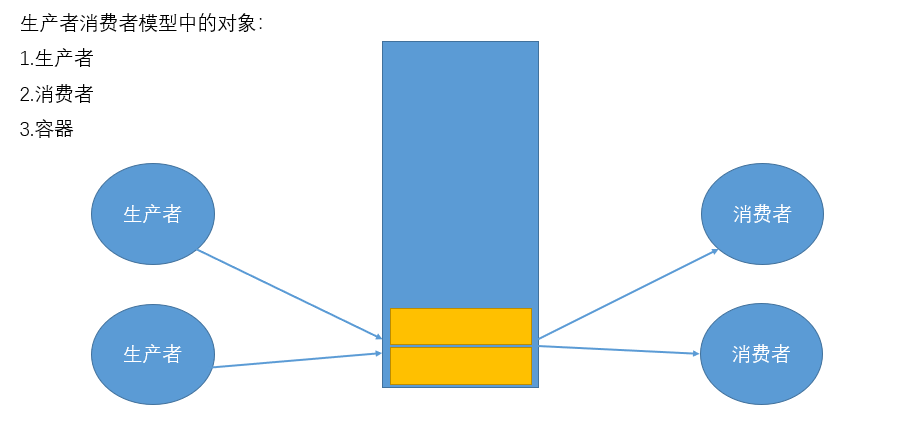
一、生产者消费者模型
/* 实现粗略的生产者消费者模型(未同步,未使用信号量) */ #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #include<unistd.h> #include <pthread.h> struct Node{ int num; struct Node* next; }; //头节点 struct Node* head = NULL; void * producer(void*arg){ //不断添加新节点到链表中 while(1){ struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->next=head; newNode->num = rand() % 1000; head = newNode; printf("add node, num: %d, tid: %ld", newNode->num, pthread_self()); usleep(100); } return NULL; } void * customer(void*arg){ while(1){ struct Node* tmp = head; head = head->next; printf("del node, num: %d, tid: %ld\n", tmp->num, pthread_self()); free(tmp); usleep(100); } return NULL; } int main(){ //创建5个生产者,5个消费者 //使用链表作为容器,不考虑存储上限的问题 pthread_t ptids[5]; pthread_t ctids[5]; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ pthread_create(&ptids[i], NULL, producer,NULL); } for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ pthread_create(&ctids[i], NULL, customer,NULL); } for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ pthread_detach(ctids[i]); pthread_detach(ptids[i]); } pthread_exit(NULL); return 0; }
以上代码未实现同步和信号,会产生段错误
二、条件变量
/* 实现生产者消费者模型(同步,使用条件变量) 条件变量的类型pthread_cond_t,满足条件阻塞(解除阻塞)线程 int pthread_cond_init (pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, constpthread_condattr_t *restrict attr); int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond) ; int pthread_cond_wait (pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,pthread _mutex_t *restrict mutex) ; 功能:等待,线程会阻塞,阻塞时会暂时解锁,解除阻塞时,会重新加锁。 int pthread_cond_timedwait (pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,const struct timespec *restrictabstime) ; 功能:等待多长时间,调用这个函数,线程会等到时间介绍 int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond) ; 功能:唤醒一个或多个等待 int pthread_ cond broadcast (pthread_ cond_ t *cond); 功能:唤醒所有等待 */ #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #include<unistd.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <stdlib.h> //创建一个互斥量 pthread_mutex_t mutex; //创建条件变量 pthread_cond_t cond; struct Node{ int num; struct Node* next; }; //头节点 struct Node* head = NULL; void * producer(void*arg){ //不断添加新节点到链表中 while(1){ pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->next=head; newNode->num = rand() % 1000; head = newNode; printf("add node, num: %d, tid: %ld\n", newNode->num, pthread_self()); //只要生产一个,就通知消费者消费 pthread_cond_signal(&cond); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); usleep(100); } return NULL; } void * customer(void*arg){ while(1){ pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); struct Node* tmp = head; //判断是否有数据 if(head!=NULL){ //有数据 head = head->next; printf("del node, num: %d, tid: %ld\n", tmp->num, pthread_self()); free(tmp); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); usleep(100); } else{ //没有数据 pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);//阻塞时会暂时解锁,解除阻塞时,会重新加锁。 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); } } return NULL; } int main(){ //创建5个生产者,5个消费者 //使用链表作为容器,不考虑存储上限的问题 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL); pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL); pthread_t ptids[5]; pthread_t ctids[5]; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ pthread_create(&ptids[i], NULL, producer,NULL); } for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ pthread_create(&ctids[i], NULL, customer,NULL); } for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ pthread_detach(ctids[i]); pthread_detach(ptids[i]); } while(1){ sleep(10); } pthread_cond_destroy(&cond); pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); pthread_exit(NULL); return 0; }
以上使用条件变量和互斥锁,完成了简单的生产者消费者模型,注意wait函数阻塞时会暂时解锁。
三、信号量
信号量可以限制同时访问线程的数量,以下为使用信号量的生产消费者模型
/* #include <semaphore.h> 信号量的类型sem_t int sem_init (sem t *sem,int pshared, unsigned int value ) ; -初始化信号量 -参数: sem:信号量 pshared:0位线程间,非0位进程间 value:信号量中的值 int sem_destroy (sem_t *sem); 释放信号量资源 int sem_wait (sem_t *sem) ; 对信号量加锁,调用一次对信号量的值-1,若值为0,则阻塞,大于0则解除阻塞 int sem_ trywait (sem_t *sem) ; int sem_timedwait (sem_t *sem,const struct timespec *abs_timeout); int sem post ( sem_t *sem) ; 对信号量解锁,调用一次对信号量的值+1 int sem_getvalue (sem_ t * sem, int *sval) ; */ #include <semaphore.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #include<unistd.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <stdlib.h> //创建一个互斥量 pthread_mutex_t mutex; //创建信号量 sem_t psem; sem_t csem; struct Node{ int num; struct Node* next; }; //头节点 struct Node* head = NULL; void * producer(void*arg){ //不断添加新节点到链表中 while(1){ sem_wait(&psem); pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->next=head; newNode->num = rand() % 1000; head = newNode; printf("add node, num: %d, tid: %ld\n", newNode->num, pthread_self()); //只要生产一个,就通知消费者消费 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); sem_post(&csem); usleep(100); } return NULL; } void * customer(void*arg){ while(1){ sem_wait(&csem); pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); struct Node* tmp = head; head = head->next; printf("del node, num: %d, tid: %ld\n", tmp->num, pthread_self()); free(tmp); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); sem_post(&psem); } return NULL; } int main(){ //创建5个生产者,5个消费者 //使用链表作为容器,不考虑存储上限的问题 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL); //初始化信号量 sem_init(&psem, 0, 8); sem_init(&csem, 0, 0); pthread_t ptids[5]; pthread_t ctids[5]; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ pthread_create(&ptids[i], NULL, producer,NULL); } for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ pthread_create(&ctids[i], NULL, customer,NULL); } for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ pthread_detach(ctids[i]); pthread_detach(ptids[i]); } while(1){ sleep(10); } pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); pthread_exit(NULL); return 0; }



