对C++程序使用输入输出重定向
一般来说,在Visual Studio使用文件重定向有三种方法:
方法一:通过命令行参数实现
项目→属性→配置属性→调试→命令参数
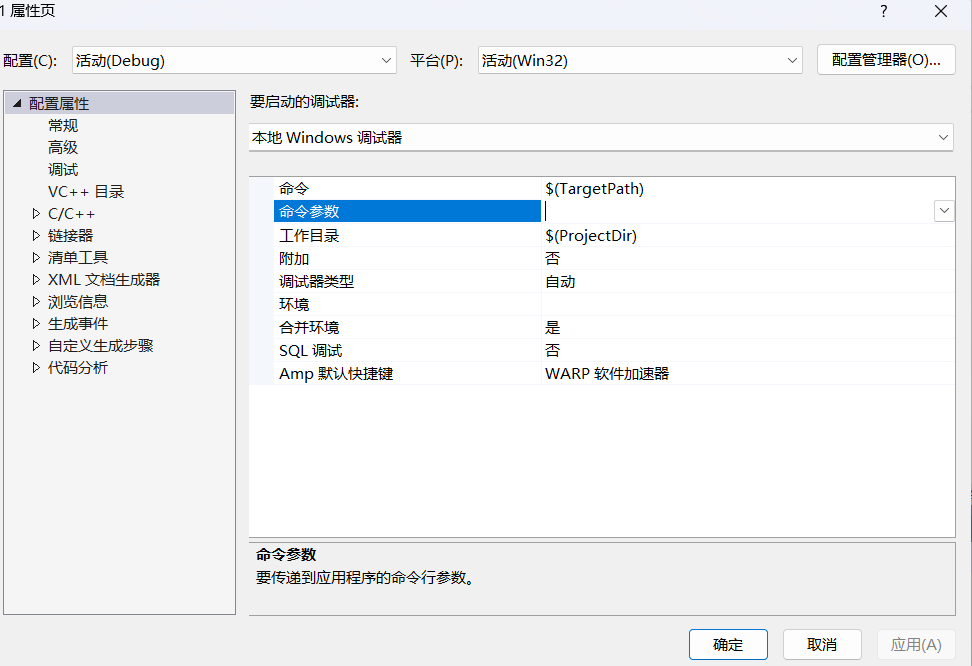
然后就在这里加上你的命令行参数
比如我有这样一段程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "Sales_item.h"
int main()
{
Sales_item trans1, trans2;
int num = 1;
std::cout << "若干销售记录在input.txt里,已文件重定向到输入:" << std::endl;
if (std::cin >> trans1)
{
while (std::cin >> trans2)
if (compareIsbn(trans1, trans2)) // ISBN相同
num++;
else
{
//ISBN不同
std::cout << trans1.isbn() << " 共有 "
<< num << " 条销售记录" << std::endl;
trans1 = trans2;
num = 1;
}
std::cout << trans1.isbn() << " 共有 "
<< num << " 条销售记录" << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "没有数据" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
传入命令行参数:
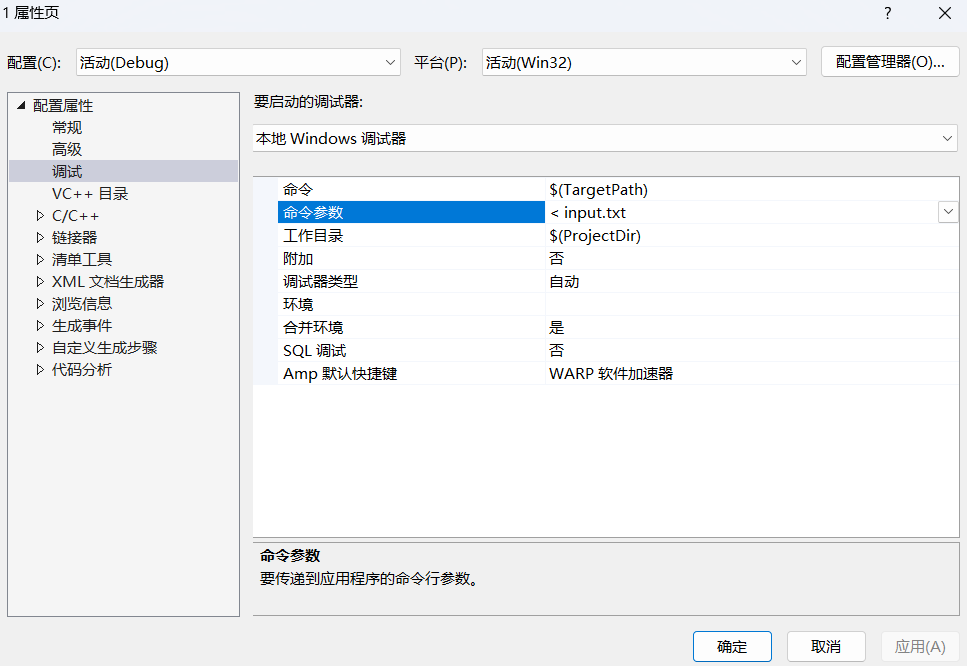
当运行程序时,它会自动从 input.txt 中读取输入。
输出如下:
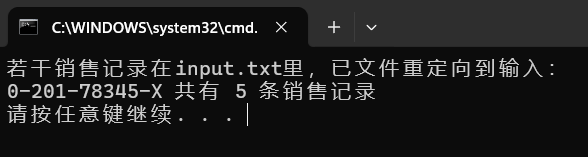
插一句题外话
如果想输出重定向,可以这样:
传入类似这样的命令行参数:> output.txt
方法二:使用C的freopen_s函数重定向
这里示范下输入重定向。
比如:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include "Sales_item.h"
int main()
{
FILE* file = nullptr;
errno_t err = freopen_s(&file, "input.txt", "r", stdin);
if (err != 0) {
std::cerr << "Failed to redirect input." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
Sales_item trans1, trans2;
int num = 1;
std::cout << "若干销售记录在input.txt里,已文件重定向到输入:" << std::endl;
if (std::cin >> trans1)
{
while (std::cin >> trans2)
if (compareIsbn(trans1, trans2)) // ISBN相同
num++;
else
{
//ISBN不同
std::cout << trans1.isbn() << " 共有 "
<< num << " 条销售记录" << std::endl;
trans1 = trans2;
num = 1;
}
std::cout << trans1.isbn() << " 共有 "
<< num << " 条销售记录" << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "没有数据" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
输出如下:
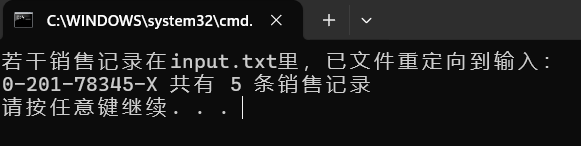
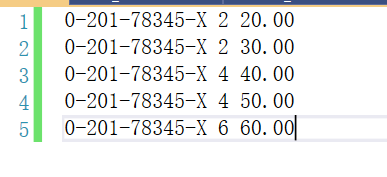
其中input.txt文件内容如下:
插一句题外话
如果想输出重定向,可以这样:
FILE* file = nullptr;
errno_t err = freopen_s(&file, "output.txt", "w", stdout);
if (err != 0) {
std::cerr << "Failed to redirect output." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
补充
freopen_s 是 C 语言标准库中提供的一个更安全的版本,主要用于将标准流(如 stdin、stdout、stderr)重定向到指定的文件。它是 freopen 函数的安全替代品,能够避免 freopen 函数可能带来的某些安全隐患。
freopen_s 函数原型:
errno_t freopen_s(
FILE** pFile, // 指向 FILE* 的指针,用于接收打开的文件流
const char* filename, // 要打开的文件名
const char* mode, // 文件打开模式
FILE* stream // 要重定向的标准流,通常是 stdin, stdout, stderr
);
参数说明:
-
pFile:这是一个指向
FILE*的指针,它会接收打开的文件流指针。传递给 freopen_s 的指针会被修改为指向新打开的文件流。-
如果文件打开成功,
*pFile会指向该文件流。 -
如果失败,
*pFile为 nullptr。
-
-
filename:需要打开的文件名或文件路径。该文件将作为输入或输出流的来源或目标。
-
mode:文件的打开模式,类似于
fopen中的模式参数。常见的模式包括:-
"r":只读模式。
-
"w":写入模式(文件不存在则创建,文件存在则清空)。
-
"a":追加模式(文件存在则追加,不存在则创建)。
-
"r+":以读写模式打开文件(文件必须存在)。
-
"w+":以读写模式打开文件(如果文件存在则清空内容,不存在则创建新文件)。
-
"a+":以读写追加模式打开文件(可以读文件内容,写入数据到文件末尾)。
-
-
stream:要重定向的标准流,通常为 stdin、stdout 或 stderr。
-
stdin:标准输入流。 -
stdout:标准输出流。 -
stderr:标准错误流。
-
-
返回值:
返回一个
errno_t类型的值。-
如果函数成功执行,返回值为 0;
-
如果发生错误,返回一个非零的错误代码。可以通过检查返回值来判断文件是否成功打开
-
方法三:使用 C++ 标准库进行输入输出流重定向
这里示范下输入重定向。
比如:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "Sales_item.h"
int main()
{
// 创建一个文件输入流对象,将其与 input.txt 文件关联
std::ifstream file("input.txt");
// 检查文件是否打开
if (!file.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "Failed to open file." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// 将 std::cin 重定向到文件输入流
std::cin.rdbuf(file.rdbuf());
Sales_item trans1, trans2;
int num = 1;
std::cout << "若干销售记录在input.txt里,已文件重定向到输入:" << std::endl;
if (std::cin >> trans1)
{
while (std::cin >> trans2)
if (compareIsbn(trans1, trans2)) // ISBN相同
num++;
else
{
//ISBN不同
std::cout << trans1.isbn() << " 共有 "
<< num << " 条销售记录" << std::endl;
trans1 = trans2;
num = 1;
}
std::cout << trans1.isbn() << " 共有 "
<< num << " 条销售记录" << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "没有数据" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
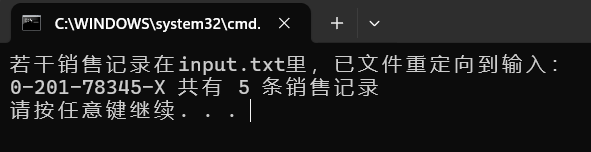
输出如下:
其中input.txt文件内容如下:

插一句题外话
如果想输出重定向,可以这样:
// 创建一个文件输出流对象,将其与 output.txt 文件关联
ofstream file("output.txt");
// 检查文件是否成功打开
if (!file.is_open()) {
cerr << "Failed to open file." << endl;
return 1;
}
// 将 std::cout 重定向到文件输出流
cout.rdbuf(file.rdbuf());
补充
rdbuf 是 C++ 中流(stream)类的一个成员函数,用于访问流的缓冲区。rdbuf() 返回与流对象关联的缓冲区指针(std::streambuf*),可以通过它来操作输入输出流的缓冲区,或者将流的缓冲区重定向到其他缓冲区。
在 C++ 中,流(例如 std::cin、std::cout、std::ifstream、std::ofstream 等)和它们的缓冲区(std::streambuf)是分开的,流本身是对输入输出的高层封装,而缓冲区则负责实际的数据读写。
rdbuf() 用法
-
rdbuf():返回当前流对象关联的缓冲区(std::streambuf*)。 -
rdbuf(streambuf*):可以使用该方法将当前流的缓冲区重定向为新的缓冲区,或者将流的输入输出目标切换到其他缓冲区。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人