实验报告(七)及第九周总结

实验代码:
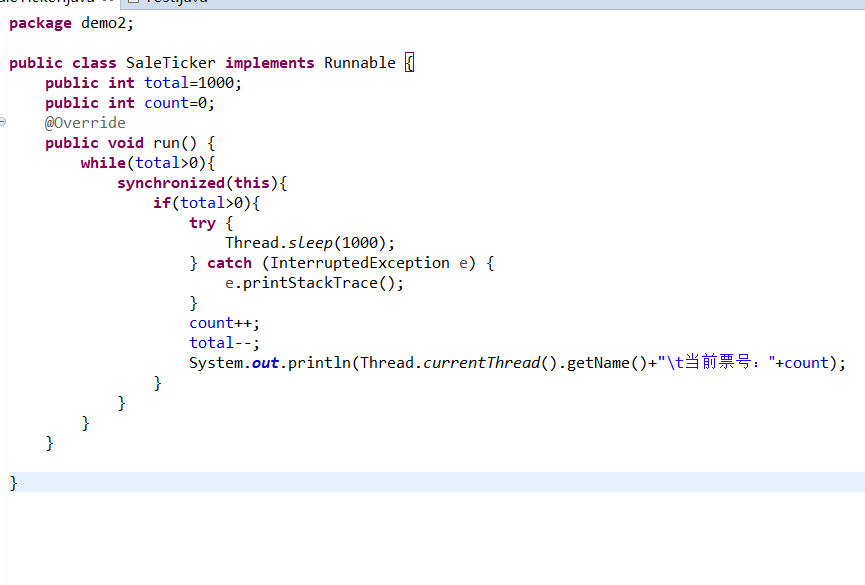
package demo2;
public class SaleTicker implements Runnable {
public int total=1000;
public int count=0;
@Override
public void run() {
while(total>0){
synchronized(this){
if(total>0){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
total--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t当前票号:"+count);
}
}
}
}
}package demo2;
public class SaleTicker implements Runnable {
public int total=1000;
public int count=0;
@Override
public void run() {
while(total>0){
synchronized(this){
if(total>0){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
total--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t当前票号:"+count);
}
}
}
}
}
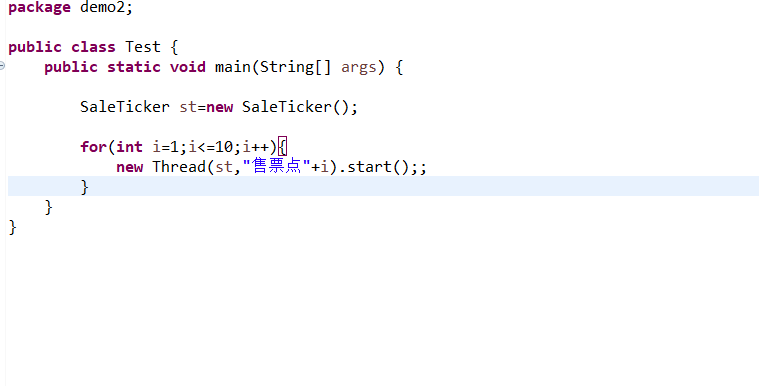
package demo2;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SaleTicker st=new SaleTicker();
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
new Thread(st,"售票点"+i).start();;
}
}
}
实验代码截图:
实验结果截图:
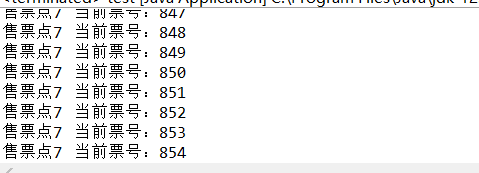
第九周总结:
本周主要学习了多线程和java的输入输出;
多线程的实现主要有两种:
1.继承thread类;
2实现runnable接口;
start()是多线程的启动方法;
run()是多线程的主体;
两种的区别:
thread不能资源共享;
runnable能实现资源共享;

java的输入输出:

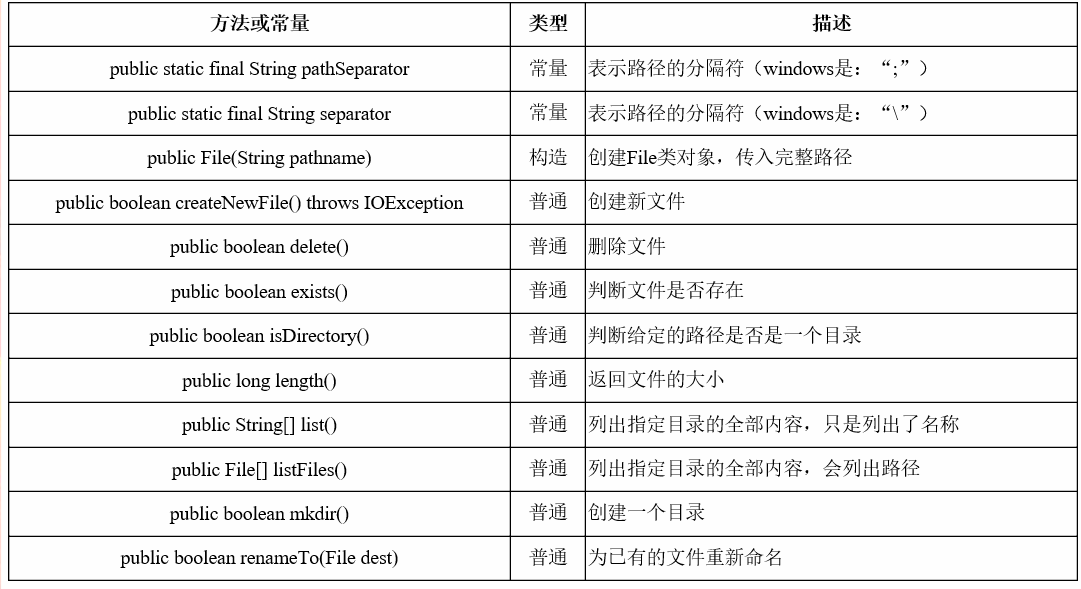
Flile的主要用法和常量:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号