C语言提高 (4) 第四天 数组与数组作为参数时的数组指针
1昨日回顾
const int
和 int const是一样的
const char *p;值不变
char * const p; 指针不能变
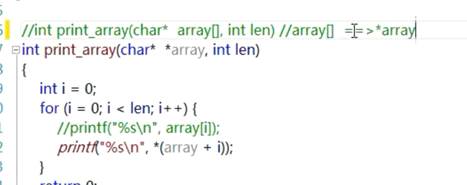
编译器对参数的退化:

第三种模型:

三级指针
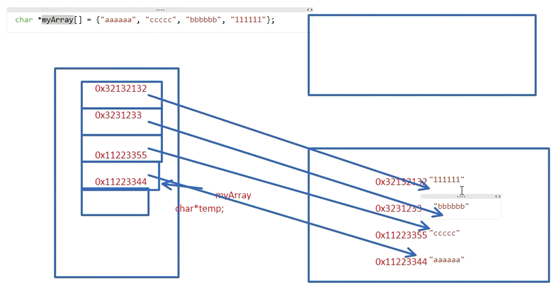
三级指针局部变量接收二级指针,并改变其内容
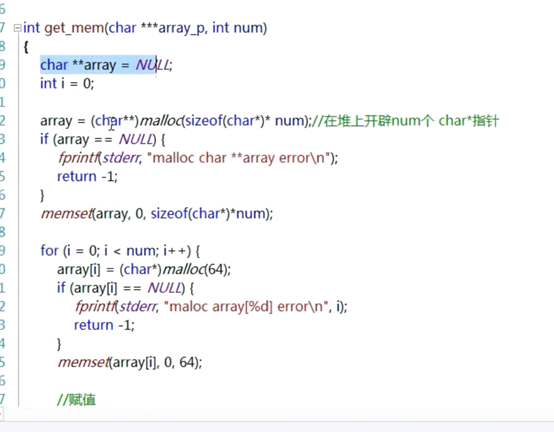
2拆分字符串第一种API

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int splitString(char *str,char ch,char array[][30],int *count)
{
char *p = str;
char *q = p;
int temp_count = 0;
int len = 0;
if (str == NULL || array == NULL || count == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "str == NULL || array == NULL || count == NULL");
return -1;
}
// 在一个字符串中找到一个字符 找到了 返回第一个字符的地址 失败返回NULL
//strchr(母串,字符)
while ( (p = strchr(p, ch))!= NULL) {
// 找到了
strncpy(array[temp_count], q, p - q);
array[temp_count][p - q] = '\0';
temp_count++;
p++;
q = p;
if (*p == '\0')
{
break;
}
}
if (*q != '\0') {
len = (str + strlen(str)) - q;
strncpy(array[temp_count], q, len);
array[temp_count][len] = '\0';
temp_count++;
}
*count = temp_count;
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
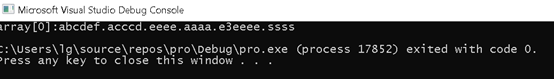
char *str = "abcdef.acccd.eeee.aaaa.e3eeee.ssss";
char array[10][30];
int count = 0;
int retn = 0;
int i = 0;
retn = splitString(str, ',', array, &count);
if (retn < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "splitString er\n");
return -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
printf("array[%d]:%s\n", i,array[i]);
}
return 0;
}
3拆分字符串第二种API
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int spitString(char *str, char ch,char ***array_p,int *count)
{
// P,q指向str
char *p= str;
char *q = p;
// 计数
int temp_count = 0;
// 二级指针
char **array = NULL;
int str_len = 0;
if (str == NULL || array_p == NULL || count == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "str == NULL || array_p == NULL || count == NULL\n");
return -1;
}
// 1 求出 字符串中 拆分的个数
while ((p = strchr(p, ch)) != NULL) {
temp_count++;
p++;
q = p;
if (*p == '\0') {
// 如果最后一位恰巧是ch那么+1就会是'\0'
break;}
}
// 如果有多余的
if (*q != '\0') {
temp_count++;
}
// 此时temp_count就是子字符串的个数
// 2 根据个数开辟指针数组 在堆上
// 在堆上开辟数组空间
array = (char**)malloc((sizeof(char*) * temp_count));
if (array == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "malloc char **array error\n");
return -1;
}
// 清0
memset(array, 0, sizeof(char *)*temp_count);
// 3 拆分字符串,为每一个指针开辟堆空间 拷贝字符串
p = str;
q = p;
temp_count = 0;
while((p = strchr(p,ch))!= NULL){
// 找到了
str_len = p - q;
// 数组的某个元素指向新分配的堆空间 堆空间大小是 sizeof(char) * str_len +1,+1是为了'\0'
array[temp_count] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*str_len+1);
if (array[temp_count] == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "malloc array[%d] error\n",temp_count);
return -1;
}
// 将值拷贝到堆空间中
strncpy(array[temp_count], q, str_len);
// 最后要增添'\0'
array[temp_count][str_len] = '\0';
// 重复这个过程
temp_count++;
p++;
q = p;
// 如果字符串最后一位恰好是要被替换的ch 那么+1后就会遇到\0
if (*p == '\0')
{
break;
}
}
// 如果字符串最后一位不是ch的情况,q指向不是'\0'
if (*q != '\0') {
str_len = (str + strlen(str)) - q;
array[temp_count] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*(str_len + 1));
// 任何分配空间都要做NULL值错误处理
if (array[temp_count] == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "malloc array[%d]error\n", temp_count);
return -1;
}
// 把最后一段复制到array中
strncpy(array[temp_count], q, str_len);
// 结尾补上'\0'
array[temp_count][str_len] = '\0';
// 计数增加
temp_count++;
}
if (array != NULL) {
// 三级指针接数组地址
*array_p = array;
*count = temp_count;
}
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
char *str = "abcdef,acccd,eeee,aaaa,e3eeee,ssss";
char **array = NULL;
int count = 0;
int retn = 0;
int i = 0;
retn = spitString(str, ',', &array, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
printf("array[%d]:%s\n", i, array[i]);
}
return 0;
}
3拆分字符串第二种API
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void free_mem(char ***array_p,int count) {
char **array = *array_p;
int i = 0;
if (array_p == NULL) {
return;
}
if (array != NULL) {
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (array[i] != NULL) {
free(array[i]);
array[i] = NULL;
}
}
free(array);
*array_p = NULL;
}
}
int spitString(char *str, char ch,char ***array_p,int *count)
{
// P,q指向str
char *p= str;
char *q = p;
// 计数
int temp_count = 0;
// 二级指针
char **array = NULL;
int str_len = 0;
int retn = 0;
if (str == NULL || array_p == NULL || count == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "str == NULL || array_p == NULL || count == NULL\n");
return -1;
}
// 1 求出 字符串中 拆分的个数
while ((p = strchr(p, ch)) != NULL) {
temp_count++;
p++;
q = p;
if (*p == '\0') {
// 如果最后一位恰巧是ch那么+1就会是'\0'
break;}
}
// 如果有多余的
if (*q != '\0') {
temp_count++;
}
// 此时temp_count就是子字符串的个数
// 2 根据个数开辟指针数组 在堆上
// 在堆上开辟数组空间
array = (char**)malloc((sizeof(char*) * temp_count));
if (array == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "malloc char **array error\n");
retn = -1;
goto END;
}
// 清0
memset(array, 0, sizeof(char *)*temp_count);
// 3 拆分字符串,为每一个指针开辟堆空间 拷贝字符串
p = str;
q = p;
temp_count = 0;
while((p = strchr(p,ch))!= NULL){
// 找到了
str_len = p - q;
// 数组的某个元素指向新分配的堆空间 堆空间大小是 sizeof(char) * str_len +1,+1是为了'\0'
array[temp_count] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*str_len+1);
if (array[temp_count] == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "malloc array[%d] error\n",temp_count);
retn = -1;
goto END;
}
// 将值拷贝到堆空间中
strncpy(array[temp_count], q, str_len);
// 最后要增添'\0'
array[temp_count][str_len] = '\0';
// 重复这个过程
temp_count++;
p++;
q = p;
// 如果字符串最后一位恰好是要被替换的ch 那么+1后就会遇到\0
if (*p == '\0')
{
break;
}
}
// 如果字符串最后一位不是ch的情况,q指向不是'\0'
if (*q != '\0') {
str_len = (str + strlen(str)) - q;
array[temp_count] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*(str_len + 1));
// 任何分配空间都要做NULL值错误处理
if (array[temp_count] == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "malloc array[%d]error\n", temp_count);
retn = -1;
goto END;
}
// 把最后一段复制到array中
strncpy(array[temp_count], q, str_len);
// 结尾补上'\0'
array[temp_count][str_len] = '\0';
// 计数增加
temp_count++;
}
if (array != NULL) {
// 三级指针接数组地址
*array_p = array;
*count = temp_count;
}
// 释放内存的步骤
END:
if (retn != 0) {
// 已经出现错误了
free_mem(&array, temp_count);
}
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
char *str = "abcdef,acccd,eeee,aaaa,e3eeee,ssss";
char **array = NULL;
int count = 0;
int retn = 0;
int i = 0;
retn = spitString(str, ',', &array, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
printf("array[%d]:%s\n", i, array[i]);
}
free_mem(&array, count);
if (array == NULL) {
printf("arraykong");
}
return 0;
}
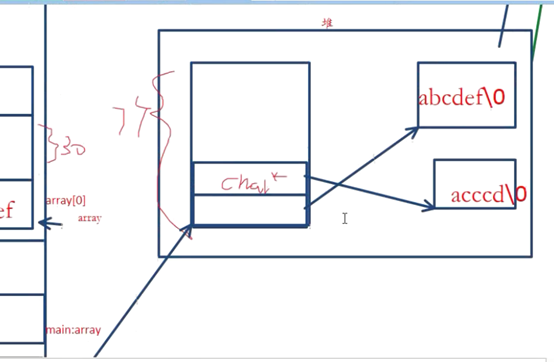
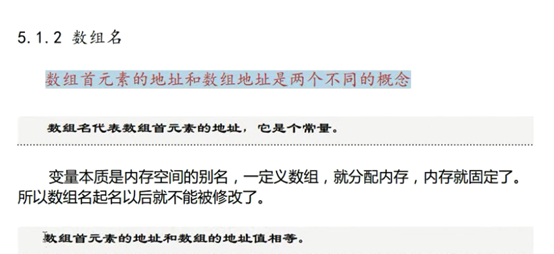
4 数组的概念
数组:1. 连续的一大片内存空间
2. 每个元素数据类型相同 (否则不知道该偏移多少

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void)
{
int a[10] = { 0 };
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
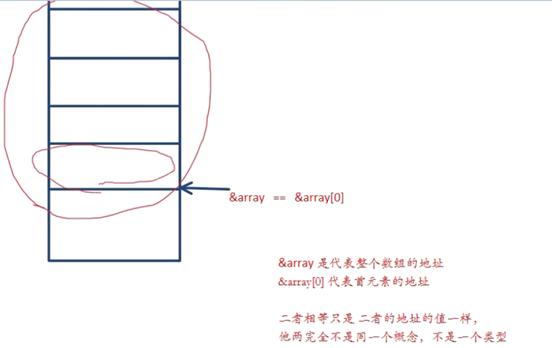
/* a是数组名 不能a++,,,,a=a+1;只能a[1]; *(a+i) //数组名是一个常量,是一个常指针,不能够被修改
数组名a本质是指向首元素地址 即&a[0]
a+1 a是int *const p; a+1 4个字节的偏移
&a+1 &a是int[10] *p &a+1 4*10 = 40个字节的偏移
*/
int aa[3][4] = {
{3,5,4,3},
{2,3,4,5}
};
// 初始化一个数组 不管是几维,如果初始化不完全,剩下的就全部填充0
for (i = 0;i<3;i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
printf("%d", aa[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
int size = sizeof(aa); //再求一个二维数组的 数据类型大小 int[3][4]
printf("size = %d\n", size);
// 如何定义指针?
// 比较好理解的方法 (int[3][4]) *p = NULL;
// 但是C语言中不能这么写,要把p放在数组前面 下面这样:
int(*p)[3][4] = NULL; // 指向二维数组int[3][4]的指针
printf("p: 0x%p, p+1:0x%p\n", p, p + 1);
// 0x0000 0030 (30是十进制的48)
// 数组也是有数据类型的
return 0;
}
5指针数组和数组指针的概念
typedef unsigned int u32;
int main(void)
{
//unsigned int a;
//u32 b;
//int a[3][4];
int a[10];
//typedef int[10] ARRAY_INT_10; 语法不能这么写,要用下面的写法:
typedef int ARRAY_INT_10 [10]; //为 int[10]这种数组 起一个别名 ARRAY_INT_10
ARRAY_INT_10 b_array; //int b_array[10]
int i = 0;
for (i = 0;i<10;i++)
{
b_array[i] = i;
}
for (i = 0;i<10;i++)
{
printf("%d\n", b_array[i]);
}
ARRAY_INT_10 *p = &b_array;
printf("p:%d,p+1:%d", p, p + 1);
return 0;
}
指针数组:

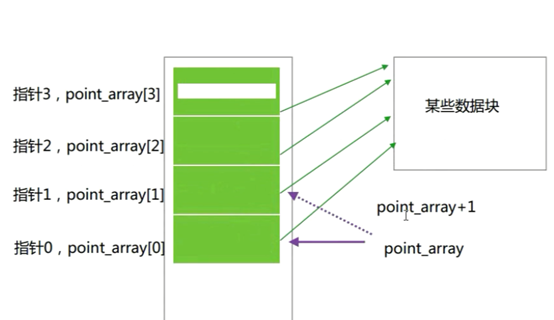
数组指针:


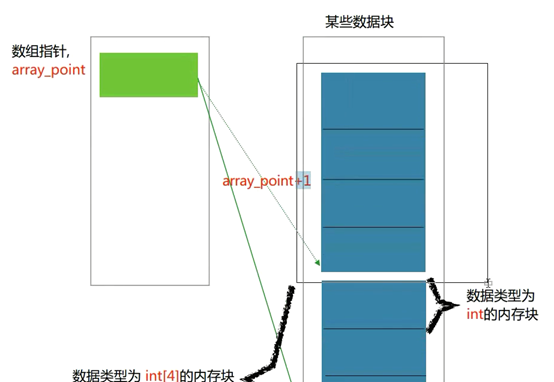
数组指针的两种定义方式:
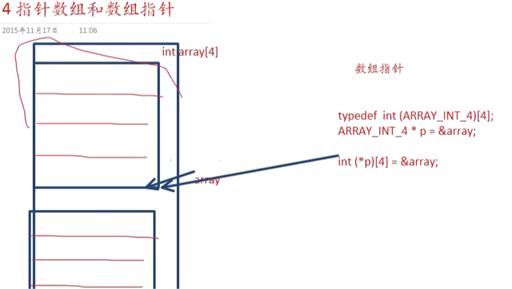

6如何定义一个数组指针
void test(){
int aa; //0维数组 一级指针
int aaa[10]; //一维数组,二级指针
int aaaa[10][20]; //二维数组,三级指针
int a[3][4];
// a是一个指针 指向此二维数组首元素int[4]地址 int (*p)[4] == 二级指针 指向一维数组
// &a也是一个指针 指向此二维数组int[3][4]的地址 int(*p)[3][4] == 三级指针 指向一个二维数组
// 推论:一个数组指针,如果是几级指针,就是指向比他低一个维度的数组。
}
int main(void)
{
// 定义一个指针数组
// 在栈上 用char* 还是void*都是一样的四个长度
char *pinter_array[4] = { "asd",NULL,NULL,NULL };
// 在堆上:
char *heap_array = malloc( 4 * sizeof(char*));
for(int i = 0;i<4;i++)
{
heap_array[i] = NULL;
}
int i = 0;
// 定义一个数组指针
// 方法一
// 直接定义一个数组类型
typedef int (ARRAY_CHAR_4) [4];
ARRAY_CHAR_4 array = { 1,2,3,4 };
ARRAY_CHAR_4 *p = NULL;
p = &array;
//方法二
typedef int (*ARRAY_CHAR_4_POINTER) [4];
ARRAY_CHAR_4_POINTER array_pointer = &array;
// 方法三
int(*array_p)[4] = NULL; // 直接定义一个数组指针
array_p = &array;
return 0;
}
7中午回顾
1这个算法: 用两个指针

2.养成好习惯:
free之后一定要 null
如果是NULL就return

free函数的返回值是void 所以不知道有没有成功,
自己接收的时候一定要用null来判断一下


8多维数组做为函数参数

(编译器并不是在栈中拷贝一份数组)
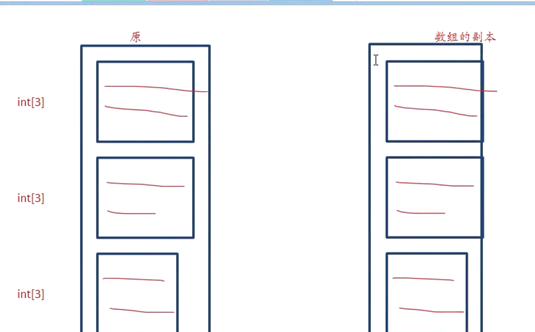
(并不是这样,否则太浪费空间了)
结论:当数组作为函数参数的时候,会退化成指针
形参用了数组的元素的指针来接收数组
(因为用了数组元素指针,就可以任意索引遍历数组
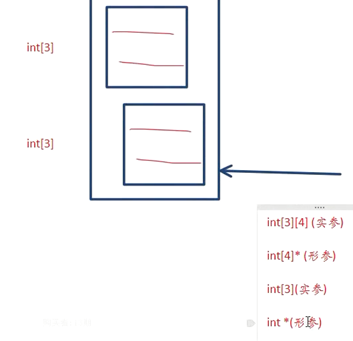
(数组作为形参被编译器退化)
。。。
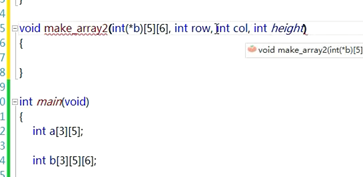
补充:
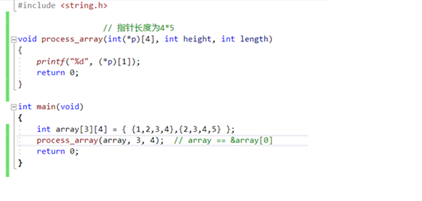
总结:
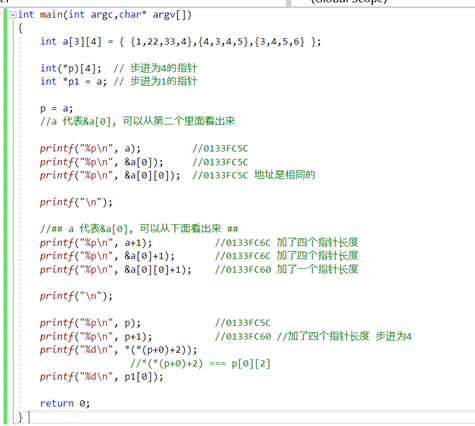
9指针数组的练习
// 数组无论是几维数组 都是一块连续的内存空间
10main函数的命令行参数
判断数组长度了 除了 sizeof(p)/sizeof(*p) 这种方法,
还有一种方法:
就是在数组最后加一个NULL
然后for循环,
for(i = 0; arr[i] !=NULL;i++)
{
// 遍历
}
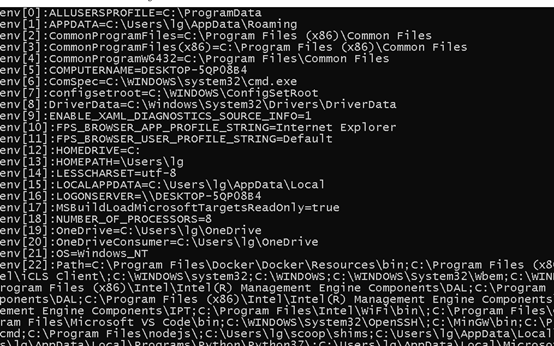
main函数入口的第三个参数是char *env[]
(前两个是int argc,char* argv
env指针数组就是这样实现的,最后一项默认是NULL
所以可以打印出来:
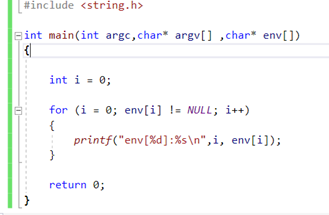
(环境变量:进程共享的变量
在windows运行桌面上的应用程序时候其实就是相当于在cmd里输入….exe 可执行程序可以拿到环境变量,环境变量是key value值的形式,value值是一段字符串