n"; } T::~T() { --cnt; cout << "T destructor called.\n"; } void T::adjust(int ratio) { m1 *= ratio; m2 *= ratio; } void T::display() const { cout << "(" << m1 << ", " << m2 << ")" ; } // 类方法 int T::get_cnt() { return cnt; } // 友元 void func() { T t5(42); t5.m2 = 2049; cout << "t5 = "; t5.display(); cout << endl; }
task1.cpp源码:
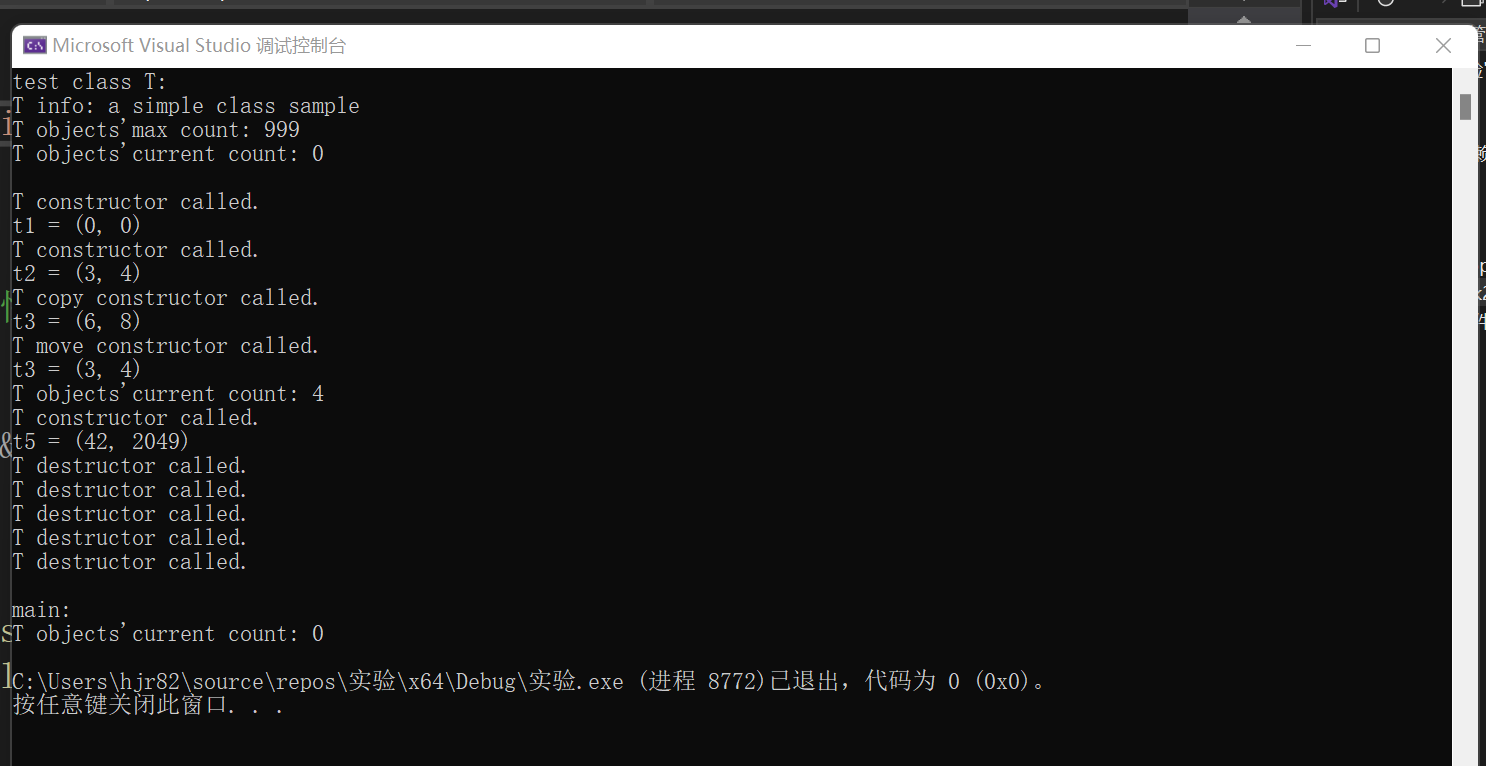
#include "t.h" #include <iostream> using std::cout; using std::endl; void test(); int main() { test(); cout << "\nmain: \n"; cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl; } void test() { cout << "test class T: \n"; cout << "T info: " << T::doc << endl; cout << "T objects'max count: " << T::max_cnt << endl; cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl << endl; T t1; cout << "t1 = "; t1.display(); cout << endl; T t2(3, 4); cout << "t2 = "; t2.display(); cout << endl; T t3(t2); t3.adjust(2); cout << "t3 = "; t3.display(); cout << endl; T t4(std::move(t2)); cout << "t3 = "; t4.display(); cout << endl; cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl; func(); }
问题一:

需要在t.h中对func()进行声明,否则t.cpp和task1.cpp找不到func()的声明。
问题二:
T(int x=0,int y=0); 是创建一个T类对象,并且初始化x,y。 调用时机:每当一个T类对象被创建时,此构造函数就会被调用
T(const T &t); 通过已有的对象T把T中的数据复制传给新对象t。调用时机:当一个对象通过另一个对象初始化时,会被调用
T(T &&t); 移动构造函数用于通过移动语义从另一个对象创建新对象。 调用时机:当对象通过 std::move 或其他移动语义传递时,移动构造函数会被调用
~T();析构函数在对象生命周期结束时被调用。 调用时机:当一个对象超出作用域或被显式删除时,析构函数会被调用
问题三:
不能正确编译运行
实验二
t.h源码:
#pragma once #include<string> class Complex { public: Complex(double a = 0, double b = 0) : real(a), imag(b) {} Complex(const Complex& c1) : real(c1.real), imag(c1.imag) {} ~Complex() = default; void add(const Complex& c1) { real += c1.real; imag += c1.imag; } double get_real() const { return real; } double get_imag() const { return imag; } static std::string doc; friend bool is_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2); friend bool is_not_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2); friend Complex add(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2); friend double abs(const Complex& c1); friend void output(const Complex& c); private: double real; double imag; };
t.cpp源码:
#include "t.h" #include<iostream> #include<string> #include<cmath> using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::string; string Complex::doc = "This is a Complex Number class"; void output(const Complex& c) { if (c.imag == 0) cout << c.real; else if (c.imag < 0) cout << c.real << " - " << abs(c.imag) << "i"; else cout << c.real << " + " << abs(c.imag) << "i"; } Complex add(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2) { return Complex(c1.real + c2.real, c1.imag + c2.imag); } bool is_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2) { return (c1.real == c2.real && c1.imag == c2.imag); } bool is_not_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2) { return !is_equal(c1, c2); } double abs(const Complex& c) { return sqrt(c.real * c.real + c.imag * c.imag); }
task2.cpp源码:
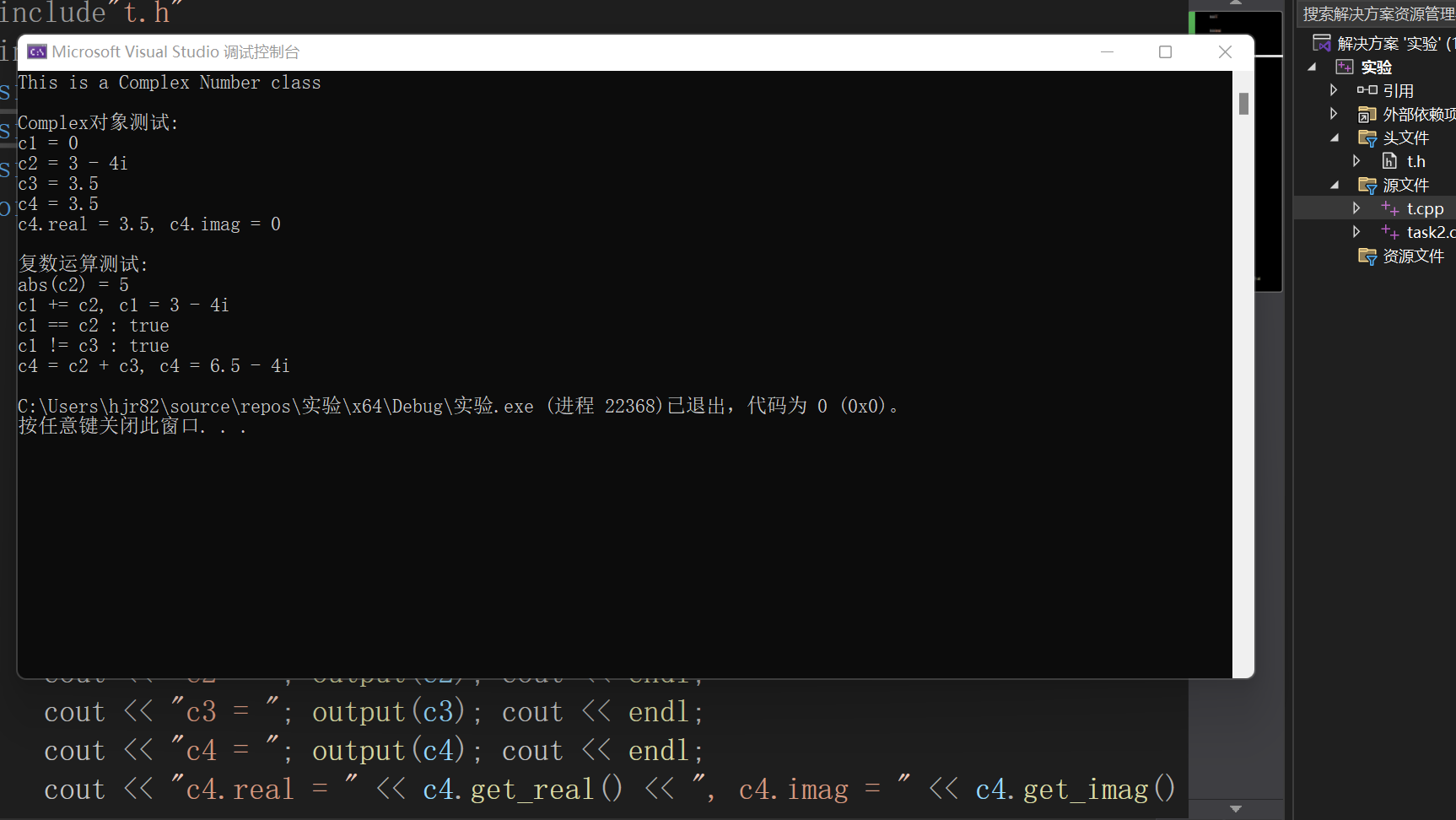
#include"t.h" #include<iostream> using std::cout; using std::endl; using namespace std; void test() { cout << Complex::doc << endl; cout << endl; cout << "Complex对象测试: " << endl; Complex c1; Complex c2(3, -4); const Complex c3(3.5); Complex c4(c3); cout << "c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; cout << "c2 = "; output(c2); cout << endl; cout << "c3 = "; output(c3); cout << endl; cout << "c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; cout << "c4.real = " << c4.get_real() << ", c4.imag = " << c4.get_imag() << endl; cout << endl; cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; c1.add(c2); cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; cout << boolalpha; cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl; cout << "c1 != c3 : " << is_not_equal(c1, c3) << endl; c4 = add(c2, c3); cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; } int main() { test(); return 0; }
实验三
#include <iostream> #include <complex> using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::boolalpha; using std::complex; void test() { cout << "标准库模板类comple测试: " << endl; complex<double> c1; complex<double> c2(3, -4); const complex<double> c3(3.5); complex<double> c4(c3); cout << "c1 = " << c1 << endl; cout << "c2 = " << c2 << endl; cout << "c3 = " << c3 << endl; cout << "c4 = " << c4 << endl; cout << "c4.real = " << c4.real() << ", c4.imag = " << c4.imag() << endl; cout << endl; cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; c1 += c2; cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = " << c1 << endl; cout << boolalpha; cout << "c1 == c2 : " << (c1 == c2) << endl; cout << "c1 != c3 : " << (c1 != c3) << endl; c4 = c2 + c3; cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = " << c4 << endl; } int main() { test(); }
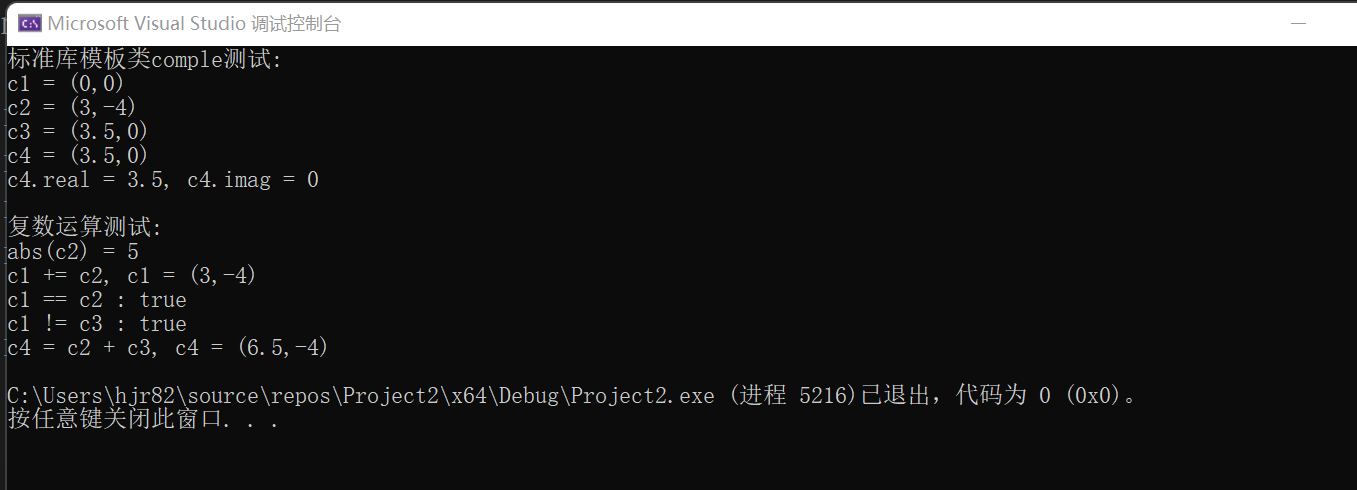
提供了默认构造函数,带参构造函数,复制构造函数,取模运算,访问实部虚部,求和运算,加法运算符重载,判断两个复数是否相等
对比任务2:
1.不需要进行类和友元函数的构造和说明 2.用标准库降低了代码的复杂度,减少出错
实验四
t.h源码:
#pragma once #include<string> class Fraction { public: Fraction(int a = 0, int b = 1) : up(a), down(b) { int k = gcd(up, down); up /= k; down /= k; } Fraction(const Fraction& f) : up(f.up), down(f.down) { int k = gcd(up, down); up /= k; down /= k; } ~Fraction() = default; int get_up() const { return up; } int get_down() const { return down; } void negative() { up = -up; } static int gcd(int a, int b) { while (b != 0) { int r = b; b = a % b; a = r; } return (a == 0 ? 1 : a); } static std::string doc; friend void output(const Fraction& f); friend Fraction add(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); friend Fraction sub(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); friend Fraction mul(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); friend Fraction div(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); private: int up; int down; };
t.cpp源码:
#include "task2.h" #include<iostream> #include<string> #include<cmath> #include <stdexcept> using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::string; std::string Fraction::doc = "Fraction类用于表示和操作分数。"; void output(const Fraction& f) { if (f.up == 0) { cout << f.up; return; } if (f.down == 1) { cout << f.up; return; } int c = Fraction::gcd(std::abs(f.up), std::abs(f.down)); int a = f.up / c; int b = f.down / c; if (b < 0) { a = -a; b = -b; } if (a < 0) { cout << "-"; a = -a; } cout << a << "/" << b; } Fraction add(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) { Fraction temp(0, 0); temp.down = f1.down * f2.down; temp.up = f1.up * f2.down + f2.up * f1.down; int k = Fraction::gcd(temp.up, temp.down); temp.up /= k; temp.down /= k; return temp; } Fraction sub(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) { Fraction temp = f1; temp.negative(); return add(temp, f2); } Fraction mul(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) { Fraction temp(f1.up * f2.up, f1.down * f2.down); int k = Fraction::gcd(temp.up, temp.down); temp.up /= k; temp.down /= k; return temp; } Fraction div(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) { if (f2.up == 0) { throw std::runtime_error("分母不能为0"); } Fraction temp(f1.up * f2.down, f1.down * f2.up); int k = Fraction::gcd(temp.up, temp.down); temp.up /= k; temp.down /= k; return temp; }
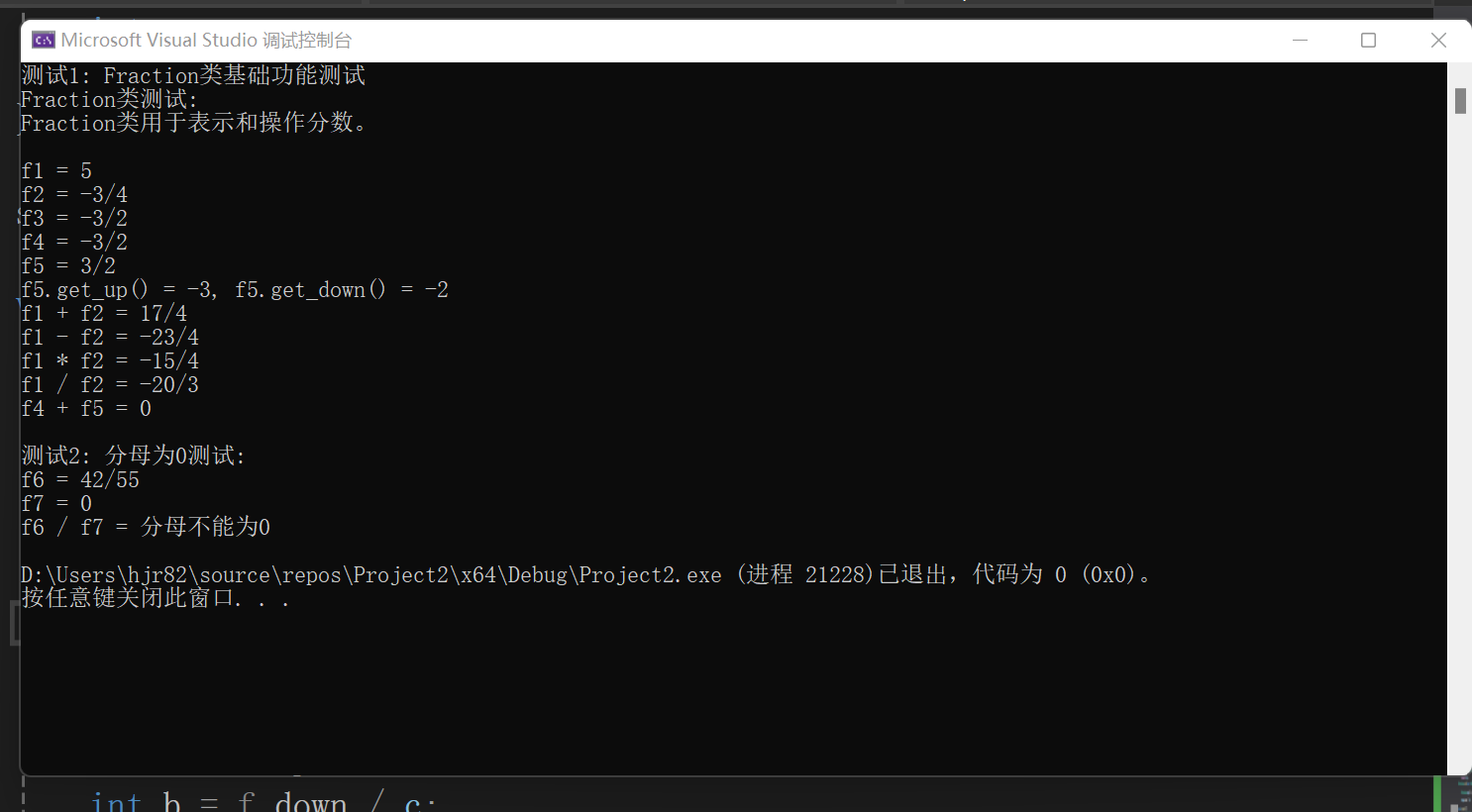
#include"task2.h" #include<iostream> using std::cout; using std::endl; using namespace std; void test1() { cout << "Fraction类测试: " << endl; cout << Fraction::doc << endl << endl; Fraction f1(5); Fraction f2(3, -4), f3(-18, 12); Fraction f4(f3); cout << "f1 = "; output(f1); cout << endl; cout << "f2 = "; output(f2); cout << endl; cout << "f3 = "; output(f3); cout << endl; cout << "f4 = "; output(f4); cout << endl; Fraction f5 = f4; f5.negative(); cout << "f5 = "; output(f5); cout << endl; cout << "f5.get_up() = " << f5.get_up() << ", f5.get_down() = " << f5.get_down() << endl; cout << "f1 + f2 = "; output(add(f1, f2)); cout << endl; cout << "f1 - f2 = "; output(sub(f1, f2)); cout << endl; cout << "f1 * f2 = "; output(mul(f1, f2)); cout << endl; cout << "f1 / f2 = "; output(div(f1, f2)); cout << endl; cout << "f4 + f5 = "; output(add(f4, f5)); cout << endl; } void test2() { Fraction f6(42, 55), f7(0, 3); cout << "f6 = "; output(f6); cout << endl; cout << "f7 = "; output(f7); cout << endl; try { cout << "f6 / f7 = "; output(div(f6, f7)); cout << endl; } catch (const std::runtime_error& e) { cout << e.what() << endl; } } int main() { cout << "测试1: Fraction类基础功能测试\n"; test1(); cout << "\n测试2: 分母为0测试: \n"; test2(); }
实验五
t.h源码:
#ifndef _ _ACCOUNT_H_ _ #define _ _ACCOUNT_H_ _ class SavingsAccount { private: int id; double balance; double rate; int lastDate; double accumulation; static double total; void record(int date, double amount); double accumulate(int date) const { return accumulation + balance * (date - lastDate); } public: SavingsAccount(int date, int id, double rate); int getId()const { return id; } double getBalance() const { return balance; } double getRate() const { return rate; } static double getTotal() { return total; } void desposit(int date, double amount); void withdraw(int date, double amount); void settle(int date); void show() const; }; #endif//_ _ACCOUNT_H _ _
t.cpp源码:
#include "account.h" #include <cmath> #include<iostream> using namespace std; double SavingsAccount::total = 0; SavingsAccount::SavingsAccount(int date, int id, double rate) :id(id), balance(0), rate(rate), lastDate(date), accumulation(0) { cout << date << "\t#" << id << "is created" << endl; } void SavingsAccount::record(int date, double amount) { accumulation = accumulate(date); lastDate = date; amount = floor(amount * 100 + 0.5) / 100; balance += amount; total += amount; cout << date << "\t#" << id << "\t" << amount << "\t" << balance << endl; } void SavingsAccount::desposit(int date, double amount) { record(date, amount); } void SavingsAccount::withdraw(int date, double amount) { if (amount > getBalance()) cout << "Error:not enough money" << endl; else record(date, -amount); } void SavingsAccount::settle(int date) { double interest = accumulate(date) * rate / 365; if (interest != 0) record(date, interest); accumulation = 0; } void SavingsAccount::show() const { cout << "#" << id << "\tBalance:" << balance; }
5_11.cpp源码:
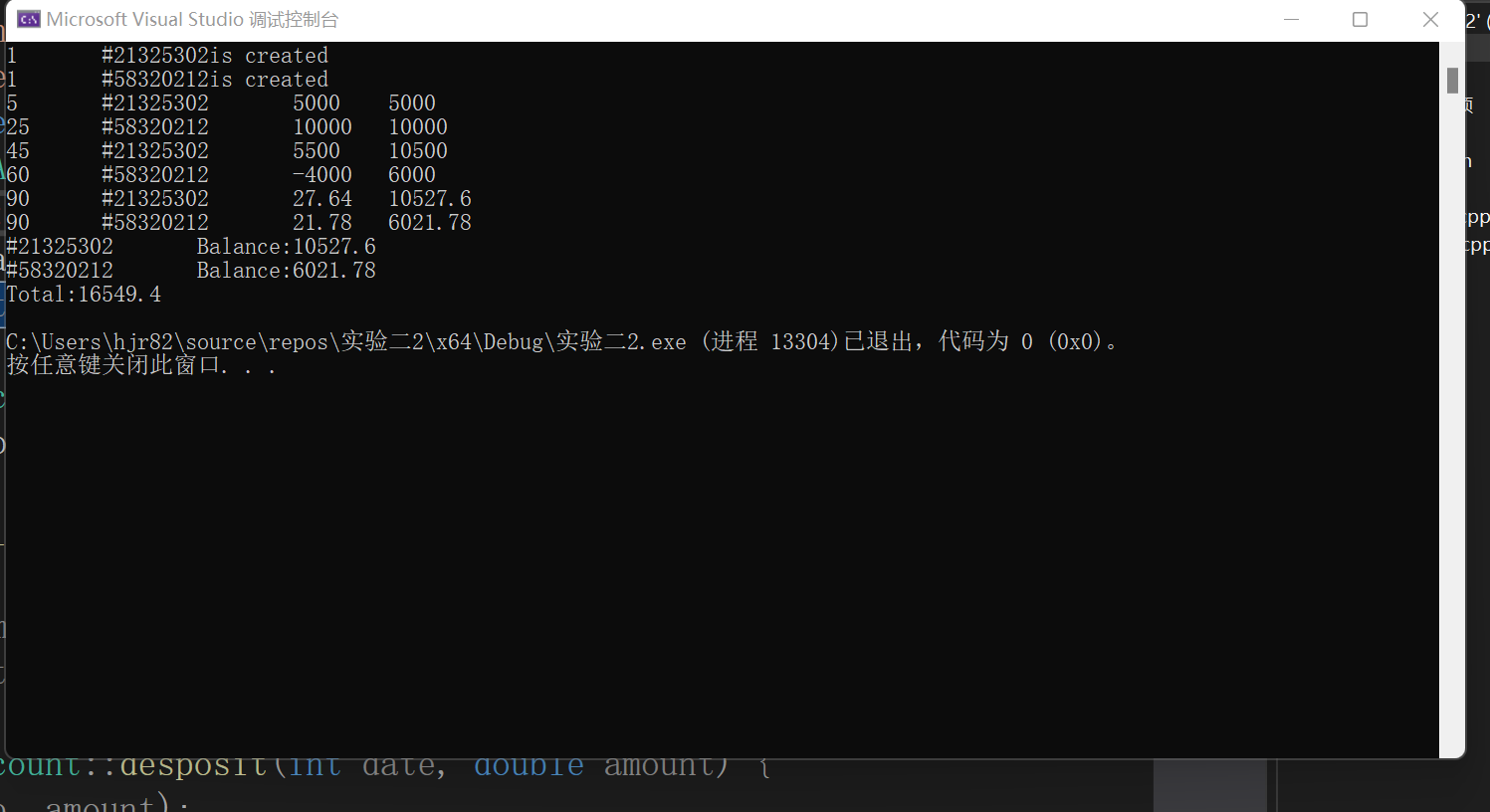
#include"account.h" #include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { SavingsAccount sa0(1, 21325302, 0.015); SavingsAccount sa1(1, 58320212, 0.015); sa0.desposit(5, 5000); sa1.desposit(25,10000); sa0.desposit(45, 5500); sa1.withdraw(60, 4000); sa0.settle(90); sa1.settle(90); sa0.show();cout << endl; sa1.show();cout << endl; cout << "Total:" << SavingsAccount::getTotal() << endl; return 0; }






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本