Opensplice的Topic简介
在Overview中,简单介绍了一下Topic,下面详细介绍一下Topic。有不对的地方希望大家可以在留言区告诉我。
Topic是由名称(name)、类型(type)以及服务(QoS)组成。
1. Topic详解
(1)Topic Types
Opensplice支持不同语法的topic,比如:IDL,XML等。同时也支持一些其他vendor的topic,比如:PrismTech、Protobuf等。这里,我们还是只关注IDL。
IDL的Primitive Types主要有:
| Primitive Type | Size (bits) |
| boolean | 8 |
| octet | 8 |
| char | 8 |
| short | 16 |
| unsigned short | 16 |
| long | 32 |
| unsigned long | 32 |
| long long | 64 |
| unsigned long long | 64 |
| float | 32 |
| double | 64 |
在IDL中,没有int,这里的short、long以及long long相当于C99中的int16_t、int32_t以及int64_t。这里对于C++的转化基本遵循与IDL基本相同的类型,octet转换为char类型。
IDL支持的template Types(个人理解主要的功能是为了兼容数据类型)主要由两种:
| Template Type | Example |
| string<length = UNBOUNDED$> |
string s1; |
| sequence<T,length = UNBOUNDED> |
sequence<octet> oseq; |
IDL的string只能根据其最大长度进行参数化,然而sequence可以根据其最大长度以及其包含的类型进行参数化。sequence有些类似于C++中的vector。
注意:如果没有提供最大长度,那么相应的类型存储空间为无穷,这样就意味着Opensplice会为这个类型尽可能多的分配存储空间。
IDL支持的Constructed Types 类型主要由三种:
| Constructed Types | Examples |
| enum | enum Dimension {1D, 2D, 3D, 4D}; |
| struct |
struct Coord1D { long x;}; |
| union |
union Coord switch (Dimension) { |
这里应该说明一下,每个topic是一个struct类型,这个struct类型可以包含enum、struct、union类型,同样也可以包含primitive types与template types类型。同样也支持DDS支持的或者用户自定义的多维数组。
(2)Topic Keys, Instances and Samples
每个Topic相当于class(类),可以声明一个或若干个instance。Topic有其特殊的地方,Topic需要用key-set(由pragma keylist声明)来区分不同instances,比如下面代码中的DataCommType,用id作为key-set,每个Key-set可能为空,也可能包含由任意数量组成,为空的称为keyless topic,不为空的称为keyed topic(但key的类型存在一些限制:采用Primitive Types(见Table 1)、enum或者string。Key不能是Constructed Types、array或者sequence类型组成。),这两者之间由本质区别:
-> keyless topic在定义的时候仅有一个instance,可以理解为唯一instance;
-> key topic在定义的时候每个key-set对应一个instance。
这里举一个key topic与没有属性的keyless topic
module DataComm {
struct DataCommType {
short id;
float data1;
float data2;
};
#pragma keylist DataCommType id
struct KeylessDataCommType {
short id;
float data1;
float data2;
};
#pragma keylist KeylessDataCommType
};
上述两个topic由#pragma keylist定义的有key-set id的Topic,以及没有属性的key-set的topic。这两个Topic定义的代码可以表示为:
dds::topic::Topic<DataComm::DataCommType> topic(dp2, "DDataComm");
dds::topic::Topic<DataComm::KeylessDataCommType> klTopic(dp, "KLDataComm");
上述例子中,topic对应不同的id产生不同的instance,而klTopic仅仅只有一个instance,不论id是否变化。
Topic instances是运行时实体,DDS全程追踪全部实体是否满足:
-> 存在writer;
-> Topic instance是否在系统中是第一次运行;
-> Topic instance是否在系统中移除。
Topic instance影响这系统的reader,同时也影响着整个系统的存储结构。
像我们刚才提起的两种topic的区别,在写一个keyless topic的时候实际上就是写唯一的一个instance(每次写只能修改唯一的topic),在写key topic的时候,可以针对不同的key-set修改不同instance。
针对keyless topic的写操作的代码可以表示为:
dds::pub::DataWriter<DataComm::KeylessDataCommType> kldw(pub, kltsTopic);
DataComm::KeylessDataCommType klts(1, 26.0F, 70.0F);
kldw.write(klts);
kldw << DataComm::KeylessDataCommType(2, 26.0F, 70.0F);
在这个代码的基础上,读操作的相应的顺序为图1所示。
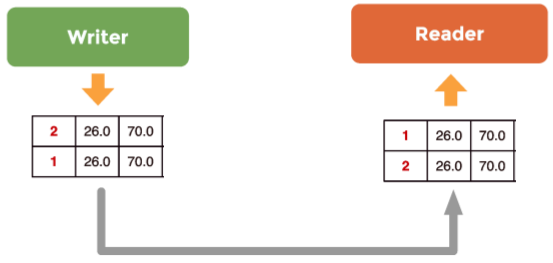
图1 keyless topic的写入/读出顺序
针对key topic 写操作的代码可以表示为:
dds::pub::DataWriter<DataComm::DataCommType> dw(pub, topic);
DataComm::DataCommType ts(1, 26.0F, 70.0F);
dw.write(ts);
dw << DataComm::DataCommType(2, 26.0F, 70.0F);
在上述代码的基础上,读写顺序应为如图2所示。
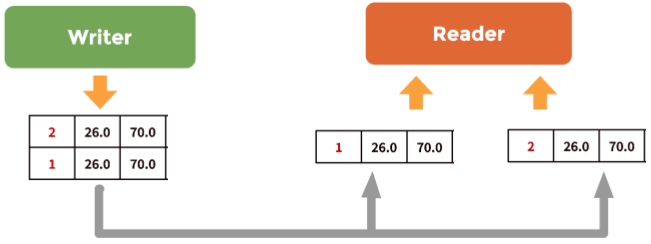
图2 key topic的写入/读出顺序
总之,Topic可以理解为面向对象语言中的类,一个key代表一个instance。每个topic instance由Opensplice管理,且分配相应的内存资源。在实际应用中,每个topic instance对应一个硬件设备。在系统运行的过程中,每由一个设备接入,系统会监测到,同时为设个设备分配相应的topic instance。
2. 范围信息(Scoping information)
DDS为范围信息提供两种机制:域(Domain)和分区(Partition)。
(1)域
域建立一个虚拟网络,链接已加入它的所有DDS应用程序。 除非由用户应用程序明确调解,否则跨域不会发生任何通信。
(2)分区
域可以进一步组织成分区,其中每个分区可以表示topic的逻辑分组。
DDS的分区由名字描述,比如:“ensorDataPartition, CommandPartition, LogDataPartition”。为了发布(publish)和订阅(subscribe)topic中的数据,分区必须显式的链接。
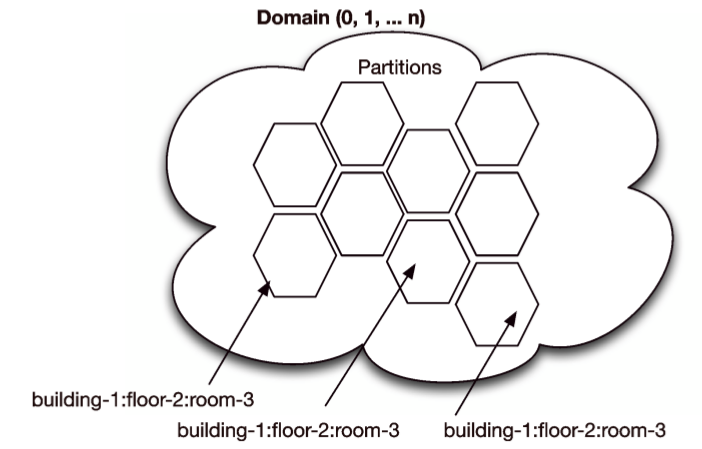
图3 Domains and partitions in DDS
DDS提供的用于加入分区的机制非常灵活,因为发布者或订阅者可以通过提供其全名来加入,比如:“SensorDataPartition”。或者可以加入所有匹配正则表达式的分区,例如Sens *或* Data *。支持的正则表达式符合POSIX标准。
分区还可用于隔离主题实例。这里没有看到具体的例子暂时保留。
3. 内容过滤(Content Filtering)
内容的过滤可以约束创建的topic instance中的值。
当订阅了(subscribe)content-filtered topic,在所有发布(publish)的消息中,只有符合topic滤波器的消息可以被接收。
| Constructed Type | Example |
| = | equal |
| <> | not equal |
| > | greater than |
| < | less than |
| >= | greater than or equal |
| <= | less than or equal |
| BETWEEN | between and inclusive range |
| LINK | matches a string pattern |
Content-filtered topic是非常有用的:
-> Content-filtered topic限制了使用内存的大小;
-> 通过检查某些数据属性,可以使用过滤来简化应用程序。
举个例子,在上节中的topic中,如果我们想得到data1在20.5~21.5之外,data2在30~50之外的数据,那么滤波器表达式可以为:
((data1 NOT BETWEEN 20.5 AND 21.5)
OR
(data2 NOT BETWEEN 30 AND 50))
Content-filtered topic在代码中的建立如下所示:
// Create the DataScope topic
dds::topic::Topic<DataComm::DataCommType> topic(dp, "DDataComm");
// Define the filter expression
std::string expression =
"(data1 NOT BETWEEN %20.5 AND %21.5) \
OR \
(data2 NOT BETWEEN %30 and %50)";
// Define the filter parameters
std::vector<std::string> params = {"20.5", "21.5", "30", "50"};
// Create the filter for the content-filtered-topic
dds::topic::Filter filter(expression, params);
// Create the ContentFilteredTopic
dds::topic::ContentFilteredTopic<DataComm::DataCommType> cfTopic(topic, "CFDDataComm", filter);
dds::sub::Subscriber sub(dp);
//This data reader will only receive data that matches the content filter
dds::sub::DataReader<DataScope::DataScopeType> dr(sub, cfTopic);
通过上述表达式,cfTopic仅接收data1在20.5~21.5之外,data2在30~50之外的数据。
4. 程序代码
keyless topic与content filter部分publish代码。
// OpslPubkeyless.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "gen/DataControl_DCPS.hpp"
#include <thread> // std::thread, std::this_thread::sleep_for
#include <chrono>
#include "util.hpp"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 2) {
std::cout << "USAGE:\n\t tspub <sensor-id>" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
int sid = atoi(argv[1]);
const int N = 100;
dds::domain::DomainParticipant dp(0);
dds::topic::Topic<DataComm::KeylessDataCommType> kltopic(dp, "DataComm");
dds::pub::Publisher pub(dp);
dds::pub::DataWriter<DataComm::KeylessDataCommType> dw(pub, kltopic);
const float avgT = 25;
const float avgH = 0.6;
const float deltaT = 5;
const float deltaH = 0.15;
// Initialize random number generation with a seed
srandom(clock());
// Write some temperature randomly changing around a set point
float temp = avgT + ((random() * deltaT) / RAND_MAX);
float hum = avgH + ((random() * deltaH) / RAND_MAX);
DataComm::KeylessDataCommType myData(sid, temp, hum);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
dw.write(myData);
std::cout << "DW << " << myData << std::endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
temp = avgT + ((random() * deltaT) / RAND_MAX);
myData.data1(temp);
hum = avgH + ((random() * deltaH) / RAND_MAX);
myData.data2(hum);
}
return 0;
}
keyless topic与content filter部分subscribe代码。
// OpslSubkeyless.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include "gen/DataControl_DCPS.hpp"
#include <thread> // std::thread, std::this_thread::sleep_for
#include <chrono>
#include "util.hpp"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 2) {
std::cout << "USAGE:\n\ttssub <filter-expression>"
<< std::endl;
exit(-1);
}
dds::domain::DomainParticipant dp(0);
dds::topic::Topic<DataComm::KeylessDataCommType> kltopic(dp, "DataComm");
dds::sub::Subscriber sub(dp);
//dds::sub::DataReader<DataComm::KeylessDataCommType> dr(sub, kltopic);
dds::topic::Filter filter(argv[1]);
dds::topic::ContentFilteredTopic<DataComm::KeylessDataCommType> cfTopic(kltopic, "CFDataComm", filter);
dds::sub::DataReader<DataComm::KeylessDataCommType> dr(sub, cfTopic);
while (true) {
auto samples = dr.read();
//std::cout << samples->id() << " " << samples->data1() << " " << samples->data2() << std::endl;
//std::cout << samples.data() << std::endl;
std::for_each(samples.begin(),
samples.end(),
[](const dds::sub::Sample<DataComm::KeylessDataCommType>& s) {
std::cout << s.data() << std::endl;
});
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
}
return 0;
}
将这两部分代码加入到上一章节的代码之中。修改上一章节的OpslSubkey.cpp,如下:
// OpslSub.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include "gen/DataControl_DCPS.hpp"
#include <thread> // std::thread, std::this_thread::sleep_for
#include <chrono>
#include "util.hpp"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 2) {
std::cout << "USAGE:\n\ttssub <filter-expression>"
<< std::endl;
exit(-1);
}
dds::domain::DomainParticipant dp(0);
dds::topic::Topic<DataComm::DataCommType> topic(dp, "DDataComm");
dds::sub::Subscriber sub(dp);
dds::topic::Filter filter(argv[1]);
dds::topic::ContentFilteredTopic<DataComm::DataCommType> cfTopic(topic, "CFDataComm", filter);
dds::sub::DataReader<DataComm::DataCommType> dr(sub, cfTopic);
while (true) {
auto samples = dr.read();
std::for_each(samples.begin(),
samples.end(),
[](const dds::sub::Sample<DataComm::DataCommType>& s) {
std::cout << s.data() << std::endl;
});
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
}
return 0;
}
程序运行:
-> keyless topic与key topic混合运行:
---> 如果OpslSub.cpp中的key topic的名称与OpslSubkeyless.cpp中的keyless topic的名字相同,那么在运行这两个程序时,会报运行时错误,如下:
terminate called after throwing an instance of 'dds::core::Error'
what(): Error: Failed to create Topic
========================================================================================
Context : dds::topic::detail::Topic<T>::Topic
Date : Thu Dec 13 07:52:48 CST 2018
Node : xxxx-GL552JX
Process : OpslSub <5848>
Thread : main thread 7efed7c99740
Internals : TTopicImpl.hpp/203/6.7.180404OSS
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Report : Error: Failed to create Topic
Internals : dds::topic::detail::Topic<T>::Topic/TTopicImpl.hpp/203
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Report : Create kernel entity failed. For Topic: <DDataComm>
Internals : u_topicNew/u_topic.c/235
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Report : Precondition not met: Create Topic "DDataComm" failed: typename <DataComm::KeylessDataCommType> differs exiting definition <DataComm::DataCommType>.
Internals : v_topicNew/v_topicImpl.c/478
Aborted (core dumped)
所以在OpslPub.cpp中的key topic的名称为“DDataComm”,OpslPubkeyless.cpp中的keyless topic名称“DataComm”。
---> 如果将OpslSub.cpp中的key topic的名称为“DataComm”,OpslSubkeyless.cpp中的keyless topic名称“DDataComm”,那么在运行OpslPub.cpp与OpslPubkeyless.cpp之后,运行OpslSub.cpp会报运行时报和上面一样的错误。
这是因为运行OpslSub.cpp之后,要接收的topic的类型与要接收相同名称的topic类型不匹配,所以产生了错误。
-> keyless topic独立运行,且测试content fliter:
---> 如果运行多个OpslPubkeyless.cpp与OpslSubkeyless.cpp,且每个OpslSubkeyless.cpp运行独立content filter,例如: “data1 > 26 AND data2 > 0.65”。那么每个OpslPubkeyless.cpp发出的keyless topic都会被OpslSubkeyless.cpp接收到。从使用的情况看,与key topic没有区别
-> 在运行程序时同样需要重针对keyless topic重载“<<”操作符。
原创博文,转载请标明出处。




