Java高级特性——反射机制(第三篇)
获取类运行时的结构
通过反射获取运行时类的完整结构
Field、Method、Constructor、Superclass、Interface、Annotation
>实现的全部接口
>所继承的父类
>全部的构造器
>全部的方法
>全部的Field
>注解
......
举例:
package test; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; //获取类的结构 public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException { Class c1 = Class.forName("test.User"); //获得类的名称 System.out.println(c1.getName()); //获得包名+类名 System.out.println(c1.getSimpleName()); //获得类名 //获得类的属性 System.out.println("============================="); Field[] fields = c1.getFields(); //只能找到public属性 for(Field f:fields) { System.out.println("public: "+f); } fields = c1.getDeclaredFields(); //找到全部属性 for(Field f:fields) { System.out.println(f); } //获得指定属性的值 Field f = c1.getDeclaredField("name"); System.out.println(f); //获得所有的方法 System.out.println("============================="); Method[] methods = c1.getMethods(); //只能获取public for(Method m:methods) { System.out.println("public: "+m); } methods = c1.getDeclaredMethods(); //获取所有 for(Method m:methods) { System.out.println(m); } //获取指定的方法 Method getName = c1.getMethod("getName", null); Method setName = c1.getMethod("setName",String.class); System.out.println(getName+"\r\n"+setName); //获取构造方法 System.out.println("============================="); Constructor[] constructor = c1.getConstructors(); for(Constructor c:constructor) { System.out.println("public: "+c); } constructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructors(); for(Constructor c:constructor) { System.out.println(c); } //获取指定构造器 Constructor c = c1.getConstructor(int.class,String.class,int.class); System.out.println(c); } } class User{ private int id; private String name; private int age; public User() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public User(int id, String name, int age) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
结果自行测试!
小结:
1.在实际的开发中,取得类的信息的操作代码并不会经常开发。
2.一定要熟悉java.lang.reflect包的作用、反射机制等。
3.如何取得属性、方法、构造器的名称,修饰符等。
有了Class对象,能做什么?
>创建类的对象,通过Class对象的newInstance()方法.
1.类必须有一个无参构造器。
2.类的构造器的访问权限必须足够。
例子(3-1):
package test; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; //通过反射动态创建对象 public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException{ Class c1 = Class.forName("test.User"); //构造一个对象 User user = (User)c1.newInstance(); //本质上调用了无参构造器 System.out.println(user); } } class User{ private int id; private String name; private int age; public User() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public User(int id, String name, int age) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
打印结果:

Tip:说明调用无参构造器创建了一个User对象。
思考:难道没有无参构造器就不能创建对象了吗?
答案:可以,只要在操作的时候明确的调用类中的构造器,并将参数传递进去后,就能够实例化。
步骤如下:
1.通过Class类的getDeclaredConstructor(Class ..ParmaterTypes)取得本类的指定形参类型的构造器。
2.向构造器的形参中传递一个数组对象进去,里边包含了构造器中所需的各个参数。
3.通过Constructor的newInstance()方法去实例化对象。
举例(修改3-1的main方法):
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException{ Class c1 = Class.forName("test.User"); //通过有参构造器构造一个User对象 Constructor constructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class,String.class,int.class); User user = (User)constructor.newInstance(1,"hgqin",20); System.out.println(user); }
运行结果:
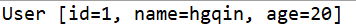
通过反射调用类中的方法,通过Method完成
1.通过Class类的getDeclaredMethod(String name,Class ...parameterTypes)方法取得一个Method对象,并设置此方法操作时所需要的参数类型。
2.之后使用Object invoke(Object obj,Object[] args)进行调用,并向方法中传递要设置的obj对象的参数信息。


举例(修改3-1的main方法):
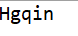
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException{ Class c1 = Class.forName("test.User"); User user = (User)c1.newInstance(); //通过反射获取一个方法 Method method = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class); //执行方法(invoke:激活) //(对象,值) method.invoke(user, "Hgqin"); System.out.print(user.getName()); }
执行结果:
通过反射操作属性
setAccessible方法:

举例(修改3-1的main方法):
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, NoSuchFieldException{ Class c1 = Class.forName("test.User"); User user = (User)c1.newInstance(); //通过反射操作属性 Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name"); //不能直接操作私有属性,我们需要关闭权限检测 name.setAccessible(true); //关闭安全检测 name.set(user, "hgqin"); System.out.println(user.getName()); }
执行结果:

性能比较
>通过比较普通方法以及反射方法 执行相同的方法所需要的时间,比较性能。大致结果为(普通方法>反射方法(关闭安全检查)>反射方法(不关闭安全检查))
package test; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; //性能分析 public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException { test01(); test02(); test03(); } public static void test01() { User user = new User(); Long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i=0;i<1000000000;i++) { user.getName(); } Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("普通方法执行10亿次需要时间:"+(endTime-beginTime)); } public static void test02() throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException{ User user = new User(); Class c1 = user.getClass(); Method m = c1.getDeclaredMethod("getName", null); Long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i=0;i<1000000000;i++) { m.invoke(user, null); } Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("反射方式执行10亿次需要时间:"+(endTime-beginTime)); } public static void test03() throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException{ User user = new User(); Class c1 = user.getClass(); Method m = c1.getDeclaredMethod("getName", null); Long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); m.setAccessible(true); for(int i=0;i<1000000000;i++) { m.invoke(user, null); } Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("关闭检测执行10亿次需要时间:"+(endTime-beginTime)); } } class User{ private int id; private String name; private int age; public User() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public User(int id, String name, int age) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
打印结果:

反射操作泛型(了解即可)
>Java采用泛型擦除的机制来引入泛型,Java中的泛型仅仅是给编译器Javac使用的,确保数据的安全性和免去强制类型的转换问题,但是一旦编译完成,所有和泛型有关的类型全部擦除。
>为了通过反射操作这些类型,Java新增了ParameterizedType、GenericArrayType、TypeVariable和WildcardType几种类型来代表不能被归一到Class类中的类型但是又和原始类型齐名的类型。
ParameterizedType:表示一种参数化类型,比如Collection<String>。
CenericArrayType:表示一种元素类型是参数化类型或者类型变量的数组类型。
WildcardType:代表一种通配符类型的表达式。
举例:
package test; import java.lang.reflect.*; import java.util.*; //通过反射获取泛型 public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException { System.out.println("通过反射获取泛型类型"); //test01 Method method = Test.class.getMethod("test01",Map.class,List.class); Type[] genericParameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes(); for(Type genericParameterType : genericParameterTypes) { System.out.println("#"+genericParameterType); if(genericParameterType instanceof ParameterizedType) { Type[] types = ((ParameterizedType)genericParameterType).getActualTypeArguments(); for(Type type : types) { System.out.println(type); } } } //test02 method = Test.class.getMethod("test02",null); Type genericReturnType = method.getGenericReturnType(); System.out.println("#"+genericReturnType); if(genericReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType) { Type[] types = ((ParameterizedType)genericReturnType).getActualTypeArguments(); for(Type type : types) { System.out.println(type); } } } public void test01(Map<String,User> map,List<User> list) { System.out.println("test01"); } public Map<String,User> test02() { System.out.println("test02"); return null; } } class User{ private int id; private String name; private int age; public User() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public User(int id, String name, int age) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
打印结果:




