Go语言之Go 语言条件语句
Go 语言条件语句
条件语句需要开发者通过指定一个或多个条件,并通过测试条件是否为 true 来决定是否执行指定语句,并在条件为 false 的情况在执行另外的语句。
下图展示了程序语言中条件语句的结构:
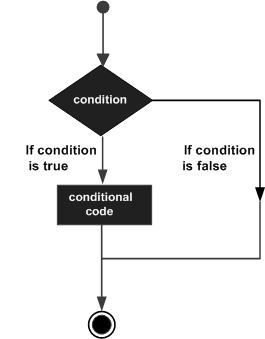
| 语句 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| if 语句 | if 语句 由一个布尔表达式后紧跟一个或多个语句组成。 |
| if...else 语句 | if 语句 后可以使用可选的 else 语句, else 语句中的表达式在布尔表达式为 false 时执行。 |
| if 嵌套语句 | 你可以在 if 或 else if 语句中嵌入一个或多个 if 或 else if 语句。 |
| switch 语句 | switch 语句用于基于不同条件执行不同动作。 |
| select 语句 | select 语句类似于 switch 语句,但是select会随机执行一个可运行的case。如果没有case可运行,它将阻塞,直到有case可运行。 |
if ,if ...else 语句和python或者C语言类似
重点讲解:
switch 语句用于基于不同条件执行不同动作,每一个 case 分支都是唯一的,从上至下逐一测试,直到匹配为止。
switch 语句执行的过程从上至下,直到找到匹配项,匹配项后面也不需要再加 break。
switch 默认情况下 case 最后自带 break 语句,匹配成功后就不会执行其他 case,如果我们需要执行后面的 case,可以使用 fallthrough 。
语法
Go 编程语言中 switch 语句的语法如下:
switch var1 {
case val1:
...
case val2:
...
default:
...
}
变量 var1 可以是任何类型,而 val1 和 val2 则可以是同类型的任意值。类型不被局限于常量或整数,但必须是相同的类型;或者最终结果为相同类型的表达式。
您可以同时测试多个可能符合条件的值,使用逗号分割它们,例如:case val1, val2, val3。
流程图:

func tyepe() {
// switch语句练习
grader := "B"
marks := 40
switch marks {
case 90:
grader = "A"
case 80:
grader = "B"
case 50, 60, 70:
grader = "C"
default:
grader = "D"
}
switch {
case grader == "A":
fmt.Println("优秀")
case grader == "B":
fmt.Println("良好")
case grader == "C":
fmt.Println("及格")
case grader == "D":
fmt.Println("不及格")
}
}
func main() {
// traversalstring()
// changeStrings()
tyepe()
}
Type Switch
switch 语句还可以被用于 type-switch 来判断某个 interface 变量中实际存储的变量类型。
Type Switch 语法格式如下:
switch x.(type){
case type:
statement(s);
case type:
statement(s);
/* 你可以定义任意个数的case */
default: /* 可选 */
statement(s);
}
func test() {
var x interface{}
switch i := x.(type) {
case nil:
fmt.Println("x的类型是 %T", i)
case int:
fmt.Println("x的类型是 %T", i)
case float32:
fmt.Println("x的类型是 %T", i)
case bool, string:
fmt.Println("x的类型是 %T", i)
default:
fmt.Println("未知类型")
}
}
func main() {
// traversalstring()
// changeStrings()
// tyepe()
test()
}
以上代码执行结果为:
x 的类型 :<nil>
fallthrough
使用 fallthrough 会强制执行后面的 case 语句,fallthrough 不会判断下一条 case 的表达式结果是否为 true。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
switch {
case false:
fmt.Println("1、case 条件语句为 false")
fallthrough
case true:
fmt.Println("2、case 条件语句为 true")
fallthrough
case false:
fmt.Println("3、case 条件语句为 false")
fallthrough
case true:
fmt.Println("4、case 条件语句为 true")
case false:
fmt.Println("5、case 条件语句为 false")
fallthrough
default:
fmt.Println("6、默认 case")
}
}
以上代码执行结果为:
2、case 条件语句为 true
3、case 条件语句为 false
4、case 条件语句为 true
从以上代码输出的结果可以看出:switch 从第一个判断表达式为 true 的 case 开始执行,如果 case 带有 fallthrough,程序会继续执行下一条 case,且它不会去判断下一个 case 的表达式是否为 true。
select语句
select 是 Go 中的一个控制结构,类似于用于通信的 switch 语句。每个 case 必须是一个通信操作,要么是发送要么是接收。
select 随机执行一个可运行的 case。如果没有 case 可运行,它将阻塞,直到有 case 可运行。一个默认的子句应该总是可运行的。
语法:
Go 编程语言中 select 语句的语法如下:
select {
case communication clause :
statement(s);
case communication clause :
statement(s);
/* 你可以定义任意数量的 case */
default : /* 可选 */
statement(s);
}
以下描述了 select 语句的语法:
-
每个 case 都必须是一个通信
-
所有 channel 表达式都会被求值
-
所有被发送的表达式都会被求值
-
如果任意某个通信可以进行,它就执行,其他被忽略。
-
如果有多个 case 都可以运行,Select 会随机公平地选出一个执行。其他不会执行。
否则:
- 如果有 default 子句,则执行该语句。
- 如果没有 default 子句,select 将阻塞,直到某个通信可以运行;Go 不会重新对 channel 或值进行求值。
实例
select 语句应用演示:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var c1, c2, c3 chan int
var i1, i2 int
select {
case i1 = <-c1:
fmt.Printf("received ", i1, " from c1\n")
case c2 <- i2:
fmt.Printf("sent ", i2, " to c2\n")
case i3, ok := (<-c3): // same as: i3, ok := <-c3
if ok {
fmt.Printf("received ", i3, " from c3\n")
} else {
fmt.Printf("c3 is closed\n")
}
default:
fmt.Printf("no communication\n")
}
}













 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号