ccpc威海 D-Sternhalma(状压DP,记忆化搜索)
题意
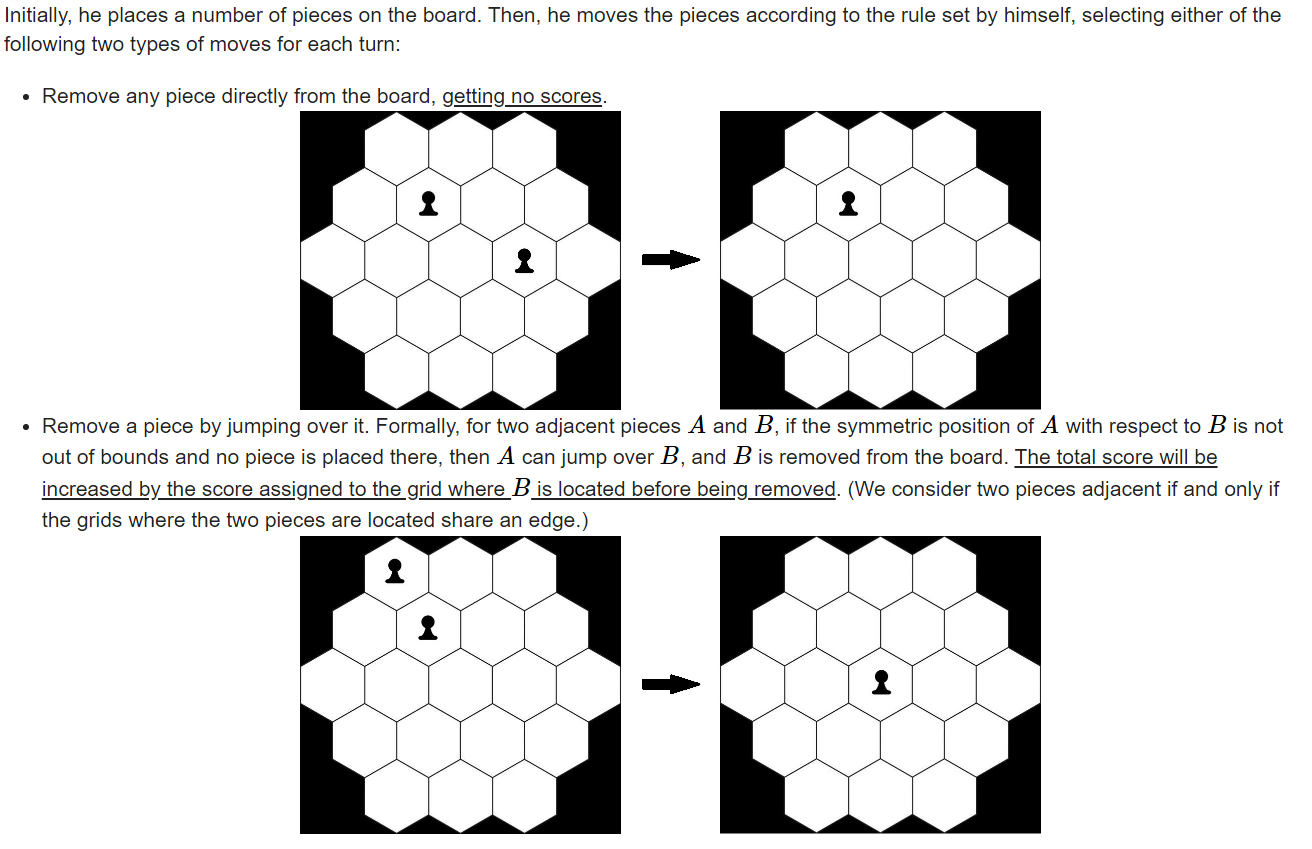
- 给定六边形棋盘每个格子的分数,询问若干初始的棋子摆放
方式,问按照规则移除棋子最多得多少分。 - 移除棋子有两种方式,一种是直接移除一个棋子,不得分;
另一种是用一个棋子跳过其相邻棋子,移除被跳过的棋子并
且得分增加被移除棋子所在的格子的分数。
原题链接
解题思路
棋盘上的每个位置只有放与不放两种选择,故最终一共有种状态。初态已知,那么我们可以用DP推出后面的所有状态,也可以用记忆化搜索。
代码细节较多,容易出错。
DP
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = (1 << 19) + 1;
//方向矩阵
const int d1[6][2] = {{0, 2}, {-1, 1}, {-1, -1}, {0, -2}, {1, -1}, {1, 1}};
const int d2[6][2] = {{0, 4}, {-2, 2}, {-2, -2}, {0, -4}, {2, -2}, {2, 2}};
//为每个点给定二维坐标
const int coor[19][2] =
{
{1, 3}, {1, 5}, {1, 7},
{2 ,2}, {2 ,4}, {2 ,6}, {2, 8},
{3, 1}, {3, 3}, {3, 5}, {3, 7}, {3, 9},
{4, 2}, {4 ,4}, {4 ,6}, {4 ,8},
{5, 3}, {5 ,5}, {5 ,7}
};
int s[6][10];//点的权值
int id[8][15];//每个区域的编号
int f[N];
//将字符串转化为十进制的状态
int trans(string &mp)
{
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 19; ++i)
{
if (mp[i] == '#')
ans += (1 << i);
}
return ans;
}
int count(int x)
{
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 19; ++i)
{
if (x & 1 << i)
++ans;
}
return ans;
}
vector<int> b;
void ini()
{
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << 19); ++i)
b.push_back(i);
//排序,从小状态推大状态
sort(b.begin(), b.end(), [](int a, int b)
{
return count(a) < count(b);
});
for (int i = 1; i < (1 << 19); ++i)
{
int state = b[i];
for (int j = 0; j < 19; ++j)
{
if (state & (1 << j))
{
int x = coor[j][0], y = coor[j][1];
f[state] = max(f[state], f[state - (1 << j)]);
for (int k = 0; k < 6; ++k)
{
int x1 = x + d1[k][0], y1 = y + d1[k][1];
int x2 = x + d2[k][0], y2 = y + d2[k][1];
if (x1 < 0 || x2 < 0 || y1 < 0 || y2 < 0)
continue;
if (id[x1][y1] == -1 || id[x2][y2] == -1)
continue;
//注意&与==的优先级
if ((state & 1 << id[x1][y1]) == 0 || (state & 1 << id[x2][y2]) == 1)
continue;
f[state] = max(f[state], f[state ^ (1 << id[x][y]) ^ (1 << id[x1][y1]) ^ (1 << id[x2][y2])] + s[x1][y1]);
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
memset(id, -1, sizeof(id));
memset(f, -0x3f, sizeof(f));
f[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 19; ++i)
{
int x = coor[i][0], y = coor[i][1];
id[x][y] = i;
cin >> s[x][y];
}
ini();
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--)
{
string mp, t;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
cin >> t, mp += t;
cout << f[trans(mp)] << endl;;
}
}
记忆化搜索
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = (1 << 19) + 1;
const int d1[6][2] = {{0, 2}, {-1, 1}, {-1, -1}, {0, -2}, {1, -1}, {1, 1}};
const int d2[6][2] = {{0, 4}, {-2, 2}, {-2, -2}, {0, -4}, {2, -2}, {2, 2}};
const int coor[19][2] =
{
{1, 3}, {1, 5}, {1, 7},
{2 ,2}, {2 ,4}, {2 ,6}, {2, 8},
{3, 1}, {3, 3}, {3, 5}, {3, 7}, {3, 9},
{4, 2}, {4 ,4}, {4 ,6}, {4 ,8},
{5, 3}, {5 ,5}, {5 ,7}
};
int s[6][10];//点的权值
int id[8][15];//每个区域的编号
int f[N];
int trans(string &mp)
{
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 19; ++i)
{
if (mp[i] == '#')
ans += (1 << i);
}
return ans;
}
int dfs(int state)
{
if (f[state] != int(0xc1c1c1c1))
return f[state];
int &val = f[state];
int grid[8][15] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < 19; ++i)
{
if (state & 1 << i)
{
int x = coor[i][0], y = coor[i][1];
int n_state = state & ~(1 << i);
grid[x][y] = 1;
val = max(val, dfs(n_state));
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 19; ++i)
{
if (state & 1 << i)
{
int x = coor[i][0], y = coor[i][1];
for (int j = 0; j < 6; ++j)
{
int x1 = x + d1[j][0], y1 = y + d1[j][1];
int x2 = x + d2[j][0], y2 = y + d2[j][1];
if (x1 < 0 || x2 < 0 || y1 < 0 || y2 < 0)
continue;
if (!~id[x1][y1] || !~id[x2][y2])
continue;
if (!grid[x1][y1] || grid[x2][y2])
continue;
int n_state = state;
n_state &= ~(1 << i);
n_state &= ~(1 << id[x1][y1]);
n_state |= (1 << id[x2][y2]);
val = max(val, dfs(n_state) + s[x1][y1]);
}
}
}
return val;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
memset(id, -1, sizeof(id));
memset(f, -0x3f, sizeof(f));
f[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 19; ++i)
{
int x = coor[i][0], y = coor[i][1];
id[x][y] = i;
cin >> s[x][y];
}
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--)
{
string mp, t;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
cin >> t, mp += t;
cout << dfs(trans(mp)) << endl;;
}
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
· 25岁的心里话