字符串的定义方式;输出和计算长度时的细节
c语言中几种字符串的定义方式:
第1种:
char a[5]="hello";
第2种:
char a[]="hello";
第3种:
char* a="hello";
第4种:
char a[10];
gets(a);
第5种:
char* a[5]={"hello",
"nihao",
"good",
"ok",
"bye"};
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 int main(){ 4 char harder[] = "hello bit."; 5 printf("%s\n",harder); 6 printf("%d\n", sizeof(harder)); 7 return 0; }
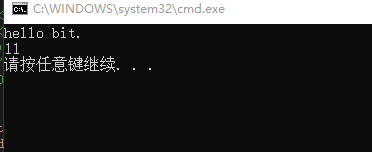
结论,在vs编译环境下:
用sizeof计算数组长度,包括 \0(\0为结束符)
例如,“ABCD”的字符数组长度为4,但是存储它的字符数组元素个数,应该为5。
即至少是char s[5](需要写成char s[5],但用strlen(s)计算时长度为4),用sizeof计算包含\0,长度为5.
sizeof 计算 数组长度
strlen计算 字符串长度
另外注意,在char s[],在s[]内尽量不要填数字,否则当用sizeof(char)时候,长度不按照实际长度而是[]内你填的长度输出。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 char str[] = {1,3,5}; 7 printf("%d\n", sizeof(str)); 8 system("pause"); 9 return 0; 10 }
用sizeof,输出结果长度为3
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 char str[6] = {1,3,5}; 7 printf("%d\n", sizeof(str)); 8 system("pause"); 9 return 0; 10 }
用sizeof,输出结果长度为6

