嵌入式系统习题3——gcc、gdb简单使用
一、创建示例文件
使用touch命令分别创建下面四个文件,放在同一目录下。
- hello.c
/*hello.c*/
void showhello() {
hello();
}
- hello.h
/*hello.h*/
#ifndef HELLO_H
#define HELLO_H
void hello() {
star1();
printf("hello,my friends\n");
}
#endif
- star.c
/*star.c*/
#include "hello.h"
#include "starfun.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
star1();
star2();
showhello();
return 0;
}
- starfun.h
/*****starfun.h*****/
#ifndef STARFUN_H
#define STARFUN_H
#define NUM 4
#define NUMBER 3
#include<stdio.h>
int star1() {
int i,j,k;
for(k=1;k<=NUM;++k) {
for(i=1;i<=(NUM-k);++i)
printf(" ");
for(j=1;j<=(2*k-1);++j)
printf("*");
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
int star2() {
int i,j,k;
for(k=NUMBER;k>=0;--k) {
for(i=1;i<=(NUMBER-k+1);++i)
printf(" ");
for(j=1;j<=(2*k-1);++j)
printf("*");
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
#endif
二、编译
- -c: 生成目标文件
- -o: 指定输出文件名
- -w: 关闭所有警告信息
结果如下:
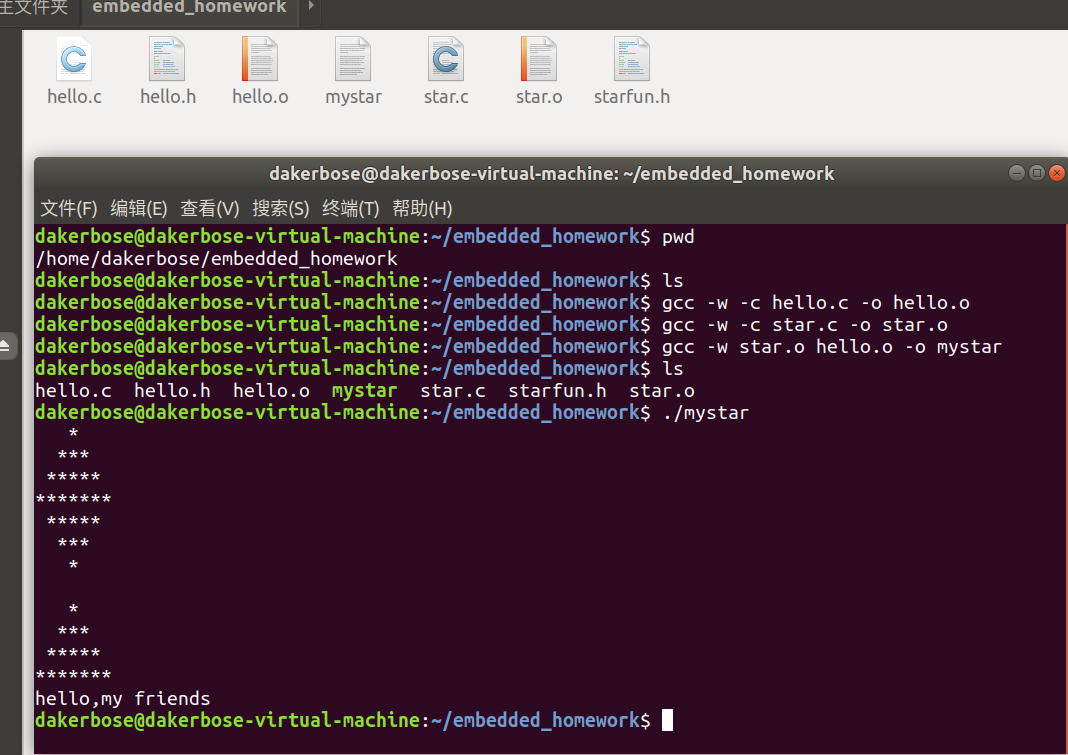
三、使用共享函数库
- -fpic:生成的目标码使用相对地址
- -shared:生成可被链接的共享可执行代码
- -s:生成的可执行代码不含gdb调试信息
- -l:指定要链接的库
- ldd mystar:列出动态库依赖关系
下面两篇博客对理解共享函数库有很大的帮助,遇到BUG时可以查一查:
详解-l的用法
GCC编译时文件依赖顺序问题
下面是结果:
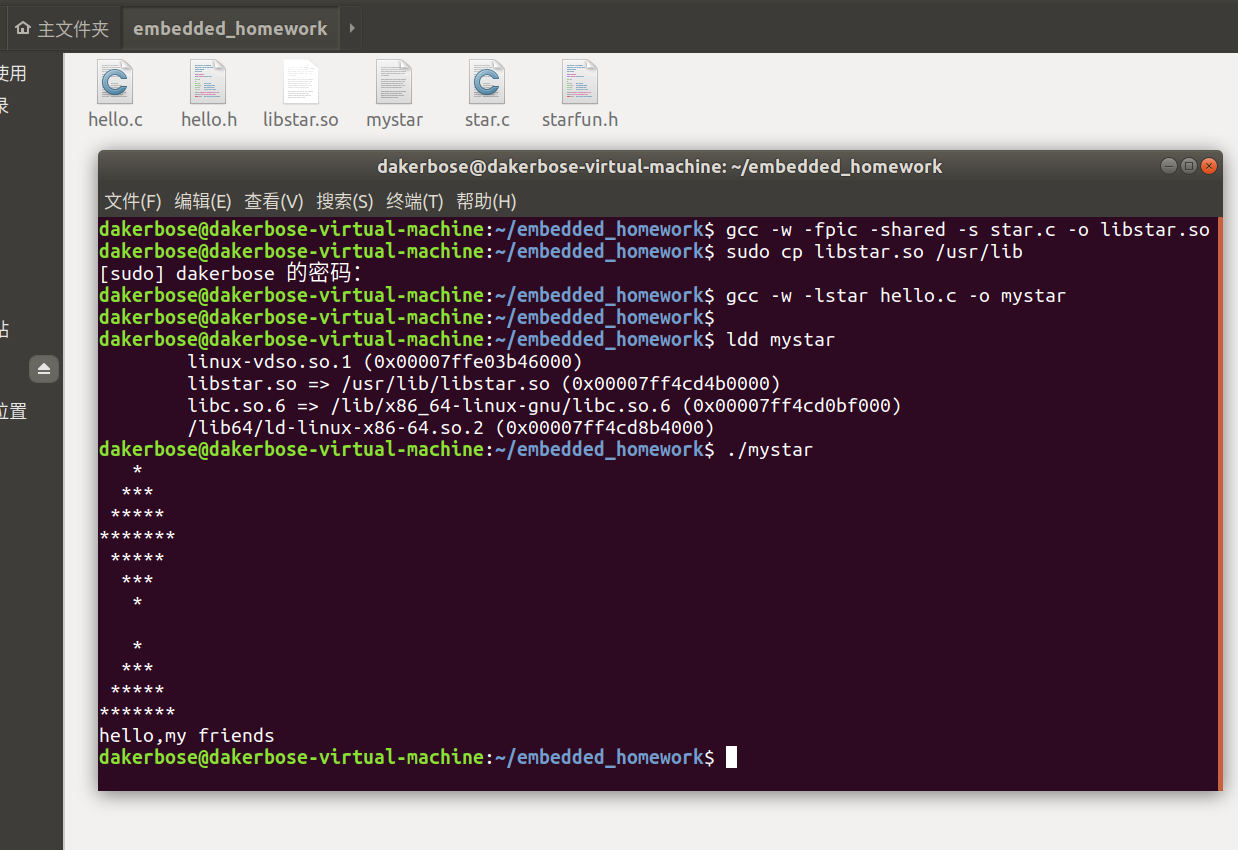
四、使用静态函数库
- -r:插入库文件
- -c:建立库文件
结果如下:
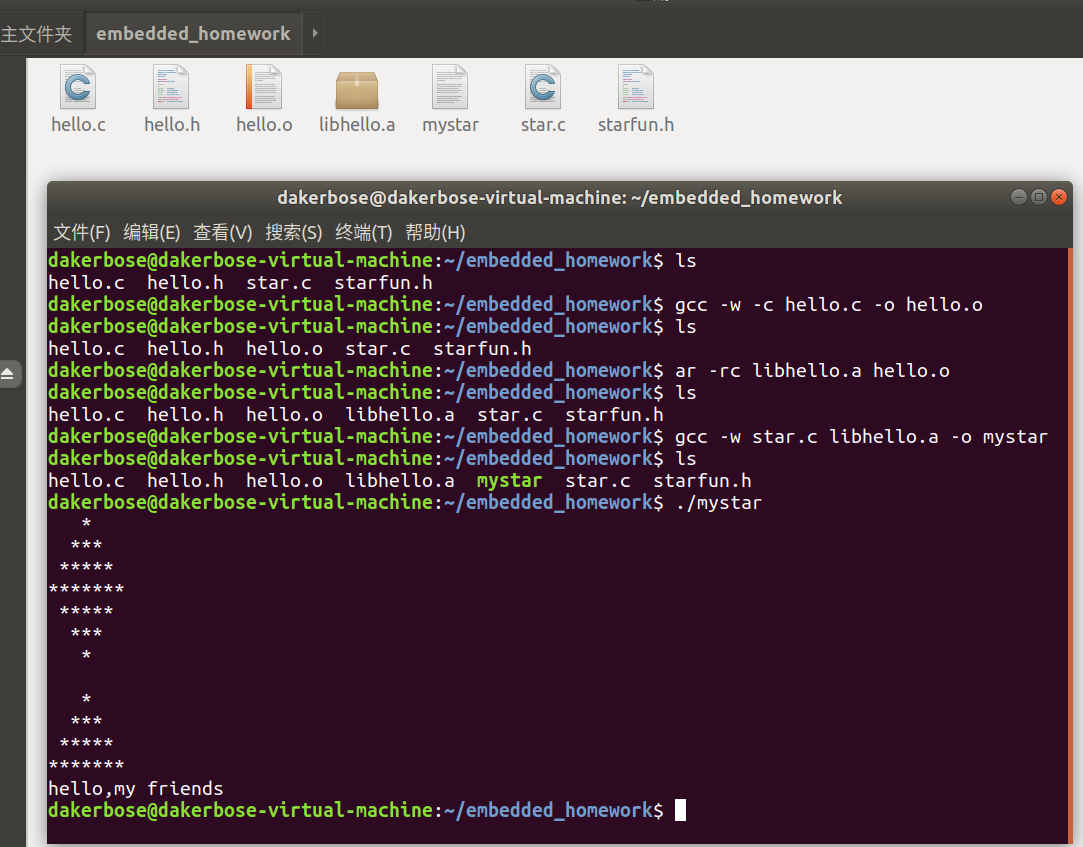
五、gdb的使用
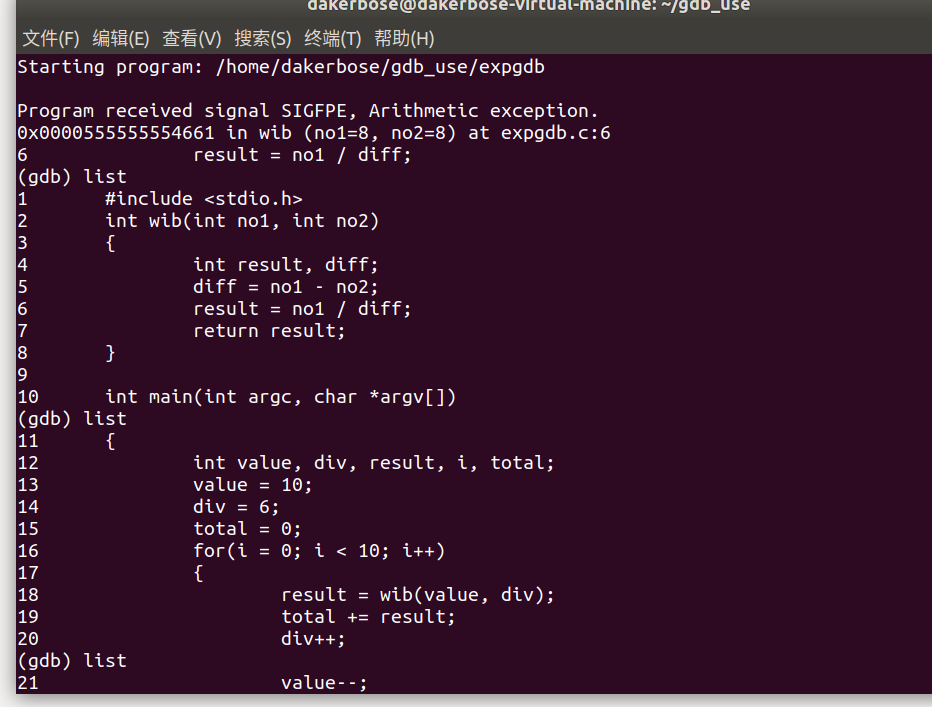
touch命令创建程序expgdb.c,代码如下。
#include <stdio.h>
int wib(int no1, int no2)
{
int result, diff;
diff = no1 - no2;
result = no1 / diff;
return result;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int value, div, result, i, total;
value = 10;
div = 6;
total = 0;
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
result = wib(value, div);
total += result;
div++;
value--;
}
printf("%d wibed by %d equals %d\n", value, div, total);
return 0;
}
- -g:生成调试信息
- run:运行命令
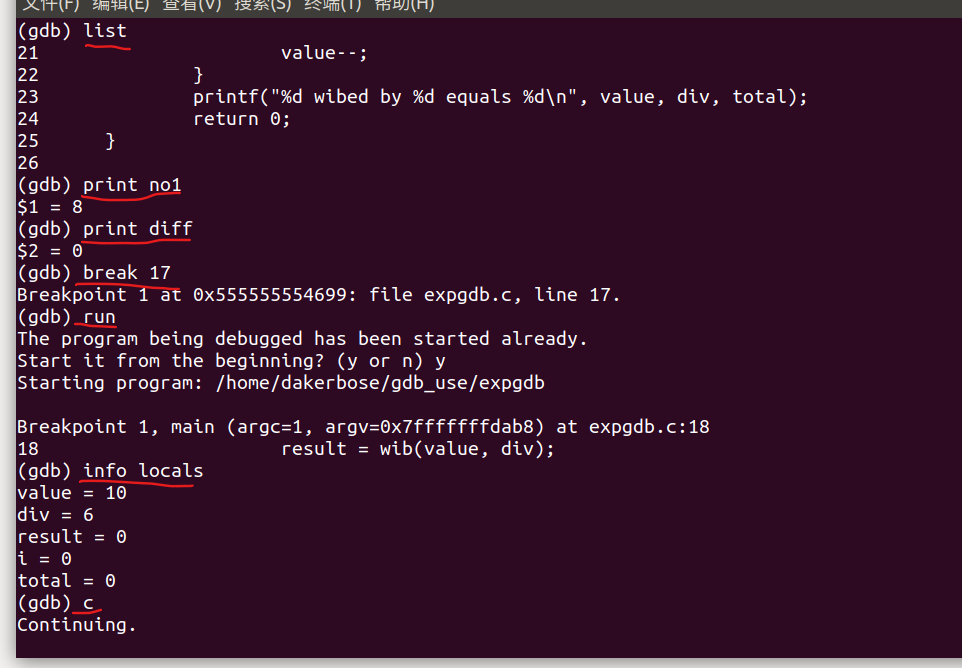
- list:列出源码
- print:输出变量
- break:设置断点
- info locals:查看当前程序的局部变量
- c:继续执行
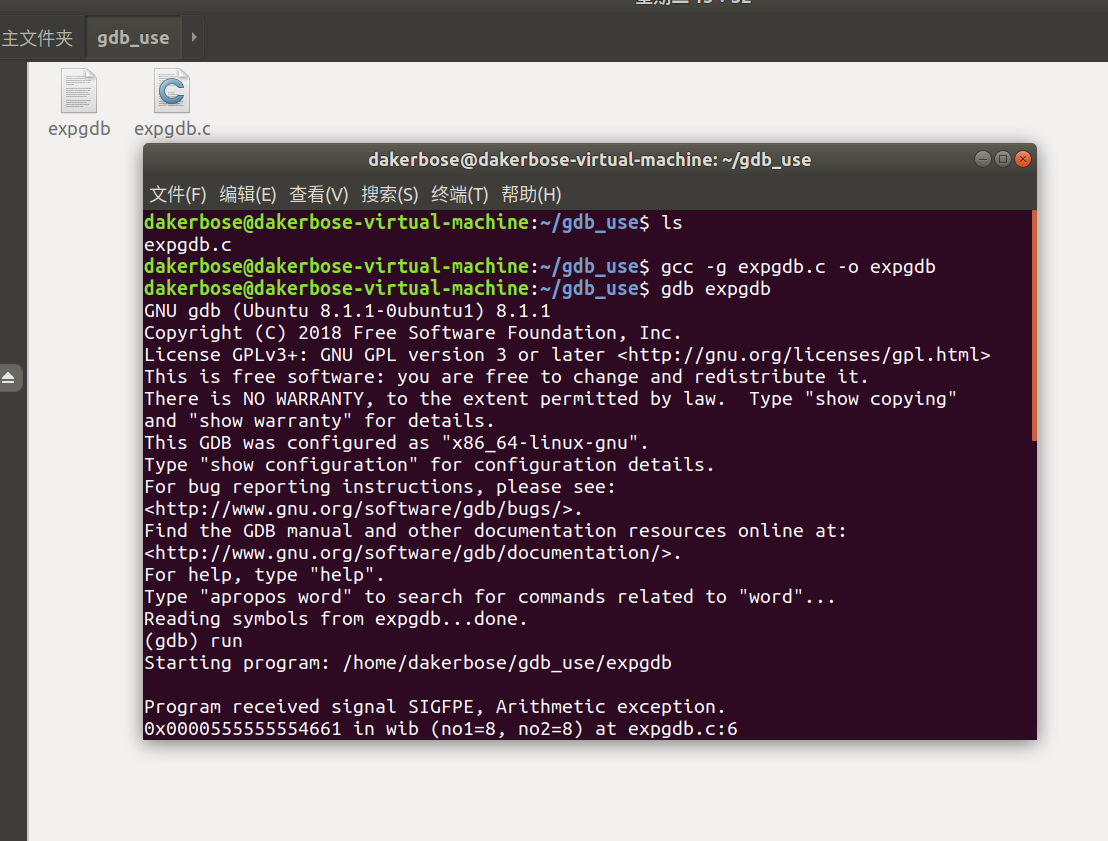
本文来自博客园,作者:静候佳茵,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hitwherznchjy/p/16072220.html
分类:
嵌入式入门学习





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步