C语言提高 (6) 第六天 文件(续) 链表的操作
1昨日回顾
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char buf[1024] = { 0 };
int len = 0;
// !可以取代scanf
if (fgets(buf, 1024, stdin) != NULL) {
len = strlen(buf);
buf[len - 1] = '\0'; // 输入以后是qwe\n 所以最后一个\n要换成\0
}
printf("buf:%s\n", buf);
return 0;
}
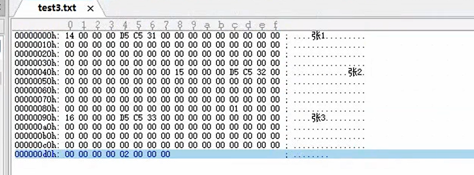
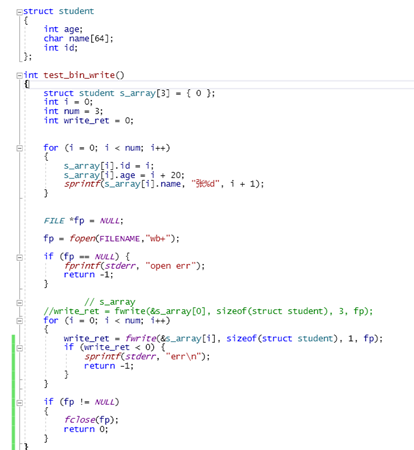
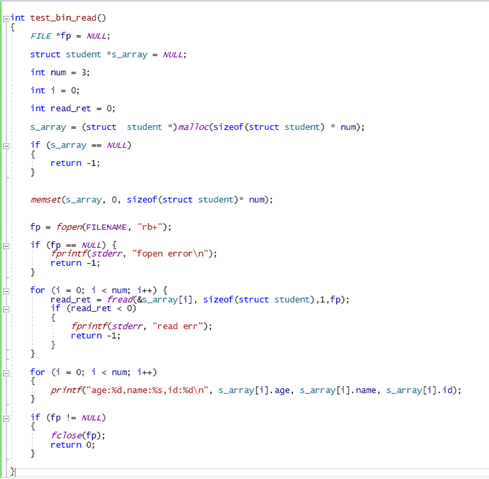
刚才的读写都是字符和字符串,下面讲二进制的读写:

(ue查看二进制文件)
2作业题
对操作系统来说都是文件 设备文件…
是写驱动的人为我们提供了接口
3文件系统体系

问:这个能编译吗?
struct 是一种数据类型
数据类型是固定内存大小的别名

这样可以:

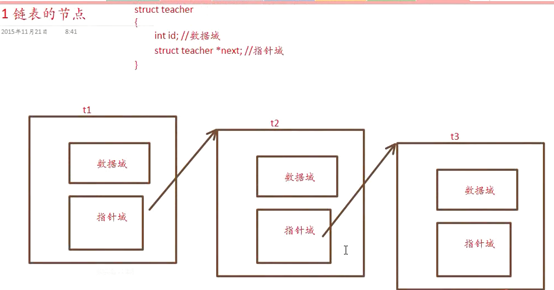
数组与链表的对比:

4文件缓冲区
再说一下fgets和fputs
fgets遇到\n结束,也就是读取一行,最后会把\n也读进去 不会读\0
fputs不会把\n put出去,fputs只是put string
5静态链表和动态链表
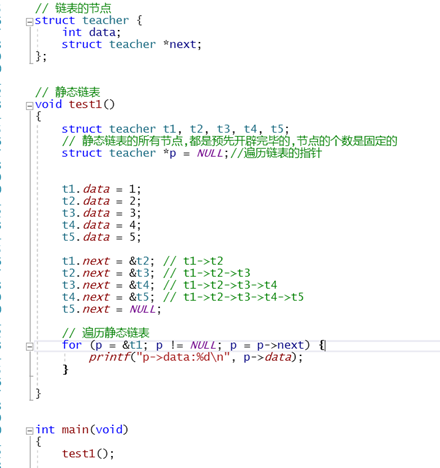
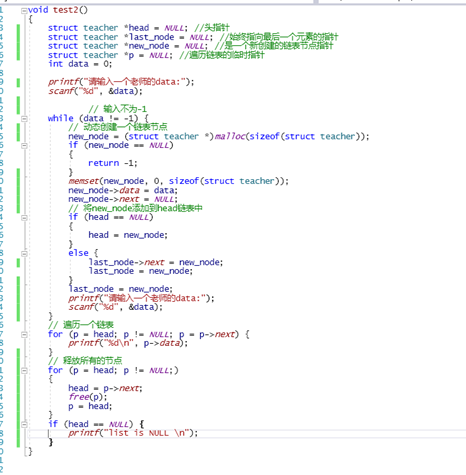
2)
带头链表和不带头链表
无头链表的插入和从头部插入,删除节点..等操作
no_head_list.h:
#ifndef _NO_HEAD_LIST_H_
#define _NO_HEAD_LIST_H_
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
// 链表的节点
struct node
{
int data; //数据域
struct node *next; //指针域
};
// 初始化链表的接口
void init_list(struct node **head_p);
// 创建一个节点的接口
struct node* make_node(int data);
// 销毁一个节点
void free_node(struct node *node);
// 将节点插入链表的接口 (插入链表的尾部
int insert_node_to_end(struct node *new_node,struct node**head_p);
// 将节点插入链表的头部
int insert_node_from_begin(struct node *new_node, struct node **head_p);
// 销毁一个链表
void destory_list(struct node **head_p);
// 遍历链表
void print_list(struct node *head);
// 删除一个节点,根据要删除节点的指针来删除
int delete_node(struct node*del_node, struct node **head_p);
// 查询一个节点
struct node * search(struct node *head, int data);
#endif
no_head_list.c:
#include "no_head_list.h"
void init_list(struct node **head_p)
{
*head_p = NULL;
}
struct node* make_node(int data)
{
struct node *new_node = NULL;
new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (new_node == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "make node malooc new_node error\n");
return NULL;
}
memset(new_node, 0, sizeof(struct node));
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
return new_node;
}
// 插入一个节点到head中
int insert_node_to_end(struct node *new_node, struct node**head_p)
{
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node* last_node = NULL;
if (new_node == NULL || head_p == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
head = *head_p;
if (head == NULL)
{
// 链表此时是空链表
head = new_node;
last_node = new_node; // 无头链表特点:需要对head是否为空 进行判断
}
else {
// 找到这个last_node
// last_node->next = new_node;
for (last_node = head; last_node->next != NULL; last_node = last_node->next);
last_node->next = new_node;
}
*head_p = head;
return 0;
}
// 遍历链表
void print_list(struct node *head)
{
struct node *p = NULL;
for (p = head; p != NULL; p = p->next) {
printf("%d\n", p->data);
}
}
int insert_node_from_begin(struct node *new_node, struct node **head_p)
{
if (new_node == NULL || head_p == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
struct node *head = *head_p;
// 插入的操作
if (head == NULL)
{
head = new_node;
}
else {
new_node->next = head;
head = new_node;
}
*head_p = head;
return 0;
}
void free_node(struct node *node)
{
if (node != NULL) {
free(node);
}
}
void destory_list(struct node **head_p)
{
struct node *head = *head_p;
struct node *p = NULL;
while (head!= NULL)
{
// 链表还有怨怒是
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
*head_p = head;
}
int delete_node(struct node*del_node, struct node **head_p)
{
struct node *head = *head_p;
struct node *p = NULL;
if (head == del_node) {
// 如果要删除的节点就是首节点
head = head->next;
free_node(del_node);
*head_p = head;
return 0;
}
// 要删除的不是头节点
for (p = head; p != NULL; p = p->next)
{
if (p->next == del_node) {
// 找到了要删除的节点,此时p是这个要删除节点的前驱节点
p->next = p->next->next;
free_node(del_node);
break;
}
}
*head_p = head;
return 0;
}
// 查询一个节点
struct node* search(struct node*head, int data)
{
struct node *p = NULL;
for (p = head; p != NULL; p = p->next) {
if (p->data == data)
{
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
main.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void)
{
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *new_node = NULL;
int num = 10;
int i = 0;
int del_data = 0;
// 初始化头节点
init_list(&head);
// 创建一个链表节点
for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {
new_node = make_node(i + 10);
//insert_node_to_end(new_node, &head);
insert_node_from_begin(new_node,&head);
}
print_list(head);
printf("请输入要删除的节点:");
scanf("%d", &del_data);
struct node *del_node = search(head, del_data);
if (del_node != NULL)
{
delete_node(del_node, &head);
}
printf("---------\n");
print_list(head);
// 销毁一个链表
destory_list(&head);
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("head === NULL");
}
return 0;
}
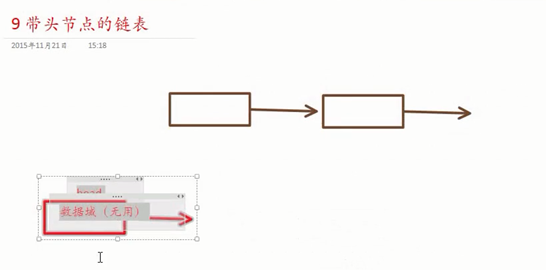
带头节点链表的操作:
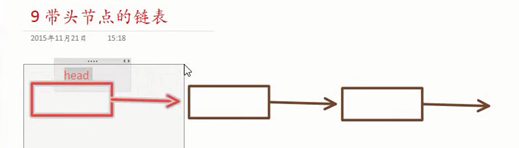
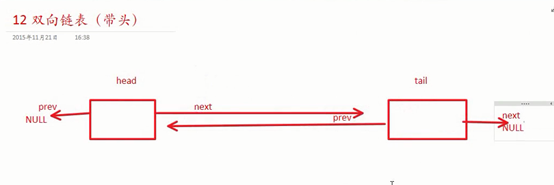
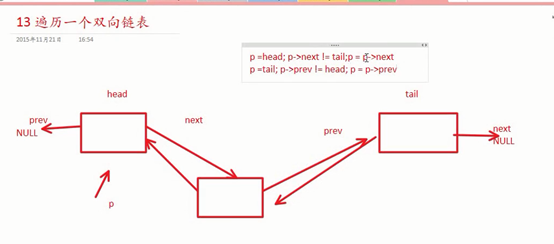
双向链表(带头):
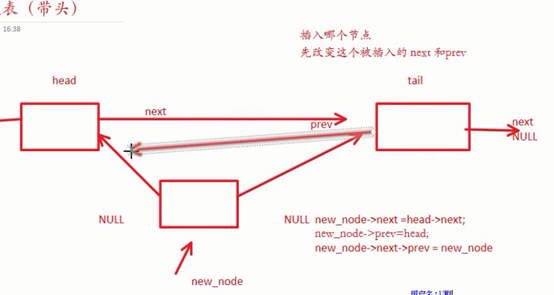
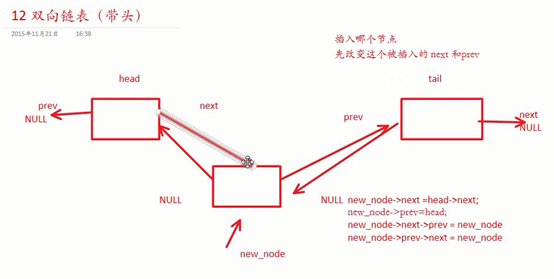
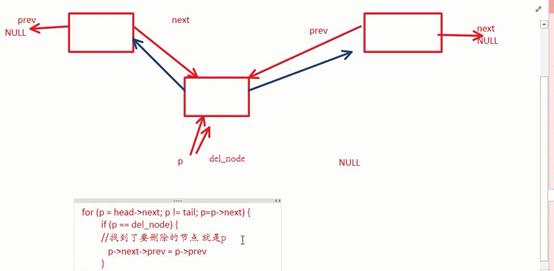
删除双向链表节点:
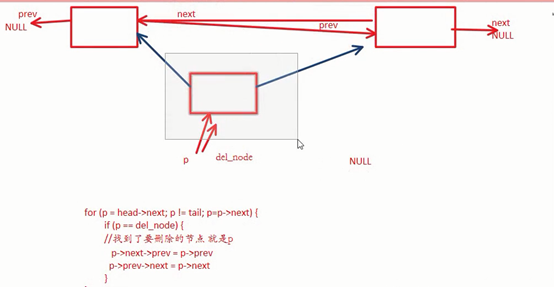
销毁一个双向链表:
dlist.h
#ifndef _D_LIST_H_
#define _D_LIST_H_
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct node
{
int data; //数据域
struct node *next; //下一个节点
struct node *prev; //上一个节点
};
// 初始化一个双向链表
void init_list(struct node **head_p,struct node**tail_p);
// 创建一个节点
struct node *make_node(int data);
// 销毁一个节点
void free_node(struct node *node);
// 插入一个节点
int insert_node(struct node*head, struct node*tail, struct node*new_node);
// 顺序遍历
void print_list_1(struct node *head, struct node *tail);
// 逆序遍历
void print_list_2(struct node *head, struct node *tail);
// 查找一个节点
struct node* search(struct node* head, struct node* tail, int data);
// 删除一个双向链表的节点
int delete_node(struct node* head, struct node* tail, struct node* del_node);
// 销毁一个双向链表
void destory_list(struct node* head, struct node* tail);
#endif
dlist.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "dlist.h"
// 初始化一个双向链表
void init_list(struct node **head_p, struct node**tail_p)
{
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *tail = NULL;
if (head_p == NULL || tail_p == NULL)
{
return;
}
head = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (head == NULL)
{
return;
}
tail = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (tail == NULL) {
return;
}
head->data = tail->data = 0;
head->next = tail;
tail->prev = head;
head->prev = tail->next = NULL;
*head_p = head;
*tail_p = tail;
return;
}
// 创建一个节点
struct node *make_node(int data)
{
struct node *p = NULL;
p = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (p == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
p->data = data;
p->next = p->prev = NULL;
return p;
}
void free_node(struct node *node) {
if (node == NULL) return;
free(node);
}
int insert_node(struct node*head, struct node*tail, struct node*new_node)
{
if (head == NULL || tail == NULL || new_node == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
//插入哪个节点就先改变哪个节点的next和prev
// 改变new_node的自身指针
new_node->next = head->next;
new_node->prev = head;
// 改变new_node两边的指针
new_node->next->prev = new_node;
new_node->prev->next = new_node;
return 0;
}
// 遍历一个链表
void print_list_1(struct node *head, struct node *tail)
{
struct node *p = NULL;
for (p = head->next; p != tail; p = p->next)
{
printf("data:%d\n", p->data);
}
}
void print_list_2(struct node *head, struct node *tail)
{
struct node *p = NULL;
for (p = tail->prev; p != head; p = p->prev)
{
printf("data:%d\n", p->data);
}
}
// 查找一个节点
struct node* search(struct node* head, struct node* tail,int data)
{
struct node* p = NULL;
for (p = head->next; p != tail; p = p->next)
{
if (p->data == data)
{
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
// 删除一个双向链表节点
int delete_node(struct node* head, struct node* tail, struct node* del_node)
{
struct node* p = NULL;
for (p = head->next; p != tail; p = p->next) {
//遍历链表中除了head和tail的每一个元素
if (p == del_node) {
// p是删除的节点
// 应该改变p的前驱节点和p的后继节点,p本身的两个指针不要动
p->next->prev = p->prev;
p->prev->next = p->next;
free_node(p);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
// 销毁一个双向链表
void destory_list(struct node** head_p, struct node** tail_p)
{
if (head_p == NULL || tail_p == NULL)
{
return;
}
struct node* head = *head_p;
struct node* tail = *tail_p;
struct node* p = NULL;
for (p = head->next; p != tail;)
{
p->next->prev = p->prev;
p->prev->next = p->next;
free_node(p);
p = head->next;
}
// 以上就删除了 除了head和tail的全部元素
if (head->next = tail && tail->prev == head)
{
printf("此时链表已经空 除了head\tail \n");
free_node(head);
free_node(tail);
*head_p = NULL;
*tail_p = NULL;
}
return;
}
main.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "dlist.h"
int main(void)
{
struct node *head = NULL;//表头
struct node *tail = NULL;//表尾
struct node *new_node = NULL;
struct node* del_node = NULL;
int num = 10;
int i = 0;
int data = 0;
init_list(&head, &tail);
for (i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
new_node = make_node(i + 10);
insert_node(head, tail, new_node);
}
print_list_1(head, tail);
printf("==========\n");
print_list_2(head, tail);
printf("data:");
scanf("%d", &data);
del_node = search(head,tail,data);
if (del_node != NULL)
{
delete_node(head, tail, del_node);
}
printf("==========\n");
print_list_2(head, tail);
destory_list(&head, &tail);
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("head == NULL\n");
}
if (tail == NULL)
{
printf("tail == NULL\n");
}
return 0;
}
总结:
对于插入删除链表效率比较高
对于索引链表效率比较低,(数组可以直接偏移
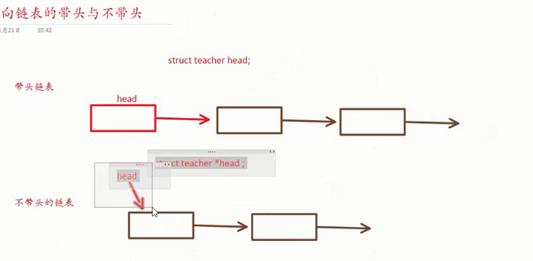
关于有头无头:
有了头结点之后,对首个结点的操作(比如删除、插入等)可以和其他节点相同,
“大家都说的差不多了,有头的好,没头的怎么找入口。”
回调函数




void(*)() 是个 返回值为 void; 参数为空 (这样些也成 void(*)(void) )的函数指针
注意 是个 函数指针
然后 把0 强制转换为 这个类型的指针
然后 取 值 *(void(*)())
这个时候 就是 取得了 一个函数指针 类型为 返回值为 void; 参数为空
然后 后面加上 括号 就是 实施这个 函数指针的调用




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号