面向对象程序设计第二次博客作业
前言
第一次题目集:本次题目集难度主要集中在第一题上,其余题目难度不大,只需要掌握一些方法即可。其中第三题我使用了哈希表以及ArrayList的复制,来进行去重;第四题使用了Replace()方法、split()方法、compareToIgnoreCase()方法以及 LinkedHashSet;第五题是要进行类的封装,没什么难度;第八题则是学习使用Scanner类中nextLine()等方法、String类中split()等方法、Integer类中parseInt()等方法、LocalDate类中of()、isAfter()、isBefore()、until()等方法以及ChronoUnit类中DAYS、WEEKS、MONTHS等单位的用法。
第二次题目集:此次题目集相对于前几次要新鲜,首先是正则表达式的简单应用,还有就是聚合关系的使用。正则表达式就是使用单个字符串来描述、匹配一系列符合某个句法规则的字符串,而此次题目集学习使用的只是基础用法,通过正则表达式来校验字符串,使用Patte中的match方法进行匹配实现字符串格式的比较。而聚合关系是一种特殊的关联形式,它是两个类之间的关系,是一种HAS-A关系,是一种单向关联,聚合关系的整体与部分是可以分离的,可以提高代码的重用性以及可维护性。
第三次题目集:此次题目集对我来说难度很大,因为题目量比以前大很多,我在阅读题目这一步就已经出现了困难,读了很久才大概看懂题目的意思,当然这也是因为在第一次题目集中我就没有完成第一题。
设计与分析
训练集一:
7-1 菜单计价程序-3
本次题目未能完成,但通过反思仍旧有所收获。当困难来临的时候,这个时候就该正视困难,而非选择逃避。不然以为选择逃避,我的能力也难以得到提升,而问题也会滚雪球般越来越大。
7-3 去掉重复的数据
import java.util.*; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){int n = input.nextInt(); int []num = new int[n]; for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){ num[i] = input.nextInt(); } LinkedHashSet<Integer> num1 = new LinkedHashSet<Integer>();//LinkedHashSet是一个基于LinkedHashMap实现的有序去重集合列表,其中的元素没有重复,因此通过它去除重复数据
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){ num1.add(num[i]); } ArrayList <Integer> num2 = new ArrayList<Integer>(num1);//将num1的内容复制给num2,再输出 int l = num2.size(); for(int i = 0;i<l-1;i++)
System.out.print(num2.get(i)+" ");
System.out.print(num2.get(l-1));//最后一个输出不要空格
}
}
分析:这题我先通过LinkedHashSet山区数组中的重复数据,后因为最好一个数据需要单独输出,就将其通过ArrayList复制到num2再进行输出,难度不高
7-4 单词统计与排序
1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 6 String sentence = input.nextLine(); 7 sentence = sentence.replace(",",""); 8 sentence = sentence.replace(".",""); 9 String[] str = sentence.split(" "); 10 for(int i = 0;i<str.length-1;i++){ 11 for(int j = 0;j<str.length-1-i;j++){ 12 if(str[j].length()<str[j+1].length()){ 13 String temp = " "; 14 temp = str[j]; 15 str[j] = str[j+1]; 16 str[j+1] = temp; 17 } 18 if(str[j].length()==str[j+1].length()){ 19 20 if(str[j].compareToIgnoreCase(str[j+1])>0){ 21 String temp1 = " "; 22 temp1 = str[j]; 23 str[j] = str[j+1]; 24 str[j+1] = temp1; 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 LinkedHashSet<String> str1 = new LinkedHashSet<String>(); 30 for(int i = 0;i<str.length;i++){ 31 str1.add(str[i]); 32 } 33 for(String str2:str1) 34 System.out.println(str2); 35 36 } 37 }
分析:在写这道题时首先要注意的就是如何分割单词,我开始是想分别按“,”、“ ”、“.”分割,但后面发现不知道该如何写,就先将所有符号都先使用replace
()方法替换成空格,再通过split方法用空格将单词分开;接下来就是排序,先比较长度,先输出长的,这一步简单,而后便是在长度相同而的情况下比较字母,这就需要使用到compareToIgnoreCase()方法,(注:该方法用于按字典顺序比较两个字符串,不考虑大小写);最后将数据赋给LinkedHashSet修饰的str1,以达到去除重复数据的目的,然后foreach输出即可。
7-7 判断两个日期的先后,计算间隔天数、周数
1 import java.util.*; 2 import java.time.LocalDate; 3 import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit; 4 5 public class Main{ 6 public static void main(String[] args){ 7 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 8 9 String str1 = input.nextLine(); 10 String str2 = input.nextLine(); 11 String[] str3 = str1.split("-"); 12 String[] str4 = str2.split("-"); 13 int year1 = Integer.parseInt(str3[0]); 14 int month1 = Integer.parseInt(str3[1]); 15 int day1 = Integer.parseInt(str3[2]); 16 int year2 = Integer.parseInt(str4[0]); 17 int month2 = Integer.parseInt(str4[1]); 18 int day2 = Integer.parseInt(str4[2]); 19 20 LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(year1,month1,day1); 21 LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.of(year2,month2,day2); 22 if(!date1.isBefore(date2)) 23 System.out.println("第一个日期比第二个日期更晚"); 24 else 25 System.out.println("第一个日期比第二个日期更早"); 26 27 long day3 = date1.until(date2, ChronoUnit.DAYS); 28 long week = date1.until(date2, ChronoUnit.WEEKS); 29 System.out.println("两个日期间隔"+Math.abs(day3)+"天"); 30 System.out.println("两个日期间隔"+Math.abs(week)+"周"); 31 32 } 33 }
分析:本题主要是学习了各种时间类方法的使用,先使用split方法将输入时间分隔开,接着通过Integer.parseInt(),将String类型的数组元素转化为int类型数据,再接着就是时间类的使用了,这里不进行过多赘述
训练集二:
7-4 正则表达式训练-学号校验
1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Main { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 6 String number = input.nextLine(); 7 boolean result = isNumber(number); 8 if(result) { 9 System.out.println("正确"); 10 } 11 else { 12 System.out.println("错误"); 13 } 14 } 15 public static boolean isNumber(String number){ 16 boolean legal = number.matches("[2][0][2][0](([1][1-7])|([8][1-2])|([7][1-3]))(([0][1-9])|([1-3][0-9])|([4][0]))"); 17 return legal; 18 } 19 }
分析:本次题目集前面几题考察的都是正则表达式的简单应用,所以我就只拿这道题进行分析。首先,正则表达式就是使用单个字符串来描述、匹配一系列符合某个句法规则的字符串,而本题则是通过其中的matches方法来校验验证码。[2][0][2][0]指的是前四位为2020;(([1][1-7])|([8][1-2])|([7][1-3]))指的是当第五位为1时,第六位为1-7中任意一位,当第五位为8时,第六位为1-2中任意一位,当第五位为7时,第六位为1-3中一位,(([0][1-9])|([1-3][0-9])|([4][0]))则意思与前一组相似。
7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
1 import java.util.*; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args){ 4 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 5 int year = 0; 6 int month = 0; 7 int day = 0; 8 9 int choice = input.nextInt(); 10 11 if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method 12 int m = 0; 13 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 14 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 15 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 16 17 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(day, month, year); 18 19 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 20 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 21 System.exit(0); 22 } 23 24 m = input.nextInt(); 25 26 if (m < 0) { 27 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 28 System.exit(0); 29 } 30 31 32 System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); 33 } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method 34 int n = 0; 35 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 36 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 37 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 38 39 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(day, month, year); 40 41 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 42 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 43 System.exit(0); 44 } 45 46 n = input.nextInt(); 47 48 if (n < 0) { 49 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 50 System.exit(0); 51 } 52 System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); 53 } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method 54 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 55 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 56 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 57 58 int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 59 int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 60 int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 61 62 DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(day, month, year); 63 DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherDay, anotherMonth, anotherYear); 64 65 if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { 66 System.out.print(fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); 67 } else { 68 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 69 System.exit(0); 70 } 71 } 72 else{ 73 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 74 System.exit(0); 75 } 76 } 77 } 78 79 class DateUtil { 80 private Day day = new Day(); 81 DateUtil(){} 82 DateUtil(int d,int m,int y){ 83 day.setValue(d); 84 day.getMonth().setValue(m); 85 day.getMonth().getYear().setValue(y); 86 } 87 88 Day getDay() { 89 return day; 90 } 91 92 void setDay(Day d) { 93 this.day = d; 94 } 95 96 boolean checkInputValidity() { 97 if(day.validate()&&day.getMonth().validate()&&day.getMonth().getYear().validate()) { 98 return true; 99 } 100 else 101 return false; 102 } 103 104 boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { 105 if(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()>date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) { 106 return true; 107 } 108 else if(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&day.getMonth().getValue()>date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) { 109 return true; 110 } 111 else if(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&day.getMonth().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()&&day.getValue()>date.getDay().getValue()) { 112 return true; 113 } 114 else 115 return false; 116 } 117 118 boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) { 119 if(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&day.getMonth().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()&&day.getValue()==date.getDay().getValue()) { 120 return true; 121 } 122 else 123 return false; 124 } 125 126 String showDate(){ 127 String dater = day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() + "-" + day.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + day.getValue(); 128 return dater; 129 } 130 131 DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { 132 while(n>365) { 133 if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&day.getMonth().getValue()<3) { 134 day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 135 n -= 366; 136 } 137 else { 138 day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 139 if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&day.getMonth().getValue()>=3) { 140 day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 141 n -= 366; 142 } 143 else { 144 day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 145 n -= 365; 146 } 147 day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); 148 } 149 150 } 151 if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) { 152 day.mon_maxnum[2] = 29; 153 } 154 day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 155 if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) { 156 day.mon_maxnum[2] = 29; 157 } 158 day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); 159 160 while(n>day.mon_maxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()]) { 161 n = n-day.mon_maxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()]; 162 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 163 if(day.getMonth().getValue()>12) { 164 day.getMonth().reseMin(); 165 day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 166 } 167 } 168 if(n>(day.mon_maxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()]-day.getValue())) { 169 n = n + day.getValue() - day.mon_maxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()]; 170 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 171 day.setValue(n); 172 if(day.getMonth().getValue()>12) { 173 day.getMonth().reseMin(); 174 day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 175 } 176 } 177 else { 178 day.setValue(day.getValue()+n); 179 n = 0; 180 } 181 DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(); 182 date1.day.getMonth().getYear().setValue(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()); 183 date1.day.getMonth().setValue(day.getMonth().getValue()); 184 date1.day.setValue(day.getValue()); 185 186 return date1; 187 } 188 189 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ 190 DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(); 191 date1.setDay(this.getDay()); 192 while(n > 0){ 193 date1.getDay().dayReduction(); 194 n--; 195 if( date1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){ 196 date1.getDay().mon_maxnum[2] = 29; 197 if( date1.getDay().getValue() < 1 ){ 198 date1.getDay().getMonth().monthReduction(); 199 date1.getDay().reseMax(); 200 if( date1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == 0){ 201 date1.getDay().getMonth().reseMax(); 202 date1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); 203 } 204 } 205 }else{ 206 date1.getDay().mon_maxnum[2] = 28; 207 if( date1.getDay().getValue() < 1 ){ 208 date1.getDay().getMonth().monthReduction(); 209 date1.getDay().reseMax(); 210 if( date1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == 0){ 211 date1.getDay().getMonth().reseMax(); 212 date1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); 213 } 214 } 215 } 216 } 217 return date1; 218 } 219 220 221 int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) { 222 int[] a ={31,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 223 int count = 0; 224 int sum = 0; 225 int phase = 0; 226 int x = day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(); 227 day.getMonth().getYear().setValue(0); 228 for(int i = 0;i<x;day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(),i++) { 229 if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) 230 count += 366; 231 else 232 count += 365; 233 } 234 for(int i = 1;i<day.getMonth().getValue();i++) { 235 if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){ 236 a[2] = 29; 237 }else{ 238 a[2] = 28; 239 } 240 count = count + a[i]; 241 } 242 count = count + day.getValue(); 243 int j = date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); 244 date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().setValue(0); 245 for(int i = 0;i<j;date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(),i++) { 246 if(date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) 247 sum += 366; 248 else 249 sum += 365; 250 } 251 for(int i = 1;i<date.getDay().getMonth().getValue();i++) { 252 if(date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){ 253 a[2] = 29; 254 }else{ 255 a[2] = 28; 256 } 257 sum = sum + a[i]; 258 } 259 sum = sum + date.getDay().getValue(); 260 261 if(equalTwoDates(date)) { 262 phase = 0; 263 } 264 else { 265 if(compareDates(date)) 266 phase = count - sum; 267 else 268 phase =sum - count; 269 } 270 return phase; 271 } 272 } 273 274 class Day { 275 private int value; 276 private Month month = new Month(); 277 int[] mon_maxnum = {31,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31,31}; 278 279 Day(){} 280 Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue){ 281 this.value = dayValue; 282 month.setValue(monthValue); 283 month.getYear().setValue(yearValue); 284 } 285 286 int getValue() { 287 return value; 288 } 289 290 void setValue(int value) { 291 this.value = value; 292 } 293 294 Month getMonth(){ 295 return month; 296 } 297 298 void setMonth(Month value) { 299 month = value; 300 } 301 302 void reseMin() { 303 this.value = 1; 304 } 305 306 void reseMax() { 307 if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()) { 308 mon_maxnum[2] = 29; 309 } 310 this.value = mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]; 311 } 312 313 boolean validate() { 314 if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()) { 315 mon_maxnum[2] = 29; 316 } 317 if(this.value>=1 && this.value<=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]) { 318 return true; 319 } 320 else 321 return false; 322 } 323 324 void dayIncrement() { 325 this.value = this.value + 1; 326 } 327 328 void dayReduction() { 329 this.value = this.value - 1; 330 } 331 } 332 333 334 335 class Month { 336 private int value; 337 private Year year = new Year(); 338 339 Month(){} 340 Month(int yearValue,int monthValue){ 341 value = monthValue; 342 year.setValue(yearValue); 343 } 344 345 int getValue() { 346 return value; 347 } 348 349 void setValue(int value) { 350 this.value = value; 351 } 352 353 Year getYear() { 354 return year; 355 } 356 357 void setYear(Year year) { 358 this.year = year; 359 } 360 361 void reseMin() { 362 this.value = 1; 363 } 364 365 void reseMax() { 366 this.value = 12; 367 } 368 369 public boolean validate() { 370 if(this.value >= 1 && this.value <= 12) { 371 return true; 372 } 373 else{ 374 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 375 System.exit(0); 376 return false; 377 } 378 379 } 380 381 void monthIncrement() { 382 this.value = this.value + 1; 383 } 384 385 void monthReduction() { 386 this.value = this.value - 1; 387 } 388 389 } 390 391 class Year { 392 private int value; 393 394 Year(){} 395 Year(int value){ 396 this.value = value; 397 } 398 399 int getValue() { 400 return value; 401 } 402 403 void setValue(int value) { 404 this.value = value; 405 } 406 407 public boolean isLeapYear(){ 408 if(this.value%400==0||(this.value%4==0&&this.value%100!=0)) 409 return true; 410 else 411 return false; 412 } 413 414 public boolean validate() { 415 if(this.value>=1900&&this.value<=2050) { 416 return true; 417 } 418 else 419 return false; 420 } 421 422 void yearIncrement() { 423 this.value = this.value + 1; 424 } 425 426 void yearReduction() { 427 this.value = this.value - 1; 428 } 429 }
分析:本题的计算方法与上一次是一样的,但在类间关系的设计上发生了改变,这一次类间是聚合,是关联关系的一种特例,是强的关联关系,是整体和部分的关系,即has-a的关系。整体和部分之间是可分离的,拥有各自的生命周期。 这是一种天生的单向关系。在聚合的关系中,两种类是可以单独存在的,不会相互影响;也就是说:一个类的是否存在不会影响与之聚合的其他类的存在与否。可以维护代码的可重用性。并且本次问题仍然需要注意数组的越界问题,为了防止越界可以在数组的前后各加一个数据,并不会影响数组的使用。

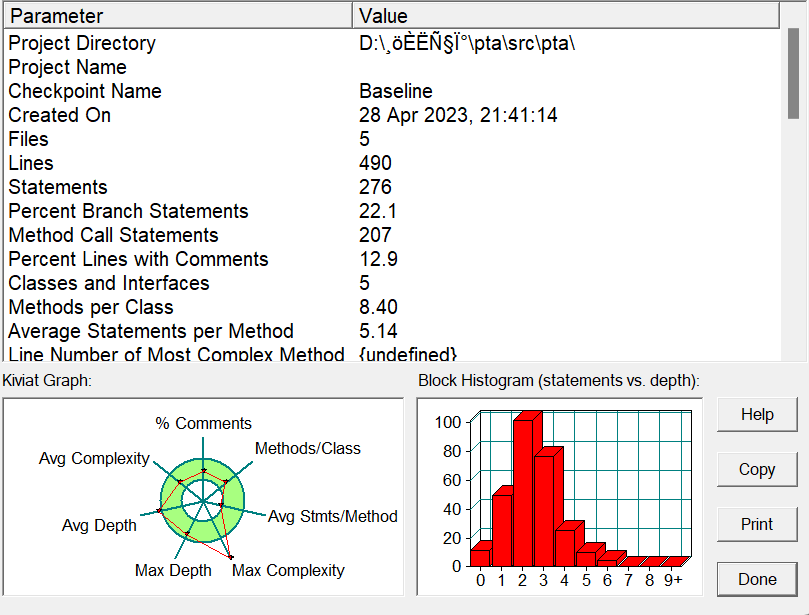
7-6 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
1 import java.util.*; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args){ 4 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 5 int year = 0; 6 int month = 0; 7 int day = 0; 8 9 int choice = input.nextInt(); 10 11 if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method 12 int m = 0; 13 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 14 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 15 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 16 17 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 18 19 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 20 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 21 System.exit(0); 22 } 23 24 m = input.nextInt(); 25 26 if (m < 0) { 27 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 28 System.exit(0); 29 } 30 31 System.out.print(date.getYear().getValue() + "-" + date.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + date.getDay().getValue() + " next " + m + " days is:"); 32 //date.getNextNDays(m); 33 System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); 34 } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method 35 int n = 0; 36 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 37 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 38 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 39 40 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 41 42 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 43 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 44 System.exit(0); 45 } 46 47 n = input.nextInt(); 48 49 if (n < 0) { 50 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 51 System.exit(0); 52 } 53 54 System.out.print( 55 date.getYear().getValue() + "-" +date.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + date.getDay().getValue() + " previous " + n + " days is:"); 56 System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); 57 } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method 58 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 59 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 60 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 61 62 int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 63 int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 64 int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 65 66 DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 67 DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); 68 69 if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { 70 System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + 71 " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:" 72 + fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); 73 } else { 74 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 75 System.exit(0); 76 } 77 } 78 else{ 79 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 80 System.exit(0); 81 } 82 } 83 } 84 85 class Day { 86 private int value; 87 88 Day(){} 89 Day(int value){ 90 this.value = value; 91 } 92 93 int getValue() { 94 return value; 95 } 96 97 void setValue(int value) { 98 this.value = value; 99 } 100 101 void dayIncrement() { 102 this.value = this.value + 1; 103 } 104 105 void dayReduction() { 106 this.value = this.value - 1; 107 } 108 } 109 110 class Month { 111 private int value; 112 113 Month(){} 114 Month(int value){ 115 this.value = value; 116 } 117 118 int getValue() { 119 return value; 120 } 121 122 void setValue(int value) { 123 this.value = value; 124 } 125 126 void reseMin() { 127 this.value = 1; 128 } 129 130 void reseMax() { 131 this.value = 12; 132 } 133 134 public boolean validate() { 135 if(this.value >= 1 && this.value <= 12) { 136 return true; 137 } 138 else 139 return false; 140 } 141 142 void monthIncrement() { 143 this.value = this.value + 1; 144 } 145 146 void monthReduction() { 147 this.value = this.value - 1; 148 } 149 150 } 151 152 class Year { 153 private int value; 154 155 Year(){} 156 Year(int value){ 157 this.value = value; 158 } 159 160 int getValue() { 161 return value; 162 } 163 164 void setValue(int value) { 165 this.value = value; 166 } 167 168 public boolean isLeapYear(){ 169 if(this.value%400==0||(this.value%4==0&&this.value%100!=0)) 170 return true; 171 else 172 return false; 173 } 174 175 public boolean validate() { 176 if(this.value>=1820&&this.value<=2020) { 177 return true; 178 } 179 else 180 return false; 181 } 182 183 void yearIncrement() { 184 this.value = this.value + 1; 185 } 186 187 void yearReduction() { 188 this.value = this.value - 1; 189 } 190 } 191 192 class DateUtil { 193 private Year year = new Year(); 194 private Month month = new Month(); 195 private Day day = new Day(); 196 private int[]mon_maxnum = {1,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31,1}; 197 198 DateUtil(){} 199 DateUtil(int y,int m,int d){ 200 year.setValue(y); 201 month.setValue(m); 202 day.setValue(d); 203 } 204 205 Year getYear() { 206 return year; 207 } 208 209 void setYear(Year year) { 210 this.year = year; 211 } 212 213 Month getMonth() { 214 return month; 215 } 216 217 void setMonth(Month month) { 218 this.month = month; 219 } 220 221 Day getDay() { 222 return day; 223 } 224 225 void setDay(Day day) { 226 this.day = day; 227 } 228 229 void setDayMin() { 230 day.setValue(1); 231 } 232 233 void setDayMax() { 234 day.setValue(12); 235 } 236 237 boolean checkInputValidity() { 238 if(day.getValue()>=1 && day.getValue()<=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()] &&month.validate() && year.validate()) { 239 return true; 240 }else { 241 return false; 242 } 243 } 244 245 DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { 246 while(n>365) { 247 if(getYear().isLeapYear()&&getMonth().getValue()<3) { 248 getYear().yearIncrement(); 249 n -= 366; 250 } 251 else { 252 getYear().yearIncrement(); 253 if(getYear().isLeapYear()&&getMonth().getValue()>=3) { 254 getYear().yearIncrement(); 255 n -= 366; 256 } 257 else { 258 getYear().yearIncrement(); 259 n -= 365; 260 } 261 getYear().yearReduction(); 262 } 263 264 } 265 if(getYear().isLeapYear()) { 266 mon_maxnum[2] = 29; 267 } 268 getYear().yearIncrement(); 269 if(getYear().isLeapYear()) { 270 mon_maxnum[2] = 29; 271 } 272 getYear().yearReduction(); 273 274 while(n>mon_maxnum[getMonth().getValue()]) { 275 n = n-mon_maxnum[getMonth().getValue()]; 276 getMonth().monthIncrement(); 277 if(getMonth().getValue()>12) { 278 getMonth().reseMin(); 279 getYear().yearIncrement(); 280 } 281 } 282 if(n>(mon_maxnum[getMonth().getValue()]-getDay().getValue())) { 283 n = n + getDay().getValue() - mon_maxnum[getMonth().getValue()]; 284 getMonth().monthIncrement(); 285 getDay().setValue(n); 286 if(getMonth().getValue()>12) { 287 getMonth().reseMin(); 288 getYear().yearIncrement(); 289 } 290 } 291 else { 292 getDay().setValue(getDay().getValue()+n); 293 n = 0; 294 } 295 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(); 296 date.getYear().setValue(getYear().getValue()); 297 date.getMonth().setValue(getMonth().getValue()); 298 date.getDay().setValue(getDay().getValue()); 299 300 return date; 301 } 302 303 DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) { 304 while(n>365) { 305 if(getYear().isLeapYear()&&getMonth().getValue()>2) { 306 getYear().yearReduction(); 307 n -= 366; 308 } 309 else { 310 getYear().yearReduction(); 311 if(getYear().isLeapYear()&&getMonth().getValue()<3) { 312 getYear().yearReduction(); 313 n -= 366; 314 } 315 else { 316 getYear().yearReduction(); 317 n -= 365; 318 } 319 getYear().yearIncrement(); 320 } 321 322 } 323 if(getYear().isLeapYear()) { 324 mon_maxnum[2] = 29; 325 } 326 getYear().yearReduction(); 327 if(getYear().isLeapYear()) { 328 mon_maxnum[2] = 29; 329 } 330 getYear().yearIncrement(); 331 while(n>mon_maxnum[getMonth().getValue()]) { 332 if( getMonth().getValue()==1) { 333 n = n-mon_maxnum[12]; 334 getMonth().monthReduction(); 335 } 336 else { 337 n = n-mon_maxnum[getMonth().getValue()-1]; 338 getMonth().monthReduction(); 339 } 340 if(getMonth().getValue()==0) { 341 getMonth().reseMax(); 342 getYear().yearReduction(); 343 } 344 } 345 if(n>day.getValue()) { 346 getMonth().monthReduction(); 347 if(getMonth().getValue()==0) { 348 getMonth().reseMax(); 349 getYear().yearReduction(); 350 } 351 getDay().setValue(mon_maxnum[getMonth().getValue()]-n+getDay().getValue()); 352 n = 0; 353 354 } 355 else { 356 getDay().setValue(getDay().getValue()-n); 357 n = 0; 358 } 359 DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(); 360 date1.getDay().setValue(getDay().getValue()); 361 date1.getMonth().setValue(getMonth().getValue()); 362 date1.getYear().setValue(getYear().getValue()); 363 364 return date1; 365 } 366 367 boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { 368 if(getYear().getValue()>date.getYear().getValue()) { 369 return true; 370 } 371 else if(getYear().getValue()==date.getYear().getValue()&&getMonth().getValue()>date.getMonth().getValue()) { 372 return true; 373 } 374 else if(getYear().getValue()==date.getYear().getValue()&&getMonth().getValue()==date.getMonth().getValue()&&getDay().getValue()>date.getDay().getValue()) { 375 return true; 376 } 377 else 378 return false; 379 } 380 381 boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) { 382 if(getYear().getValue()==date.getYear().getValue()&&getMonth().getValue()==date.getMonth().getValue()&&getDay().getValue()==date.getDay().getValue()) { 383 return true; 384 } 385 else 386 return false; 387 } 388 389 String showDate(){ 390 String dater = getYear().getValue() + "-" + getMonth().getValue() + "-" + getDay().getValue(); 391 return dater; 392 } 393 394 int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) { 395 int count = 0; 396 int sum = 0; 397 int phase = 0; 398 int x = getYear().getValue(); 399 getYear().setValue(0); 400 for(int i = 0;i<x;getYear().yearIncrement(),i++) { 401 if(getYear().isLeapYear()) 402 count += 366; 403 else 404 count += 365; 405 } 406 for(int i = 1;i<getMonth().getValue();i++) { 407 if(getYear().isLeapYear()){ 408 mon_maxnum[2] = 29; 409 }else{ 410 mon_maxnum[2] = 28; 411 } 412 count = count + mon_maxnum[i]; 413 } 414 count = count + getDay().getValue(); 415 int j = date.getYear().getValue(); 416 date.getYear().setValue(0); 417 for(int i = 0;i<j;date.getYear().yearIncrement(),i++) { 418 if(date.getYear().isLeapYear()) 419 sum += 366; 420 else 421 sum += 365; 422 } 423 for(int i = 1;i<date.getMonth().getValue();i++) { 424 if(date.getYear().isLeapYear()){ 425 mon_maxnum[2] = 29; 426 }else{ 427 mon_maxnum[2] = 28; 428 } 429 sum = sum + mon_maxnum[i]; 430 } 431 sum = sum + date.getDay().getValue(); 432 433 if(equalTwoDates(date)) { 434 phase = 0; 435 } 436 else { 437 if(compareDates(date)) 438 phase = count - sum; 439 else 440 phase =sum - count; 441 } 442 return phase; 443 } 444 }
分析:本次题目集的日期计算方法仍旧和上一道题一样,但类间关系又发生了一些改变。本次题目的所有类均只和DateUtil有聚合关系,这样子使得代码的耦合度更小,便于代码进行维护。

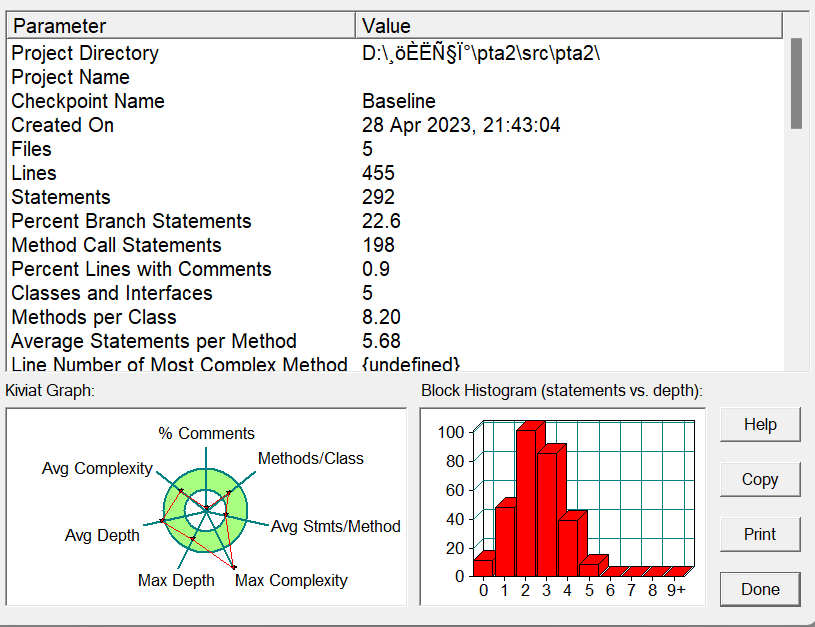
训练集三:
7-1 菜单计价程序-4
分析:本次题目只写出了部分功能,但Main类方法没有写出来。我的思路是便输入边输出,将输出放在类的方法中进行。我设计了如下几个类:Dish、Menu、Order、Record、Main以及Table。但写到后面,在主类时写不出来,就放弃了,这是我可能最大的缺点了,没有解决难题的勇气,并且还有从众心理。
总结
通过本次题目集,我了解了正则表达式的简单使用,时间类的使用,以及一些其他实用方法。在类的设计方面,也进一步了解了聚合关系的使用。当然也了解到了缺点所在,在以后的一定要改变懒惰怕困难的缺点。对于老师的授课方式,我觉得老师可以在上上课前将ppt或是下节课的主要教学内容发出来,便于提前学习,提高课堂效率。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号