Data Persistence with cv::FileStorage(数据存储)
主要函数
构造一个文件对象
FileStorage::FileStorage(); FileStorage::FileStorage( string fileName, int flag );
打开文件对象
FileStorage::open( string fileName, int flag );
读入文件数据
cv::Mat anArray; myFileStorage["calibrationMatrix"] >> anArray; int aNumber; myFileStorage["someInteger"] >> aNumber; int aNumber; aNumber = (int)myFileStorage["someInteger"]; //mapping类型数据,KEY=someInteger //或通过iterator cout << (int)lbpVal[i] //sequence类型数据的的i个元素
关闭文件
cv::FileStorage::release()
写出
将数据保存在“*.xml” , “*.yml”里
- 构建文件对象cv::FileStorage
- 打开文件cv::FileStorage::open FileStorage::WRITE
- 写数据
- mapping 键值对 标志:
- sequence 一系列未命名条目 [ ]
- 释放文件对象cv::FileStorage::release
读入
-
创建对象并打开 FileStorage::READ
-
data can be read with
|-([]操作符重载) cv::FileStorage::operator
| |-类型 | []中的值
| |-mapping | string KEY
| |-sequence | integer
| |
| |-返回一个cv::FileNode类型的对象
|-(文件节点(file node)的迭代器)cv::FileNode::Iterator -
对于cv::FileNode类型的对象,如果为基本数据类型,可通过强转(或隐式)直接获取
-
通过 = 或 >> 保存在变量中
-
release
source code
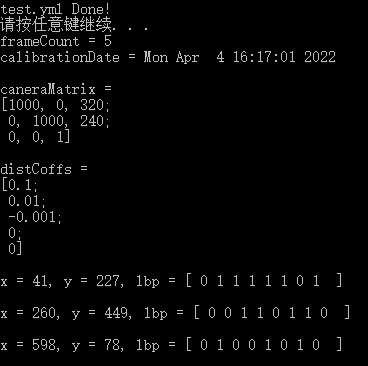
//vs2019,OpenCV4.5.1 #include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <opencv2/core.hpp> using namespace cv; #include <ctime> int main() { /************* 写出 *************/ FileStorage fs; fs.open("test.yml", FileStorage::WRITE); //FileStorage fs("test.yml", FileStorage::WRITE); // 构建+打开 fs << "frameCount" << 5; time_t rowTime; time(&rowTime); fs << "calibrationDate" << asctime(localtime(&rowTime)); Mat caneraMatrix = (Mat_<double>(3,3)<<1000,0,320,0,1000,240,0,0,1); Mat distCoffs = (Mat_<double>(5, 1) << 0.1, 0.01, -0.001, 0, 0); fs << "caneraMatrix" << caneraMatrix << "distCoffs" << distCoffs; fs << "features" << "["; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { int x = rand() % 640; int y = rand() % 480; uchar lbp = rand() % 256; fs << "{:" << "x" << x << "y" << y << "lbp" << "[:"; for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) fs << ((lbp >> j) & 1); // 疑问 fs << "]" << "}"; } fs << "]"; fs.release(); cout << "test.yml Done!" << endl; system("pause"); /************* 读入 *************/ fs.open("test.yml", FileStorage::READ); //读入法1, 等号 int frameCount = (int)fs["frameCount"]; //读入法2, >> String calibrationDate; fs["calibrationDate"] >> calibrationDate; fs["caneraMatrix"] >> caneraMatrix; fs["distCoffs"] >> distCoffs; cout << "frameCount = " << frameCount << "\ncalibrationDate = " << calibrationDate << "\ncaneraMatrix = \n" << caneraMatrix << "\n\ndistCoffs = \n" << distCoffs << endl; //通过迭代器访问元素 FileNode features = fs["features"]; FileNodeIterator iterator = features.begin(), iteratorEnd = features.end(); vector<unsigned char> lbpVal; for (; iterator != iteratorEnd; iterator++) { cout << "\nx = " << (int)(*iterator)["x"] << ", " << "y = " << (int)(*iterator)["y"]<<", "<<"lbp = [ "; (*iterator)["lbp"] >> lbpVal; for (int i{ 0 }; i < lbpVal.size(); i++) { cout << (int)lbpVal[i]<<" " ; } cout << " ]" << endl; } fs.release(); return 0; }
test.yml
%YAML:1.0 --- frameCount: 5 calibrationDate: "Mon Apr 4 16:11:42 2022\n" caneraMatrix: !!opencv-matrix rows: 3 cols: 3 dt: d data: [ 1000., 0., 320., 0., 1000., 240., 0., 0., 1. ] distCoffs: !!opencv-matrix rows: 5 cols: 1 dt: d data: [ 1.0000000000000001e-01, 1.0000000000000000e-02, -1.0000000000000000e-03, 0., 0. ] features: - { x:41, y:227, lbp:[ 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1 ] } - { x:260, y:449, lbp:[ 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0 ] } - { x:598, y:78, lbp:[ 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 ] }
result
本文作者:榴红八色鸫
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hezexian/p/16100154.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步