网络流的认识
网络流的认识
什么是流网络
网络(network)是指一个特殊的有向图
其中,我们有以下变量来方便表示:
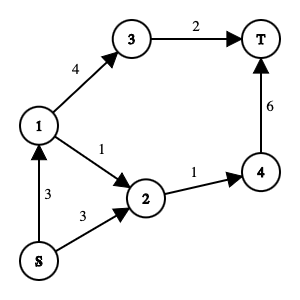
如上图,这就是一个流网络,其中
什么是可行流
可行流,通俗点讲,就是在每条变分配流水的多少,使能满足条件(这个在生活实际也能推出)。
条件显然为以下:
- 流量限制:
- 流量守恒:抽象点讲,也就是你当前的点为
形象点讲,也就是我当前流入到这个点的水的量最终都会流出到我可以到的点。
我们用
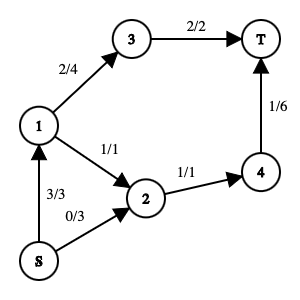
其中在
你可以试试看,能否满足第二个条件?
什么是最大流
最大流(也称最大可行流)实际是在可行流中找一个方案,使得流入汇点
在这里,右边的式子的第二个单项式
What is 残留网络
概念和构建
残留网络总是针对原图
残留网络中的容量记为
作用
可以通过 增广路径 的配合找到更大的流,使最后图中的最大流最大。
增广路径
定义
如果从源点
在这里我们发现:原网络可行流+残留网络可行流也是原网络的一个可行流
抽象点说(正式点说),
割
在网络中定点的一个划分,把所有顶点分成两个集合
割的容量
指连接两个点集的边的容量总和,即
割的流量
指指连接两个点集的边的流量总和,
由上同理可得:
有反向边时,
显然:
最小割
指
最大流最小割定理
以下
证明:
- 证明
反证即可,若存在增广路就会使得当前的 - 证明
我们将对于 - 证明
因为
求最大流
基于上述定理,我们可以不断寻找增广路,利用增广路更新残留网络,直到找不到增广路,即可求得最大流。
EK 算法
时间复杂度
Code1
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int INF=1e9;
const int N=1005, M=10010;
int n, m, S, T;
struct node{
int to, c, next;
}e[M<<1];
int h[N], tot;
// 残量网络建图,初始时正向的容量是 c, 反向容量是 0 。
void add(int u, int v, int c){
e[tot].to=v, e[tot].c=c, e[tot].next=h[u], h[u]=tot++;
e[tot].to=u, e[tot].c=0, e[tot].next=h[v], h[v]=tot++;
}
int lim[N], pre[N]; // lim[u] 表示 S 到点 u 路径容量的最小值, pre[u] 表示 u 的前驱边。
bool vis[N];
int q[N];
// bfs 找增广路。
bool bfs(){
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
int hh=0, tt=-1;
q[++tt]=S, vis[S]=true, lim[S]=INF;
while(tt>=hh){
int hd=q[hh++];
for(int i=h[hd]; ~i; i=e[i].next){
int go=e[i].to;
if(vis[go] || !e[i].c) continue;
vis[go]=true, q[++tt]=go;
lim[go]=min(lim[hd], e[i].c);
pre[go]=i;
if(go==T) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int EK(){
int res=0;
while(bfs()){
res+=lim[T];
for(int i=T; i!=S; i=e[pre[i]^1].to){
e[pre[i]].c-=lim[T], e[pre[i]^1].c+=lim[T];
}
}
return res;
}
int main(){
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
cin>>n>>m>>S>>T;
while(m--){
int u, v, c; cin>>u>>v>>c;
add(u, v, c);
}
cout<<EK()<<endl;
return 0;
}
Code2
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#define N 1007
#define M 10007
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int INF = 1e9 + 7;
struct node{
int to,val,nxt;
}e[M << 1];
int n, m, S, T, tot;
int head[N],dis[N],pre[N];
bool vis[N];
queue<int> q;
void add(int a,int b,int c) {
e[tot].to = b, e[tot].val = c, e[tot].nxt = head[a], head[a] = tot++;
e[tot].to = a, e[tot].val = 0, e[tot].nxt = head[b], head[b] = tot++;
}
bool bfs() {
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
memset(vis,false,sizeof vis);
q.push(S), vis[S] = true, dis[S] = INF;
while(!q.empty()) {
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = head[t];i != -1;i = e[i].nxt) {
int v = e[i].to;
if (!vis[v] && e[i].val) {
vis[v] = true;
dis[v] = min(dis[t],e[i].val);
pre[v] = i;
if (v == T) return true;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return false;
}
int EK(){
int r = 0;
while(bfs()) {
r += dis[T];
for (int i = T;i != S;i = e[pre[i] ^ 1].to)
e[pre[i]].val -= dis[T], e[pre[i] ^ 1].val += dis[T];
}
return r;
}
signed main(){
cin >>n >> m >> S>> T;
memset(head, -1,sizeof head);
for(;m--;) {
int a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
add(a,b,c);
}
cout << EK();
return 0;
}
Dinic 算法
多路增广,时间复杂度
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define gc() (st==ed&&(ed=(st=buf)+fread(buf,1,100000,stdin),st==ed)?EOF:*st++)
char buf[100001],*st=buf,*ed=buf;
void read(int &a){
a=0;char c=gc();
while(c>'9'||c<'0')c=gc();
while(c>='0'&&c<='9')a=a*10+c-48,c=gc();
}
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N=10010, M=1e5+5;
struct node{
int to, c, next;
}e[M<<1];
int h[N], tot;
void add(int u, int v, int cap){
e[tot].to=v, e[tot].c=cap, e[tot].next=h[u], h[u]=tot++;
e[tot].to=u, e[tot].c=0, e[tot].next=h[v], h[v]=tot++;
}
int n, m, S, T;
int d[N], q[N], cur[N];
bool bfs(){
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
int tt=-1, hh=0;
q[++tt]=S, d[S]=0, cur[S]=h[S];
while(tt>=hh){
int hd=q[hh++];
for(int i=h[hd]; ~i; i=e[i].next){
int go=e[i].to;
if(d[go]==-1 && e[i].c){
d[go]=d[hd]+1;
cur[go]=h[go];
if(go==T) return true;
q[++tt]=go;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int find(int u, int limit){
if(u==T) return limit;
int flow=0;
for(int i=cur[u]; ~i && flow<limit; i=e[i].next){
cur[u]=i;
int go=e[i].to;
if(d[go]==d[u]+1 && e[i].c){
int t=find(go, min(e[i].c, limit-flow));
if(!t) d[go]=-1;
e[i].c-=t, e[i^1].c+=t, flow+=t;
}
}
return flow;
}
int dinic(){
int res=0, flow;
while(bfs()) while(flow=find(S, INF)) res+=flow;
return res;
}
signed main(){
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
read(n), read(m), read(S), read(T);
while(m--){
int u, v, cap; read(u), read(v), read(cap);
add(u, v, cap);
}
cout<<dinic()<<endl;
return 0;
}
完结。
本文作者:high-sky
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/high-sky/p/18515629
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步