异常
异常体系结构
-
Java把异常当做一个对象来处理,并定义一个基类java.lang.Throwable作为所有异常的超类。
-
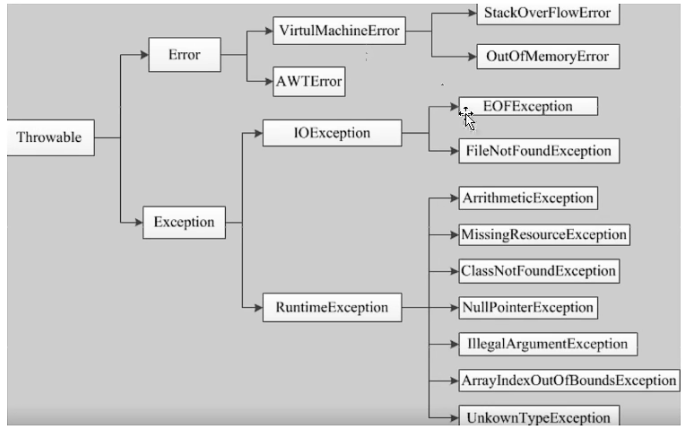
在Java API中已经定义了许多异常类,这些异常类分为两大类,错误的Error和异常Exception
-
int a=10;
int b=0;
//idea快捷键选中代码Ctrl+Alt+T
try {//try监控区域
System.out.println(a/b);
} catch (Error err) {//系统错误
System.out.println("Error");
} catch (Exception exce) {//系统异常(ArithmeticException)
System.out.println("Exception");
} catch (Throwable th) {//捕捉系统全部异常
System.out.println("Throwable");
} finally{//处理善后工作用于资源关闭
System.out.println("finally");
}对应输出:
Exception
finally捕获异常
public class demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new demo3().mm(10,0);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
}
}
public void mm(int a, int b)throws ArithmeticException{
if (b==0){
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
}
}
总结:
-
处理运行时异常时,采用逻辑去合理的规避同时辅助try-catch 处理
-
在多重catch块后面,可以加一个catch(Exception)来处理可能被遗漏的异常
-
对于不确定的代码,也可以加上try-catch,处理潜在的异常
-
尽量去处理异常,切记只是简单地调用printStackTrace()去打印输出
-
具体如何处理异常,要根据不同的业务需求和异常类型去决定
-



