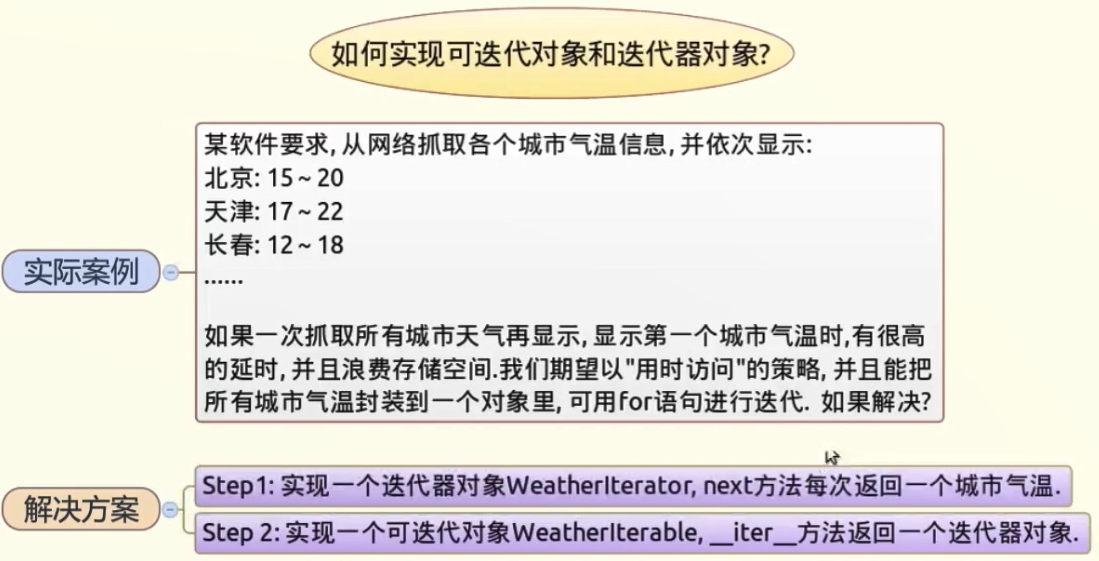
实现可迭代对象和迭代器对象去查询天气
方式一:一个个的用函数实现
#_*_ encoding: utf-8 _*_ @author: ty hery 2019/1/12
import requests
def getWeather(city):
r = requests.get(u'http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city='+city)
data = r.json()['data']['forecast'][0]
print( '%s: %s, %s' %(city,data['low'],data['high']))
getWeather('北京')
getWeather('长春')
方式二:构造一个可迭代对象和迭代器(Iterator)对象
In [7]: from collections import Iterable , Iterator
In [8]: Iterable.abstractmethods
Out[8]: frozenset({'iter'})
In [9]: Iterator.abstractmethods
Out[9]: frozenset({'next'})
from collections import Iterable, Iterator
class WeatherIterator(Iterator):
def init(self, cities):
self.cities = cities
self.index = 0
def getWeather(self, city):
r = requests.get(u'http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=' + city)
print(r)
data = r.json()['data']['forecast'][0]
return '%s:%s ,%s' % (city, data['low'], data['high'])
# data = r.json() # ['data']['forecast'][0]
# return data
def __next__(self):
if self.index == len(self.cities):
raise StopIteration
city = self.cities[self.index]
self.index += 1
return self.getWeather(city)
class WeatherIterable(Iterable):
def init(self, cities):
self.cities = cities
def __iter__(self):
return WeatherIterator(self.cities)
for x in WeatherIterable([u'北京',u'上海', u'广州',u'长春']):
print(x)
输出:
<Response [200]>
北京:低温 -6℃ ,高温 3℃
<Response [200]>
上海:低温 1℃ ,高温 8℃
<Response [200]>
广州:低温 9℃ ,高温 14℃
<Response [200]>
长春:低温 -18℃ ,高温 -12℃
写入自己的博客中才能记得长久


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号