SpringMVC流程解析学习【doDispatch】
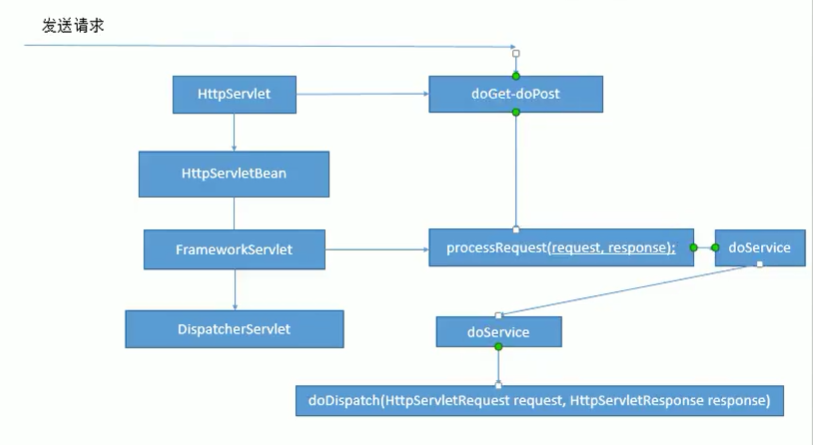
流程概述
所有请求经过DispatcherServlet
调用doDispatch()进行处理
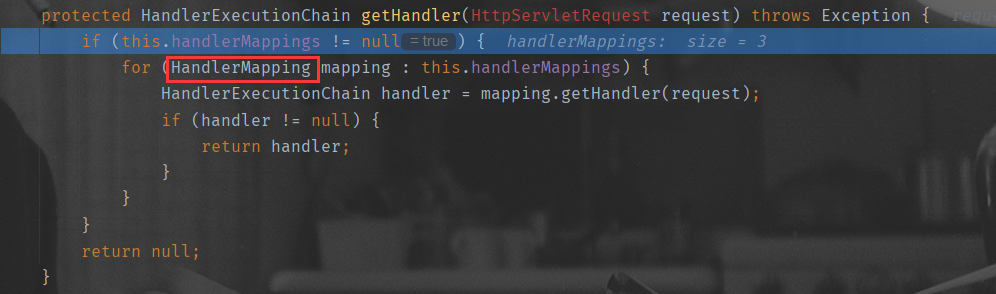
1.gerHandler()根据当前请求在HandlerMapping中找到请求的映射信息,找到能处理请求的目标处理器
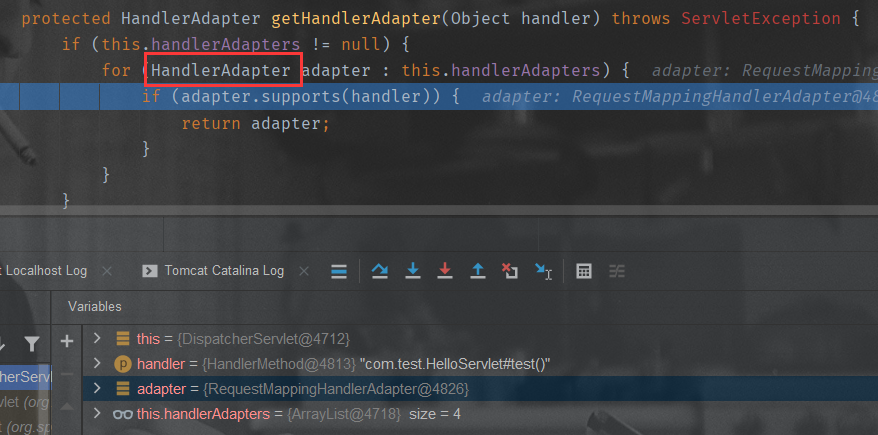
2.getHandlerAdapter()根据获取到的处理器找到对应的HandlerAdapter(Spring3.1后使用RequestMappingHandlerAdapter代替Spring2.5中的AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter),执行目标方法
3.HandlerAdapter通过反射执行方法,返回一个 ModelAndView对象
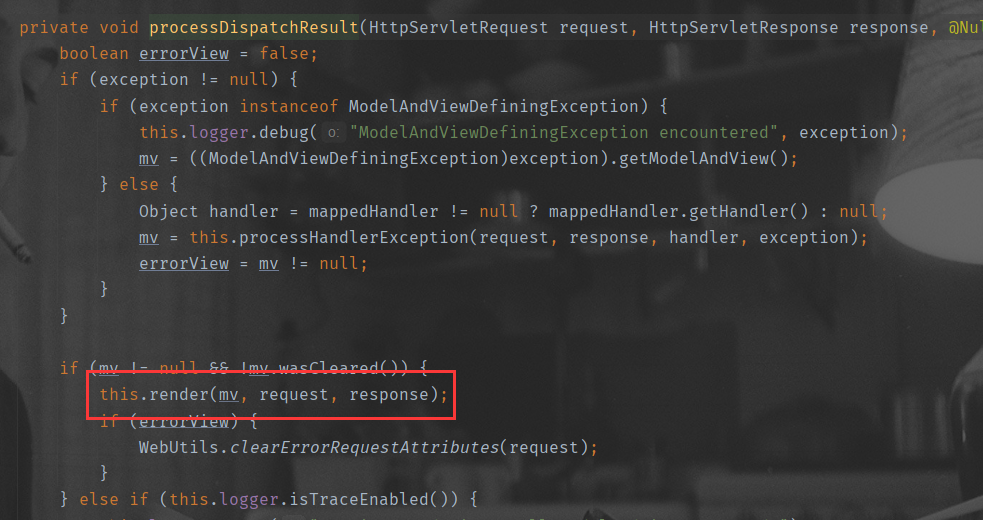
4.processDispatchResult( ) 根据封装的ModelAndView转发到对应的页面,且ModelAndView中的数据可以由请求域中获取
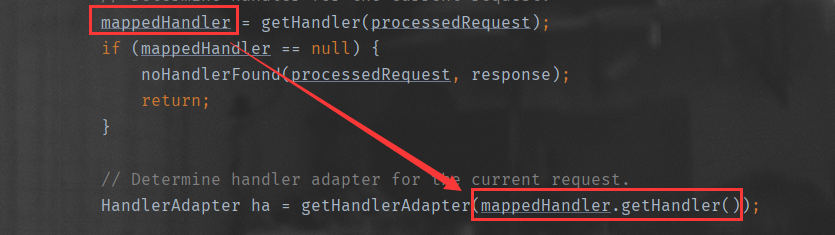
gerHandler
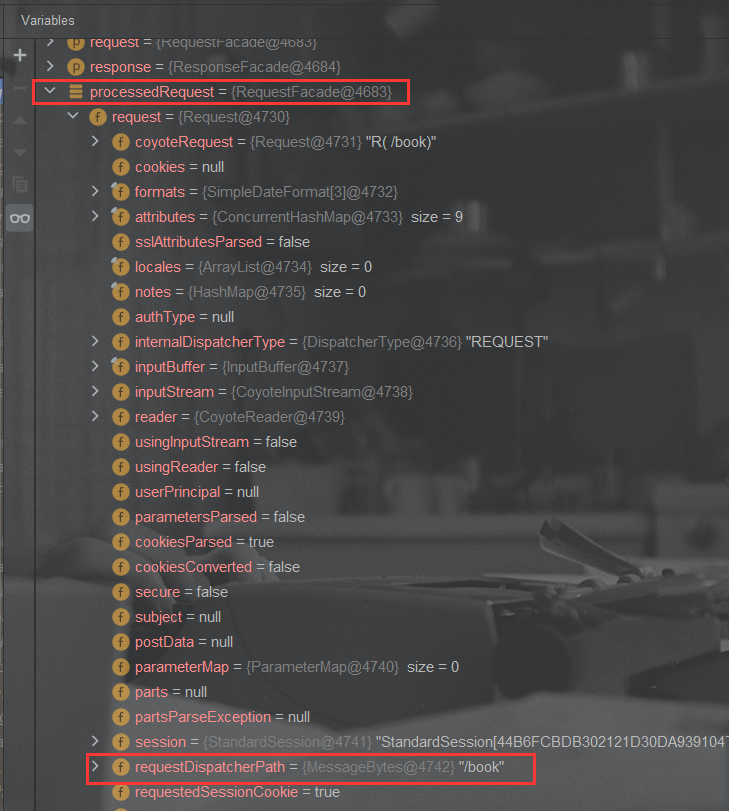
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
processedRequest得到请求地址
HandlerMapping:handlerMap参数保存了请求对应的处理器(IOC启动扫描时保存)
遍历HandlerMapping,判断processedRequest中的请求由哪个Handler处理。
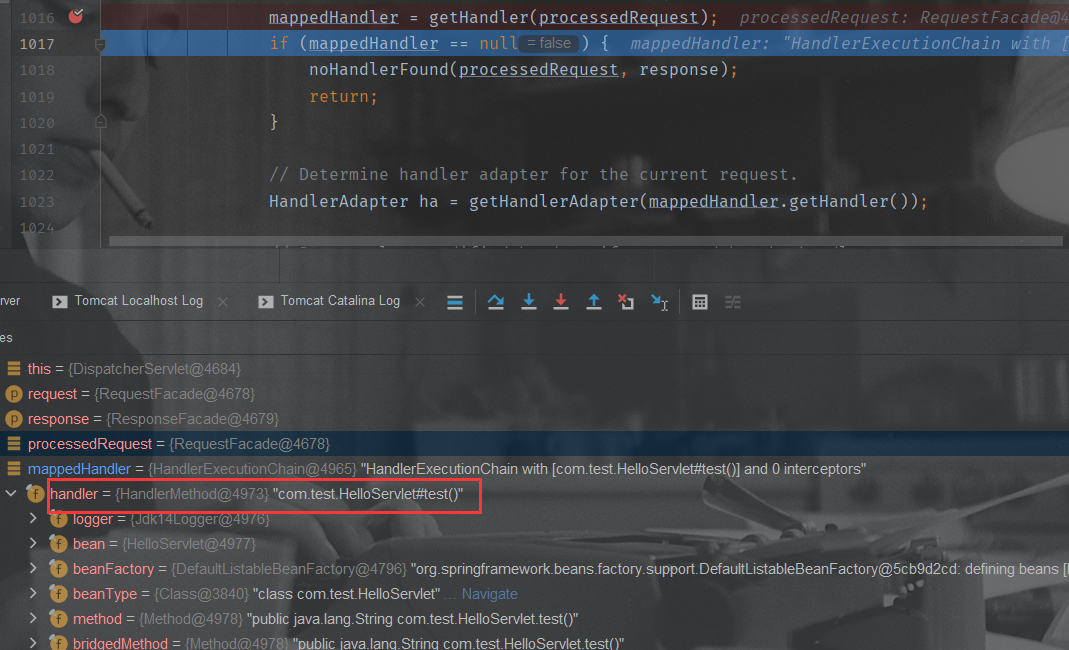
getHandlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler())
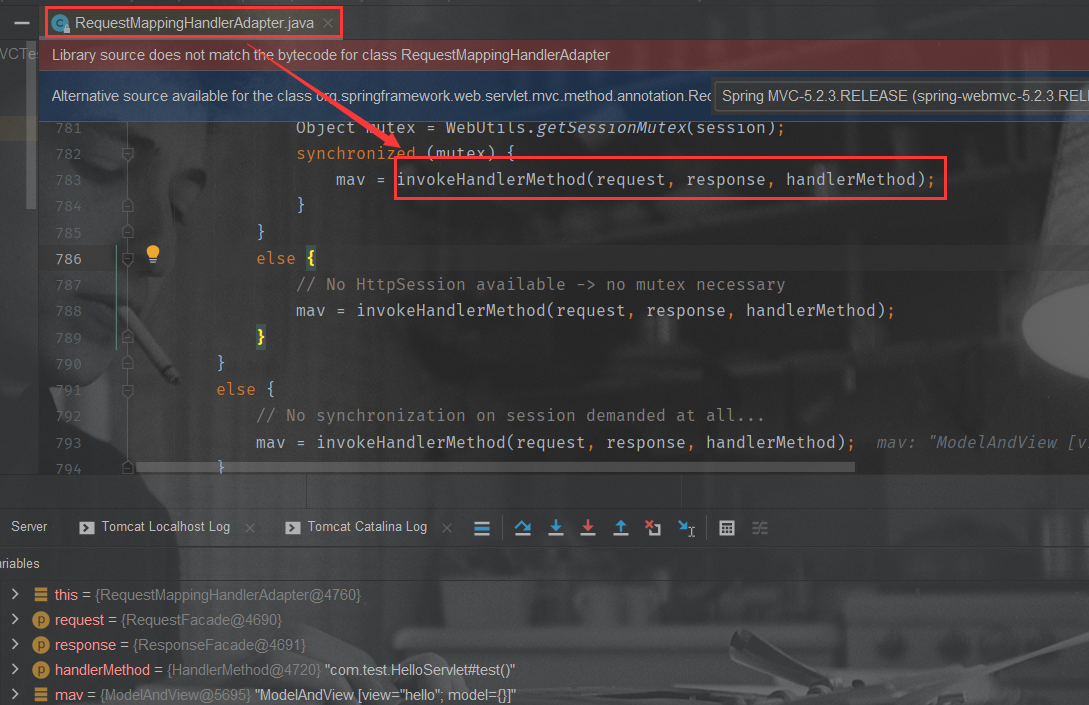
ModelAndView
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
得到handler对应handlerAdapter后通过反射执行目标方法,返回ModelAndView对象
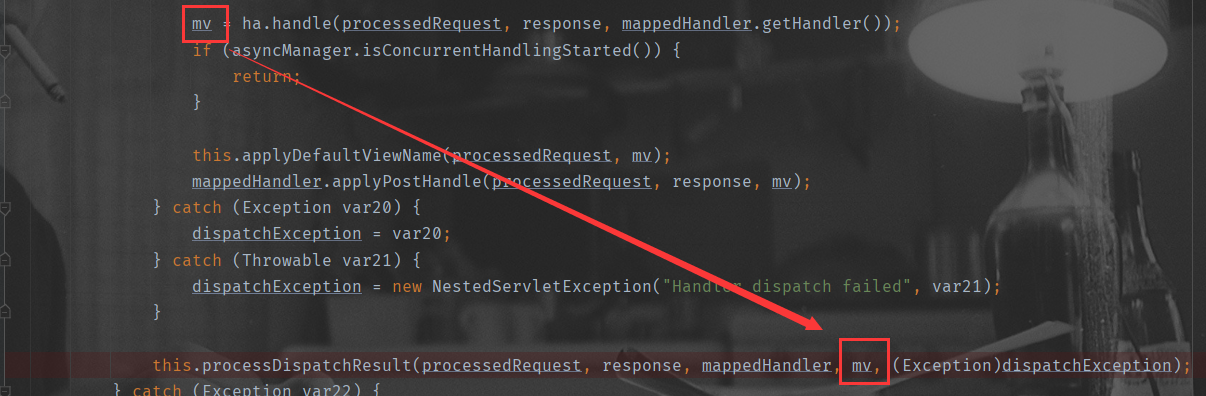
processDispatchResult
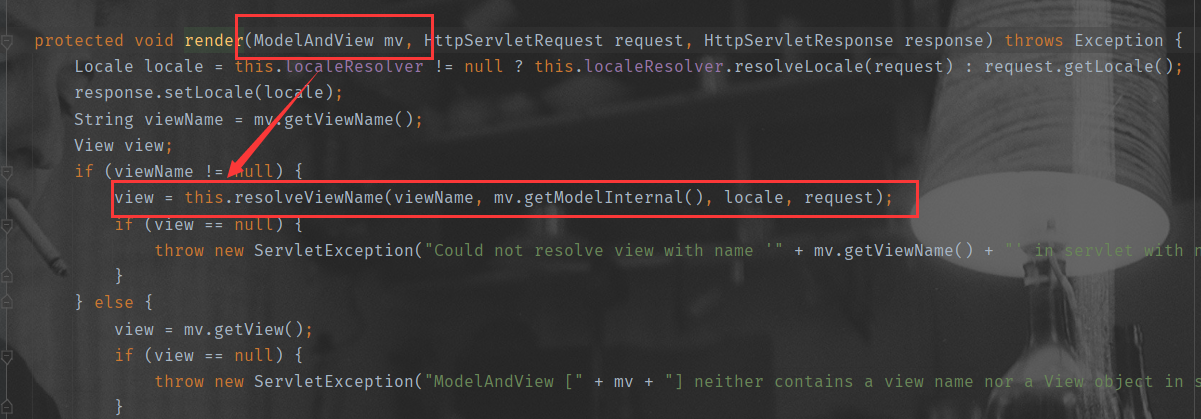
得到ModelAndView后,processDispatchResult()根据ModelAndView封装的信息转发到对应的页面
源码
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}

