netty学习总结(二)
JDK Byte Buffer的缺点:长度是固定的,不能动态扩容,API使用复杂,因此Netty封装了自己ByteBuf,Bytebuf有三个重要属性:Capacity容量、readerIndex读取位置和writerIndex写入位置,提供两个指针来支持顺序读写操作.同时三者满足如下关系:0<=readerIndex<=writerIndex<=capacity.下面给出ByteBuf使用demo
public class ByteBufDemo { @Test public void apiTest() { // +-------------------+------------------+------------------+ // | discardable bytes | readable bytes | writable bytes | // | | (CONTENT) | | // +-------------------+------------------+------------------+ // | | | | // 0 <= readerIndex <= writerIndex <= capacity // 1.创建一个非池化的ByteBuf,大小为10个字节 ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.buffer(10); System.out.println("原始ByteBuf为====================>" + buf.toString()); System.out.println("1.ByteBuf中的内容为===============>" + Arrays.toString(buf.array()) + "\n"); // 2.写入一段内容 byte[] bytes = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; buf.writeBytes(bytes); System.out.println("写入的bytes为====================>" + Arrays.toString(bytes)); System.out.println("写入一段内容后ByteBuf为===========>" + buf.toString()); System.out.println("2.ByteBuf中的内容为===============>" + Arrays.toString(buf.array()) + "\n"); // 3.读取一段内容 byte b1 = buf.readByte(); byte b2 = buf.readByte(); System.out.println("读取的bytes为====================>" + Arrays.toString(new byte[]{b1, b2})); System.out.println("读取一段内容后ByteBuf为===========>" + buf.toString()); System.out.println("3.ByteBuf中的内容为===============>" + Arrays.toString(buf.array()) + "\n"); // 4.将读取的内容丢弃 buf.discardReadBytes(); System.out.println("将读取的内容丢弃后ByteBuf为========>" + buf.toString()); System.out.println("4.ByteBuf中的内容为===============>" + Arrays.toString(buf.array()) + "\n"); // 5.清空读写指针 buf.clear(); System.out.println("将读写指针清空后ByteBuf为==========>" + buf.toString()); System.out.println("5.ByteBuf中的内容为===============>" + Arrays.toString(buf.array()) + "\n"); // 6.再次写入一段内容,比第一段内容少 byte[] bytes2 = {1, 2, 3}; buf.writeBytes(bytes2); System.out.println("写入的bytes为====================>" + Arrays.toString(bytes2)); System.out.println("写入一段内容后ByteBuf为===========>" + buf.toString()); System.out.println("6.ByteBuf中的内容为===============>" + Arrays.toString(buf.array()) + "\n"); // 7.将ByteBuf清零 buf.setZero(0, buf.capacity()); System.out.println("将内容清零后ByteBuf为==============>" + buf.toString()); System.out.println("7.ByteBuf中的内容为================>" + Arrays.toString(buf.array()) + "\n"); // 8.再次写入一段超过容量的内容 byte[] bytes3 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11}; buf.writeBytes(bytes3); System.out.println("写入的bytes为====================>" + Arrays.toString(bytes3)); System.out.println("写入一段内容后ByteBuf为===========>" + buf.toString()); System.out.println("8.ByteBuf中的内容为===============>" + Arrays.toString(buf.array()) + "\n"); // 随机访问索引 getByte // 顺序读 read* // 顺序写 write* // 清除已读内容 discardReadBytes // 清除缓冲区 clear // 搜索操作 // 标记和重置 // 完整代码示例:参考 // 搜索操作 读取指定位置 buf.getByte(1); // }
ByteBuf扩容机制

ByteBuf从堆内/堆外、是否池化、访问方式三个纬度分为8种:
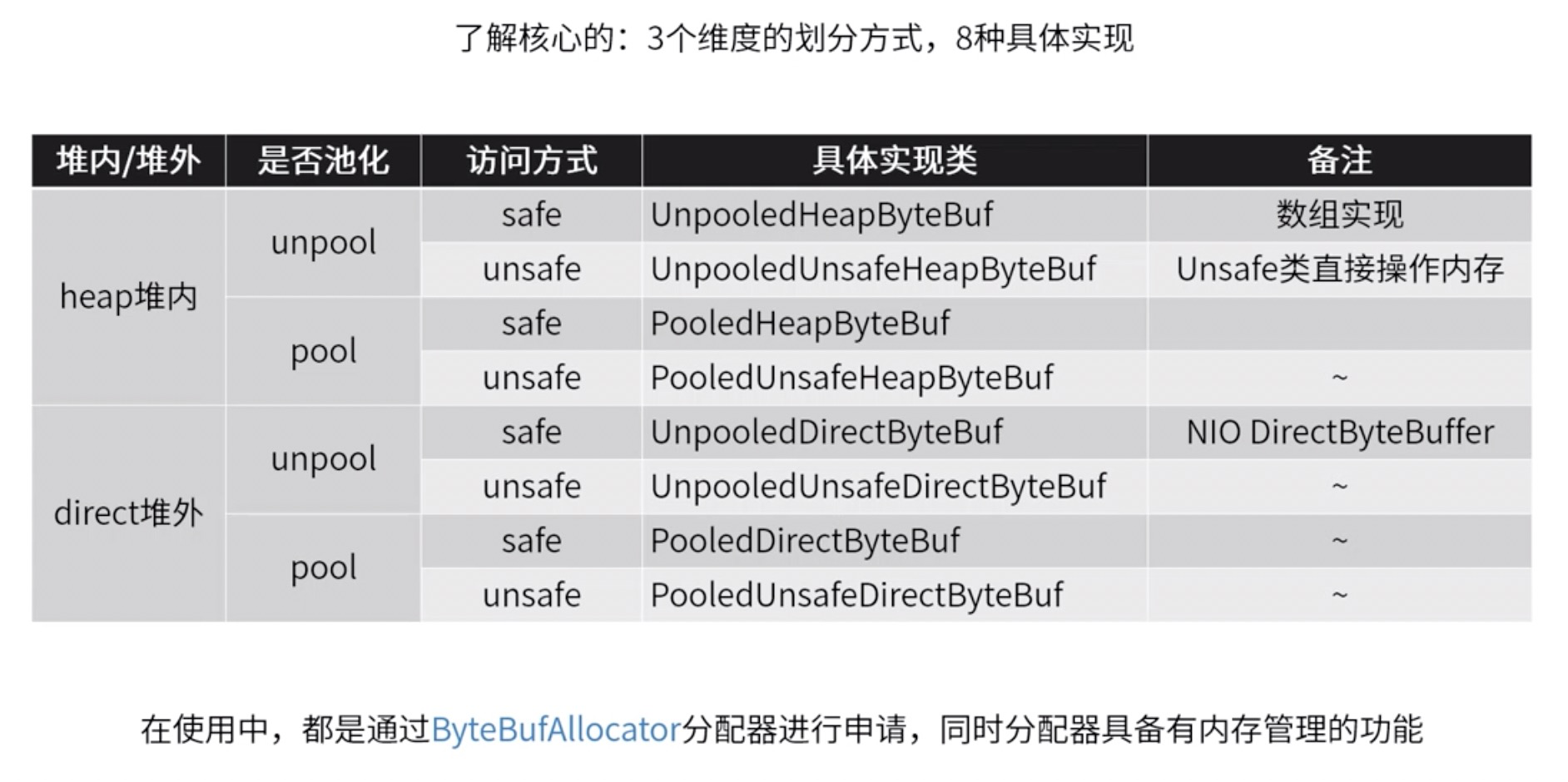
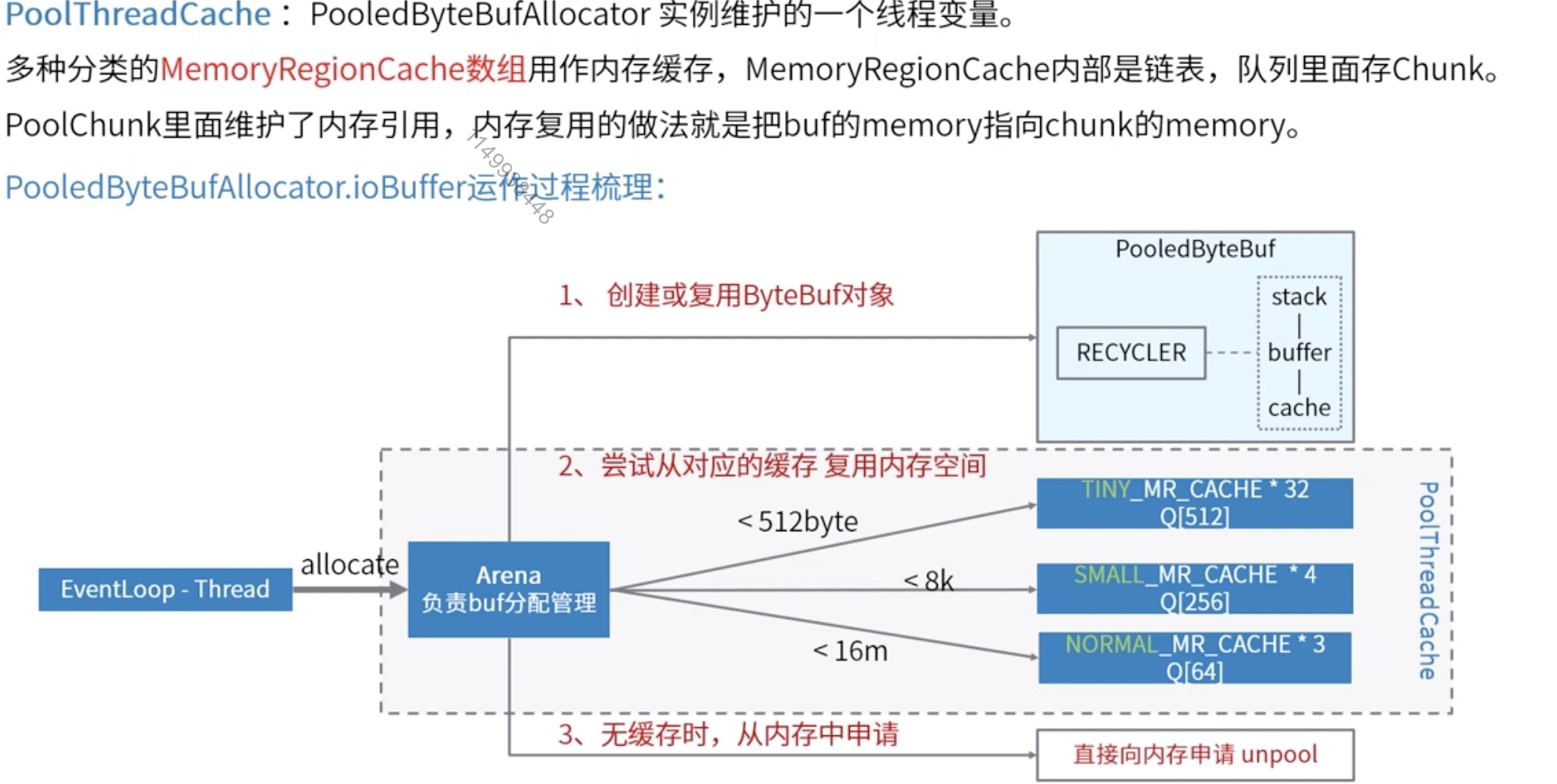
就访问而言,safe和unsafe的主要区别就是是否使用底层是否使用unsafe直接操作内存,堆内/堆外则是指Bytebuf使用jvm堆内内存还是直接使用操作系统的内存,而是否池化则是Bytebuf是否能够放入对象池中复用,Netty为了最求极致的性能默认使用PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf,Netty对于池化的Bytebuf内存分配算法原理如下
ByteBuf的零copy机制

测试demo如下
public class ZeroCopyTest { @org.junit.Test public void wrapTest() { byte[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(arr); System.out.println(byteBuf.getByte(4)); arr[4] = 6; System.out.println(byteBuf.getByte(4)); } @org.junit.Test public void sliceTest() { ByteBuf buffer1 = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer("hello".getBytes()); ByteBuf newBuffer = buffer1.slice(1, 2); newBuffer.unwrap(); System.out.println(newBuffer.toString()); } @org.junit.Test public void compositeTest() { ByteBuf buffer1 = Unpooled.buffer(3); buffer1.writeByte(1); ByteBuf buffer2 = Unpooled.buffer(3); buffer2.writeByte(4); CompositeByteBuf compositeByteBuf = Unpooled.compositeBuffer(); CompositeByteBuf newBuffer = compositeByteBuf.addComponents(true, buffer1, buffer2); System.out.println(newBuffer); } }



