JNI简易开发
JNI简易开发
Whg,20210324
1 基础配置
Oracle官方文档:
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/jni/spec/jniTOC.html
其他参考:
https://www.eg.bucknell.edu/~mead/Java-tutorial/native1.1/TOC.html#invoking
1.1 JDK
n javac,将java文件编译成.class文件
n javah,使用class文件生成JNI头文件h使用
n javap,反编译器。解析class文件,输出编译信息
n java,在jvm上运行java文件和class文件
1.2 g++、gdb、clion
sudo apt install g++
c++编译器,调试器
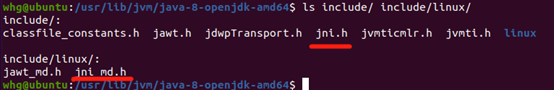
1.3 native开发使用到的jni头文件
2 基础介绍
2.1 java基础
此外,还应注意java的垃圾回收机制,这会影响到jni Function的不同调用。
2.1.1 对c++的要求
由于jvm是多线程的,native要求被编译成支持多线程,以支持jvm多线程特性
2.2 JNI基础
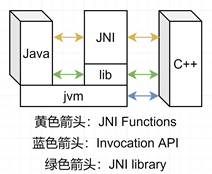
This chapter introduces the Java Native Interface (JNI). The JNI is a native programming interface. It allows Java code that runs inside a Java Virtual Machine (VM) to interoperate with applications and libraries written in other programming languages, such as C, C++, and assembly.
JNI基于jvm特性实现了java和native的互通操作,其互通操作分为2种类型:
l JNI function,用于在java和native之间实现功能上的互通。提供了对java field、method、static等域的操作
l Invocation API,实现了native与jvm的互通
2.2 JNI设计概览
2.2.1 JNI function
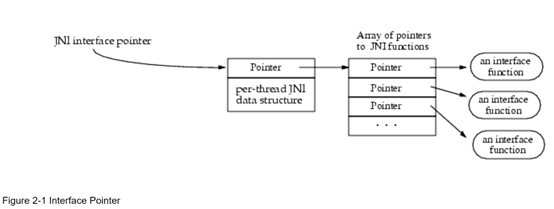
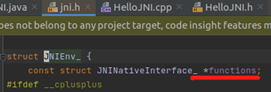
JNI function被设计成类似c++ virtual table的二级指针结构,JNI function有以下特点:
l JNI interface pointer内部维护了functions table,指向具体的JNi function实现
l JNI interface pointer与线程绑定,不可跨线程访问,其使用thread-local特性实现
l JNI interface pointer 作为native 方法的参数传入
l Jvm保证,单线程中的多个native 方法的JNI interface pointer一致,多线程中的native方法收到的JNI interface pointer不一致
该设计的优点:
l 该设计具有很高的灵活度,与native的实现完全剥离
l 比如,一个jvm可以同时拥有多个JNI interface pointer的内部实现(function table),而native代码,完全不必关心JNI interface pointer内部function table的组织结构
JNI interface pointer的代码示例(二级指针表的结构):
2.2.2 Invocation API
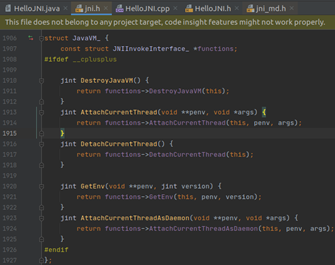
Invocation API主要用作native method操作jvm,因jvm负责整体环境,所以Invocation API涉及了一些环境上的操作,如:
l 创建、销毁jvm
l 将线程与jvm注册、分离
2.2.3 JNI libraries
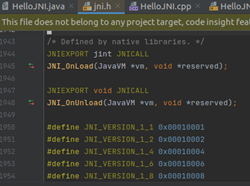
l jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM *vm, void *reserved);
当java加载so时,jvm会调用JNI_OnLoad。JNI_OnLoad必须返回当前使用的JNI版本号,jvm对返回的版本号进行识别,指定JNI的具体实现。所以,有必要了解一下不同jni版本号的功能特性
如果native不实现JNI_OnLoad,则jvm默认版本为JNI_VERSION_1_1
如果native实现了JNI_OnLoad但返回的版本号无效,则so会加载失败
附:Changes in JNI 1.1.2

l void JNI_OnUnload(JavaVM *vm, void *reserved);
当java加载so的class loader被垃圾回收后,jvm才调用OnUnload。该函数可用于清理native的缓存
下图是JNI_OnLoad、JNI_OnUnload在JNI library中的定义,以及JDK8支持支持的JNI版本类型,高16字节是大版本,低16字节是小版本
3 JNI基础类型和数据结构
3.1 基础类型映射

3.2 JNI reference type
Java数据类型,除了基础数据类型外,别的几乎都是object的子类。对于java object对象,obj1 = ojb2,相当于c++ 传递reference or pointer,而非assign or construct。

3.2.1 LocalReference
局部对象引用仅存活在native method方法期间,return后自动释放referfence
如若native method占用时间太长,大对象无法得到及时释放,此时,需要显示使用DeleteLocalRef释放局部对象
3.2.2 GlobalReference
全局对象由NewGlobalRef从局部对象或者全局对象产生,局部对象只在显示调用DeleteGlobalRef后才会销毁
3.2.3 WeakReference
WeakReference也是一种全局引用,但与GlobalReference的区别在于,weakReference指向的对象,可能会被垃圾收集器回收。
3.2.4 IsSameObject
以上对象引用,均可以使用jbool IsSameObject(Obj1, Obj2); 判断对象引用是否有效(与NULL对比)
3.3 field id

3.4 method id

3.5 function argument array value type
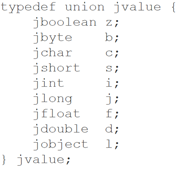
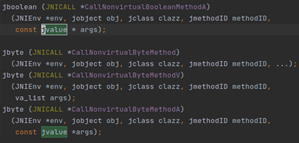
该类型用作native调用java方法的参数列表类型使用,如
3.6 Type Signatures
3.6.1 argument signature
Java的filed和method都有类型签名,native调用java方法时,必须告知jvm的java method 的name和signatures,以便jvm查找到java 方法。
Java类型签名的定义:
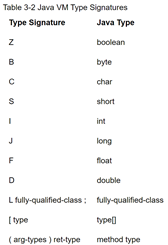
可以使用javap -s参数进行查看。如:
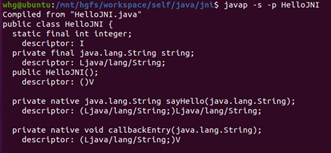
3.6.2 native method signature
Java方法名称:
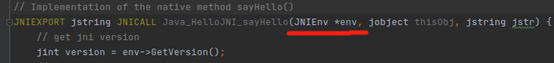
private native String sayHello(String msg);
由javah生成的native方法:
/*
* Class: HelloJNI
* Method: sayHello
* Signature: (Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/String;
*/
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_HelloJNI_sayHello (JNIEnv *, jobject, jstring);
Native方法名的格式如下:
l 前缀Java_
l 完整的包名HelloJNI_
l 方法名sayHello
l 如果是重载的方法,两个下划线__后紧跟参数签名
对于下面的方法:
class Cls1 {
int g(int i);
native int g(double d);
}
上述的native method g并不属于重载,因为另外一个g不是native方法
3.7 Modified UTF-8 Strings
JNI使用修改后的UTF8格式(非标准UTF8格式)。所以,需要使用GetStringUTFChars等方法转成c++ 的string。
也可以使用GetStringUTFLength查询UTF8的长度。
4 library 操作
见2.2.3
4.1 JNI_OnLoad
jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM *vm, void *reserved)
4.2 JNI_OnUnload
void JNI_OnUnload(JavaVM *vm, void *reserved)
5 jvm操作
5.1 GetEnv
通过jvm获取当前线程的env
5.2 GetJavaVM
通过jenv获取jvm
5.3 AttachCurrentThread
5.4 DetachCurrentThread
JNI function与线程环境挂钩,如果native方法回调java方法时
l 已保存当前线程的JNIEnv,则使用当前线程的env调用JNI Function
l 如果未保存当前线程的JNIEnv(不考虑是主线程还是主线程),则使用GetEnv获取当前线程的JNIEnv,再执行JNI Function操作
l 使用完后,可以解除与线程的绑定。或者保存,供下次子线程调用
子线程attach、detach的大致过程为:
1 ... 2 3 std::thread::id currentThreadId = std::this_thread::get_id(); 4 if (mainThreadId_.load() == currentThreadId) { 5 DLOG(INFO) << "shell thread : async result using main thread : " << std::hex << currentThreadId; 6 SyncResultCallback(queryText, results, candidateStartIndex, flag, highLightIndex); 7 return; 8 } 9 10 if (jvm_ == nullptr) { 11 DLOG(ERROR) << "shell thread : " << std::hex << currentThreadId << " global JavaVM is invalid "; 12 return; 13 } 14 JNIEnv* env {nullptr}; 15 jint jresult = jvm_->GetEnv((void**)&env, global_jni_version); 16 // if (jresult != JNI_OK || env == nullptr) { 17 // return; 18 // } 19 20 jresult = jvm_->AttachCurrentThread(&env, NULL); 21 if (jresult != JNI_OK) { 22 DLOG(ERROR) << "thread : " << std::hex << currentThreadId << std::dec << ", AsyncResultCallback : cannot attach current thread, error code " << jresult; 23 return; 24 } 25 26 ... do something ... 27 28 jresult = jvm_->DetachCurrentThread(); 29 if (jresult != JNI_OK) { 30 DLOG(ERROR) << "shell thread : " << std::hex << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::dec << ", AsyncResultCallback : cannot detach current thread, error code " << jresult; 31 return; 32 } 33 34 ...
6 JNI操作
6.1 java调用native方法
Java代码直接调用即可
6.2 native操作reference
详细介绍见3.2节
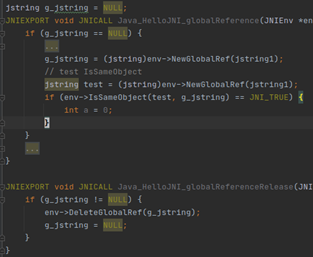
l NewGlobalRef
l DeleteGlobalRef
l DeleteLocalRef
l EnsureLocalCapacity
l PushLocalFrame
l PopLocalFrame
l NewLocalRef
l NewWeakGlobalRef
l DeleteWeakGlobalRef
6.3 native访问java field
如访问:

实现步骤:
- 使用GetObjectClass(thisObj)获取jclass
- 使用GetFieldID(jclass, filed name, field signature)获取jfieldid
- 使用GetObjectField(object, fieldid)获取field的值
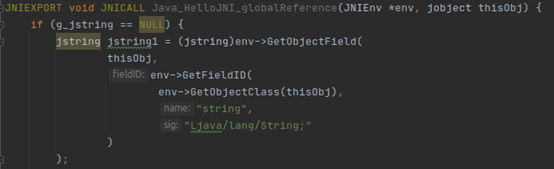
l GetFieldID
l Get<type>Field Routines
l Set<type>Field Routines
l GetStaticFieldID
l GetStatic<type>Field Routines
l SetStatic<type>Field Routines
6.4 native访问java method
如native访问java的方法
![]()
实现步骤:
- 使用GetObjectClass(thisObj)获取jclass
- 使用GetMethodId(jclass, method name,method signature)获取jmethodid
- 使用CallMethodID(object, methodid, argument)访问method
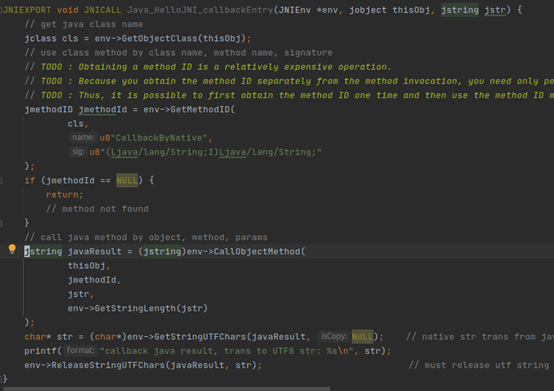
l Call<type>Method Routines
l Call<type>MethodA Routines,
l Call<type>MethodV Routines
l CallNonvirtual<type>Method Routines
l CallNonvirtual<type>MethodA Routines
l CallNonvirtual<type>MethodV Routines
l GetStaticMethodID
l CallStatic<type>Method Routines
l CallStatic<type>MethodA Routines
l CallStatic<type>MethodV Routines
6.5 native操作jstring
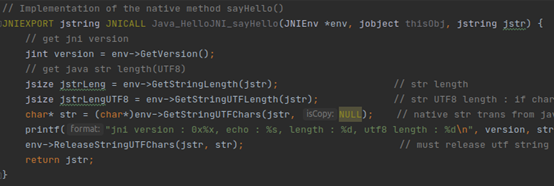
l NewString
l GetStringLength
l GetStringChars
l ReleaseStringChars
l NewStringUTF
l GetStringUTFLength
l GetStringUTFChars
l ReleaseStringUTFChars
l GetStringRegion
l GetStringUTFRegion
l GetStringCritical
l ReleaseStringCritical
6.6 native操作jarray
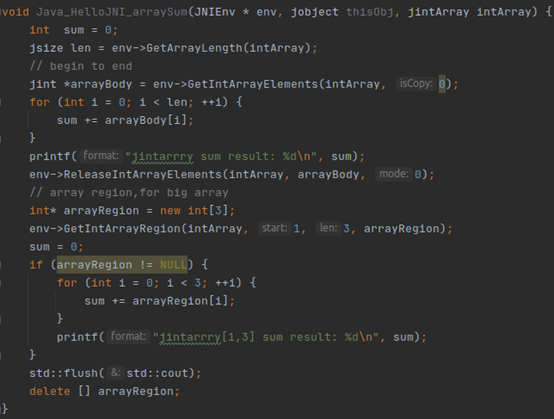
l GetArrayLength
l NewObjectArray
l GetObjectArrayElement
l SetObjectArrayElement
l New<PrimitiveType>Array Routines
l Get<PrimitiveType>ArrayElements Routines
l Release<PrimitiveType>ArrayElements Routines
l Get<PrimitiveType>ArrayRegion Routines
l Set<PrimitiveType>ArrayRegion Routines
l GetPrimitiveArrayCritical
l ReleasePrimitiveArrayCritical
6.7 native操作java exception
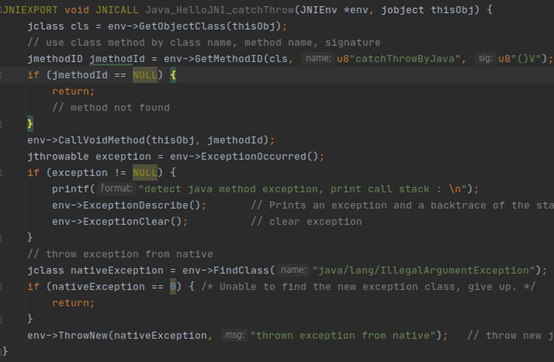
l Throw
l ThrowNew
l ExceptionOccurred
l ExceptionDescribe
l ExceptionClear
l FatalError
l ExceptionCheck
6.8 native访问java class
l DefineClass
l FindClass
l GetSuperclass
l IsAssignableFrom
6.9 native操作java object
l AllocObject
l NewObject, NewObjectA, and NewObjectV
l GetObjectClass
l GetObjectRefType
l IsInstanceOf
l IsSameObject
6.10 java操作native class
一般流程:
1:通过static native方法创建native类实例,将native 类地址(int)返回给java
2:native同时提供出带指针地址的方法
3:java调用步骤2的native方法,将1中获取的类地址作为参数传递
4:native方法收到类地址时,使用类型转换将地址转为class类型,紧跟调用类对应方法
如下所示,nativeInterface为native创建的类地址
1 JNI_GENERATOR_EXPORT jboolean 2 Java_com_Interface_nativeNMethod(JNIEnv* env, jobject 3 jcaller, 4 jlong nativeInterface, 5 jstring languageToken) { 6 Interface* native = reinterpret_cast<Interface*>(nativeInterface); 7 CHECK_NATIVE_PTR(env, jcaller, native, "NMethod", false); 8 return native->NMethod(env, base::android::JavaParamRef<jobject>(env, 9 jcaller), base::android::JavaParamRef<jstring>(env,param)); 10 }
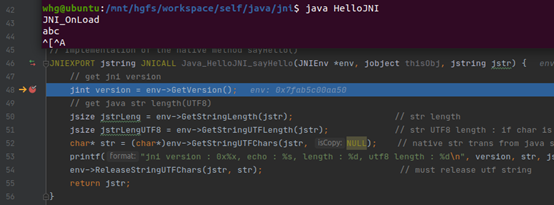
7 JNI测试-HelloJNI为例

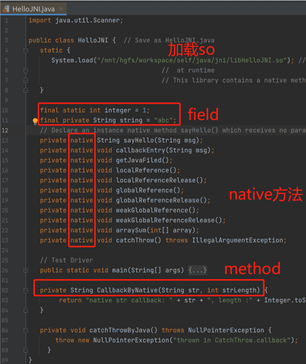
源文件HelloJNI.java:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class HelloJNI { // Save as HelloJNI.java 4 static { 5 System.load("/mnt/hgfs/workspace/self/java/jni/libHelloJNI.so"); // Load native library hello.dll (Windows) or libhello.so (Unixes) 6 // at runtime 7 // This library contains a native method called sayHello() 8 } 9 10 final static int integer = 1; 11 final private String string = "abc"; 12 // Declare an instance native method sayHello() which receives no parameter and returns void 13 private native String sayHello(String msg); 14 private native void callbackEntry(String msg); 15 private native void getJavaFiled(); 16 private native void localReference(); 17 private native void localReferenceRelease(); 18 private native void globalReference(); 19 private native void globalReferenceRelease(); 20 private native void weakGlobalReference(); 21 private native void weakGlobalReferenceRelease(); 22 private native void arraySum(int[] array); 23 private native void catchThrow() throws IllegalArgumentException; 24 25 // Test Driver 26 public static void main(String[] args) { 27 HelloJNI helloJNI = new HelloJNI(); 28 29 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 30 String val = input.next(); 31 do { 32 if (val != null) { 33 if (val.equals("callJavaMethod")) { 34 // call java method 35 helloJNI.callbackEntry("callbackEntry from java"); 36 } else if (val.equals("getJavaField")) { 37 // access java member variables 38 helloJNI.getJavaFiled(); 39 } else if (val.equals("catchThrow")) { 40 boolean exceptionOccur = false; 41 // catch and throw exception 42 try { 43 helloJNI.catchThrow(); 44 } 45 catch(Exception e) { 46 exceptionOccur = true; 47 System.out.println("catch native exception, show call stack"); 48 e.printStackTrace(); 49 } 50 finally { 51 // 52 if (exceptionOccur) { 53 System.out.println("recover from exception"); 54 } 55 } 56 } else if (val.equals("localReference")) { 57 helloJNI.localReference(); 58 } else if (val.equals("localReferenceRelease")) { 59 helloJNI.localReferenceRelease(); 60 } else if (val.equals("globalReference")) { 61 helloJNI.globalReference(); 62 } else if (val.equals("globalReferenceRelease")) { 63 helloJNI.globalReferenceRelease(); 64 } else if (val.equals("weakReference")) { 65 helloJNI.weakGlobalReference(); 66 } else if (val.equals("weakReferenceRelease")) { 67 helloJNI.weakGlobalReferenceRelease(); 68 } else if (val.equals("arraySum")) { 69 helloJNI.arraySum(new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,6}); 70 } else { 71 // Accessing Java Strings 72 String str = helloJNI.sayHello(val); 73 System.out.println("return native str : " + str); 74 } 75 } 76 System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------"); 77 val = input.next(); 78 } while(!val.equals("exit")); 79 input.close(); 80 } 81 82 private String CallbackByNative(String str, int strLength) { 83 return "native str callback: " + str + ", length :" + Integer.toString(strLength); 84 } 85 86 private void catchThrowByJava() throws NullPointerException { 87 throw new NullPointerException("thrown in CatchThrow.callback"); 88 } 89 }
源文件Hello JNI.cpp
1 #include <iostream> // C++ standard IO header 2 #include "HelloJNI.h" // Generated 3 #include <cstring> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL NativeCallJavaMethod(JNIEnv *env, jobject thisObj, const char* str) { 7 // // get java class name 8 // jclass cls = env->GetObjectClass(thisObj); 9 // // use class method by class name, method name, signature 10 // jmethodID jmethodId = env->GetMethodID(cls, u8"CallbackByNative", u8"(Ljava/lang/String;I)Ljava/lang/String;"); 11 // if (jmethodId == NULL) { 12 // return NULL; 13 // // method not found 14 // } 15 // // new native str 16 // size_t strLength = std::strlen(str); 17 // char* newStr = new char[strLength + 1]; 18 // memcpy(newStr, str, strLength); 19 // memset(newStr + strLength, 0, 1); 20 // jstring newJavaStr = env->NewStringUTF(newStr); // new string 21 // // call java method by object, method, params 22 // jstring javaResult = (jstring)env->CallObjectMethod(thisObj, jmethodId, newJavaStr, strLength); 23 // // jstring to native str 24 // char* nativeStr = (char*)env->GetStringUTFChars(javaResult, NULL); // native str trans from java string 25 // printf("result str from java callback : %s\n", nativeStr); 26 // env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(javaResult, nativeStr); 27 // delete [] newStr; 28 //} 29 30 // In order to use any of the new JNI functions, a native library must export a JNI_OnLoad function that returns JNI_VERSION_1_2. 31 // If the native library does not export a JNI_OnLoad function, the VM assumes that the library only requires JNI version JNI_VERSION_1_1. 32 JNIEXPORT jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM *vm, void *reserved) { 33 JNIEnv* env = NULL; 34 jint ret = vm->AttachCurrentThread(reinterpret_cast<void **>(&env), NULL); 35 printf("JNI_OnLoad\n"); 36 std::flush(std::cout); 37 return JNI_VERSION_1_6; 38 } 39 40 JNIEXPORT void JNI_OnUnload(JavaVM *vm, void *reserved) { 41 printf("JNI_OnUnload\n"); 42 std::flush(std::cout); 43 } 44 45 // Implementation of the native method sayHello() 46 JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_HelloJNI_sayHello(JNIEnv *env, jobject thisObj, jstring jstr) { 47 // get jni version 48 jint version = env->GetVersion(); 49 // get java str length(UTF8) 50 jsize jstrLeng = env->GetStringLength(jstr); // str length 51 jsize jstrLengUTF8 = env->GetStringUTFLength(jstr); // str UTF8 length : if char is chinese, UTF8length = length * 3 52 char* str = (char*)env->GetStringUTFChars(jstr, NULL); // native str trans from java string 53 printf("jni version : 0x%x, echo : %s, length : %d, utf8 length : %d\n", version, str, jstrLeng, jstrLengUTF8); 54 env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(jstr, str); // must release utf string 55 return jstr; 56 } 57 58 JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_HelloJNI_callbackEntry(JNIEnv *env, jobject thisObj, jstring jstr) { 59 // get java class name 60 jclass cls = env->GetObjectClass(thisObj); 61 // use class method by class name, method name, signature 62 // TODO : Obtaining a method ID is a relatively expensive operation. 63 // TODO : Because you obtain the method ID separately from the method invocation, you need only perform this operation once. 64 // TODO : Thus, it is possible to first obtain the method ID one time and then use the method ID many times at later points to invoke the same method. 65 jmethodID jmethodId = env->GetMethodID( 66 cls, 67 u8"CallbackByNative", 68 u8"(Ljava/lang/String;I)Ljava/lang/String;" 69 ); 70 if (jmethodId == NULL) { 71 return; 72 // method not found 73 } 74 // call java method by object, method, params 75 jstring javaResult = (jstring)env->CallObjectMethod( 76 thisObj, 77 jmethodId, 78 jstr, 79 env->GetStringLength(jstr) 80 ); 81 char* str = (char*)env->GetStringUTFChars(javaResult, NULL); // native str trans from java string 82 printf("callback java result, trans to UTF8 str: %s\n", str); 83 env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(javaResult, str); // must release utf string 84 } 85 86 JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_HelloJNI_getJavaFiled(JNIEnv *env, jobject thisObj) { 87 jclass cls = env->GetObjectClass(thisObj); 88 // access static int 89 jfieldID jfieldId = env->GetStaticFieldID(cls, "integer", "I"); 90 if (jfieldId == NULL) { 91 return; 92 } 93 jint jint1 = env->GetStaticIntField(cls, jfieldId); 94 printf("java class integer is assigned to %d\n", jint1); 95 // access member string 96 jfieldId = env->GetFieldID(cls, "string", "Ljava/lang/String;"); 97 if (jfieldId == NULL) { 98 return; 99 } 100 jstring jstring1 = (jstring)env->GetObjectField(thisObj, jfieldId); 101 char* str = (char*)env->GetStringUTFChars(jstring1, NULL); // native str trans from java string 102 printf("java object string is assigned to %s\n", str); 103 env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(jstring1, str); // must release utf string 104 } 105 106 JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_HelloJNI_catchThrow(JNIEnv *env, jobject thisObj) { 107 jclass cls = env->GetObjectClass(thisObj); 108 // use class method by class name, method name, signature 109 jmethodID jmethodId = env->GetMethodID(cls, u8"catchThrowByJava", u8"()V"); 110 if (jmethodId == NULL) { 111 return; 112 // method not found 113 } 114 env->CallVoidMethod(thisObj, jmethodId); 115 jthrowable exception = env->ExceptionOccurred(); 116 if (exception != NULL) { 117 printf("detect java method exception, print call stack : \n"); 118 env->ExceptionDescribe(); // Prints an exception and a backtrace of the stack to a system error-reporting channel, such as stderr. This is a convenience routine provided for debugging. 119 env->ExceptionClear(); // clear exception 120 } 121 // throw exception from native 122 jclass nativeException = env->FindClass("java/lang/IllegalArgumentException"); 123 if (nativeException == 0) { /* Unable to find the new exception class, give up. */ 124 return; 125 } 126 env->ThrowNew(nativeException, "thrown exception from native"); // throw new java exception 127 } 128 129 // TODO : This program is illegal because the local reference returned from GetObjectClass is valid only until the native method returns. 130 // TODO : When the Java application calls the native method Java_FieldAccess_accessFields a second time, the native method tries to use an invalid local reference. 131 // TODO : This leads to either the wrong results or to a VM crash. 132 jstring l_jstring = NULL; 133 JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_HelloJNI_localReference(JNIEnv *env, jobject thisObj) { 134 if (l_jstring == NULL) { 135 l_jstring = (jstring)env->GetObjectField(thisObj, 136 env->GetFieldID( 137 env->GetObjectClass(thisObj), 138 "string", 139 "Ljava/lang/String;" 140 ) 141 ); 142 } 143 char* str = (char*)env->GetStringUTFChars(l_jstring, NULL); // native str trans from java string 144 printf("java object string is assigned to %s\n", str); 145 env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(l_jstring, str); // must release utf string 146 } 147 148 JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_HelloJNI_localReferenceRelease(JNIEnv *env, jobject thisObj) { 149 if (l_jstring != NULL) { 150 env->DeleteLocalRef(l_jstring); 151 l_jstring = NULL; 152 } 153 } 154 155 jstring g_jstring = NULL; 156 JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_HelloJNI_globalReference(JNIEnv *env, jobject thisObj) { 157 if (g_jstring == NULL) { 158 jstring jstring1 = (jstring)env->GetObjectField( 159 thisObj, 160 env->GetFieldID( 161 env->GetObjectClass(thisObj), 162 "string", 163 "Ljava/lang/String;" 164 ) 165 ); 166 g_jstring = (jstring)env->NewGlobalRef(jstring1); 167 // test IsSameObject 168 jstring test = (jstring)env->NewGlobalRef(jstring1); 169 if (env->IsSameObject(test, g_jstring) == JNI_TRUE) { 170 int a = 0; 171 } 172 } 173 char* str = (char*)env->GetStringUTFChars(g_jstring, NULL); // native str trans from java string 174 printf("java object string is assigned to %s\n", str); 175 env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(g_jstring, str); // must release utf string 176 } 177 178 JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_HelloJNI_globalReferenceRelease(JNIEnv *env, jobject thisObj) { 179 if (g_jstring != NULL) { 180 env->DeleteGlobalRef(g_jstring); 181 g_jstring = NULL; 182 } 183 } 184 185 jweak g_weak = NULL; 186 void Java_HelloJNI_weakGlobalReference(JNIEnv *env, jobject thisObj) { 187 if (env->IsSameObject(g_weak, NULL) == JNI_FALSE) { 188 printf(" weak reference point is valid, underlying object is still valid\n"); 189 char* str = (char*)env->GetStringUTFChars((jstring)g_weak, NULL); // native str trans from java string 190 printf("java object string is assigned to %s\n", str); 191 env->ReleaseStringUTFChars((jstring)g_weak, str); // must release utf string 192 } else { 193 printf(" weak reference point to NULL, create new one \n"); 194 if (g_jstring == NULL) { 195 jstring jstring1 = (jstring)env->GetObjectField(thisObj, 196 env->GetFieldID( 197 env->GetObjectClass(thisObj), 198 "string", 199 "Ljava/lang/String;" 200 ) 201 ); 202 g_jstring = (jstring)env->NewGlobalRef(jstring1); 203 g_weak = env->NewWeakGlobalRef(g_jstring); 204 if (env->IsSameObject(g_jstring, g_weak)) { 205 int a = 0; 206 } 207 } 208 } 209 } 210 211 void Java_HelloJNI_weakGlobalReferenceRelease(JNIEnv *env, jobject thisObj) { 212 if (g_weak != NULL) { 213 env->DeleteWeakGlobalRef(g_weak); 214 g_weak = NULL; 215 } 216 } 217 218 void Java_HelloJNI_arraySum(JNIEnv * env, jobject thisObj, jintArray intArray) { 219 int sum = 0; 220 jsize len = env->GetArrayLength(intArray); 221 // begin to end 222 jint *arrayBody = env->GetIntArrayElements(intArray, 0); 223 for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) { 224 sum += arrayBody[i]; 225 } 226 printf("jintarrry sum result: %d\n", sum); 227 env->ReleaseIntArrayElements(intArray, arrayBody, 0); 228 // array region,for big array 229 int* arrayRegion = new int[3]; 230 env->GetIntArrayRegion(intArray, 1, 3, arrayRegion); 231 sum = 0; 232 if (arrayRegion != NULL) { 233 for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) { 234 sum += arrayRegion[i]; 235 } 236 printf("jintarrry[1,3] sum result: %d\n", sum); 237 } 238 std::flush(std::cout); 239 delete [] arrayRegion; 240 }
7.1 javac生成HelloJNI.class
javac HelloJNI.java
7.2 javah生成HelloJNI.h头文件
javah HelloJNI
7.3 实现c++代码,编译so
或者使用g++生成so
g++ --shared HelloJNI.cpp -o libHelloJNI.so -I/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/include -I/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/include/linux
7.4 java执行HelloJNI
java HelloJNI
7.5 查找进程id
7.6 attach debug