tensorflow 2.0 学习(四)MNIST 训练与测试
这次的mnist学习加入了测试集,看看学习的准确率,代码如下
# encoding: utf-8 import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #加载下载好的mnist数据库 60000张训练 10000张测试 每一张维度(28,28) path = r'G:\2019\python\mnist.npz' (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data(path) #第一层输入256, 第二次输出128, 第三层输出10 #第一,二,三层参数w,b w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([784, 256], stddev=0.1)) #正态分布的一种 b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256])) w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([256, 128], stddev=0.1)) b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([128])) w3 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([128, 10], stddev=0.1)) b3 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) #两种数据预处理的方法 #(一)预处理训练数据 x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x_train, dtype = tf.float32)/255. #0:1 ; -1:1(不适合训练,准确度不高) x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28*28]) y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y_train, dtype=tf.int32) y = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10) #将60000组训练数据切分为600组,每组100个数据 train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x, y)) train_db = train_db.shuffle(60000) #尽量与样本空间一样大 train_db = train_db.batch(100) #128 #(二)自定义预处理测试函数 def preprocess(x, y): x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255. #先将类型转化为float32,再归一到0-1 x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28*28]) #不知道x数量,用-1代替,转化为一维784个数据 y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32) #转化为整型32 y = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10) #训练数据所需的one-hot编码 return x, y #将10000组测试数据预处理 test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test)) test_db = test_db.shuffle(10000) test_db = test_db.batch(100) #128 test_db = test_db.map(preprocess) lr = 0.001 #学习率 losses = [] #储存每epoch的loss值,便于观察学习情况 acc = [] #准确率 for epoch in range(30): #20 #一次性处理100组(x, y)数据 for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_db): #遍历切分好的数据step:0->599 with tf.GradientTape() as tape: #向前传播第一,二,三层 h1 = x@w1 + tf.broadcast_to(b1, [x.shape[0], 256]) #可以直接写成 +b1 h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1) h2 = h1@w2 + b2 h2 = tf.nn.relu(h2) out = h2@w3 + b3 #计算mse loss = tf.square(y - out) loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss) #计算参数的梯度,tape.gradient为自动求导函数,loss为目标数据,目的使它越来越接近真实值 grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3]) #更新w,b w1.assign_sub(lr*grads[0]) #原地减去给定的值,实现参数的自我更新 b1.assign_sub(lr*grads[1]) w2.assign_sub(lr*grads[2]) b2.assign_sub(lr*grads[3]) w3.assign_sub(lr*grads[4]) b3.assign_sub(lr*grads[5]) #观察学习情况 if step%100 == 0: print('训练第 ',epoch,'轮',', 第',step,'步, ','loss:', float(loss)) losses.append(float(loss)) #将每100step后的loss情况储存起来,最后观察 if step%500 == 0: total, total_correct = 0., 0. for x, y in test_db: h1 = x @ w1 + b1 h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1) h2 = h1 @ w2 + b2 h2 = tf.nn.relu(h2) out = h2 @ w3 + b3 pred = tf.argmax(out, axis=1) # 选取概率最大的类别 y = tf.argmax(y, axis=1) # 类似于one-hot逆编码 correct = tf.equal(pred, y) # 比较真实值和预测值是否相等 total += x.shape[0] # 统计正确的个数 total_correct += tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct, dtype=tf.int32)).numpy() print('训练第 ',epoch,'轮',', 第',step,'步, ', 'Evaluate Acc:', total_correct/total) acc.append(total_correct/total) #plt.subplot(121) x1 = [i*100 for i in range(len(losses))] plt.plot(x1, losses, marker='s', label='training') plt.xlabel('Step') plt.ylabel('MSE') plt.legend() #plt.savefig('exam_mnist_forward.png') #plt.show() #plt.subplot(122) plt.figure() x2 = [i for i in range(len(acc))] plt.plot(x2, acc, 'r',marker='d', label='testing') plt.xlabel('Step') plt.ylabel('Accuracy') plt.legend() #plt.savefig('test_mnist_forward.png') plt.show()
误差何准确率如下
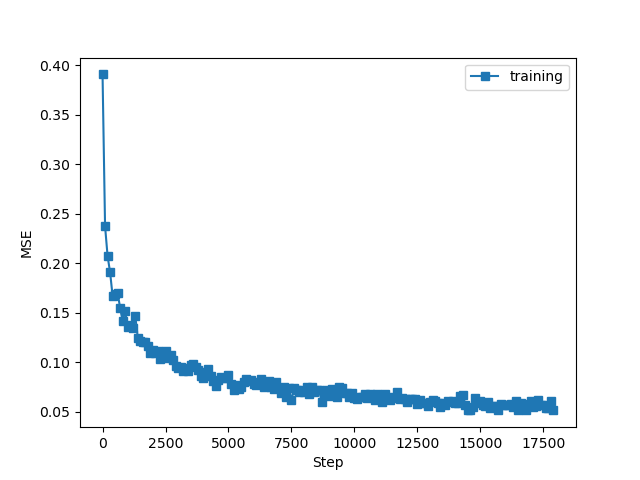
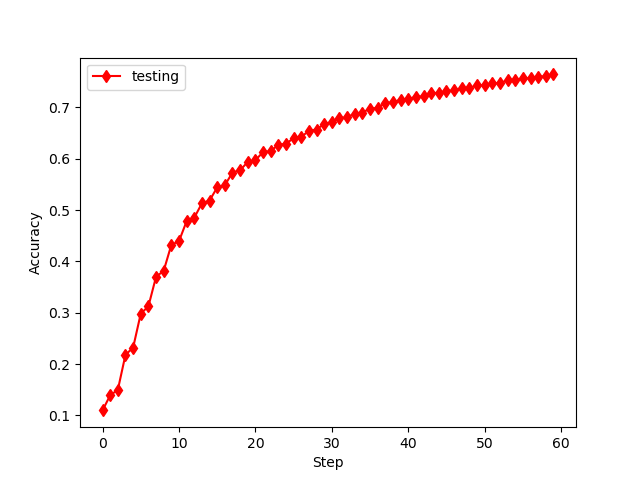
发现和书中类似,但要注意的如下:
(1)数据预处理时,打散值选择和数据空间一样大;
(2)数据处理选择0-1之间,而不用(-1 :1),是因为后者学习效率不理想!
(3)代码还可以进行优化处理!
总的来说,代码还是容易理解,使用也更加简洁!
下一次更新,全连接网络,关于汽车油耗的预测。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号