Linux samba服务器配置
samba服务器配置
配置文件
- /etc/samba/smb.conf
samba的主要配置文件,可设置全局参数和共享目录的参数 - /etc/samba/lmhosts
通过hostname来访问samba: - /etc/samba/smbusers
由于windows和linux里的管理员和访客账号名称不一致,可使用此配置文件来设置一个映射,比如administrator映射成root: - /etc/sysconfig/samba
配置smbd,nmbd启动时带的参数 - /var/lib/samba/private/{passdb.tdb, secrets.tdb}
管理samba的用户账号/密码时,会用到的数据库档案
可用命令
smbd, nmbd:smbd提供文件和打印共享服务器,nmbd提供NetBIOS名称服务和浏览支持,帮助客户端定位服务器,处理所有基于UDP的协议
tdbdump, tdbtool:samba使用了tdb数据库,可以使用tdb工具来查看数据库内容
smbstatus:查看samba的状态
smbpasswd, pdbedit:服务器功能,用于管理samba的用户账号和密码,早期是使用smbpasswd命令,后来因为使用了tdb数据库,所以推荐使用pdbedit命令来管理用户数据
mount.cifs:用来挂载分享目录
smbclient:samba客户端
nmblookup:查找NetBIOS name
smbtree:未知,可能是用来查找网络邻居的吧
testparm:验证smb.conf文件的内容是否合法
工作模式
samba服务器有5种工作模式,分别为:
- share,用户对samba服务器的访问不需要身份验证,允许匿名访问,用户的访问权限仅由相应用户对共享文件的访问权限决定
- user,使用用户名和密码访问samba服务器,
- server,使用另外一台服务器专门用来做身份验证,samba服务只提供文件和打印机共享服务
- domain,域模式,不常用
- ads,最新的一种工作模式,也不太常用
通过设置security选项即可设置samba的工作模式:security = share
配置项
全局
全局必须的配置项有:workgroup,netbios name,serverstirng,log file,max log size,security,passdb backend,load printer
workgroup = rhel_6.3
server string = Samba Server Version %v
netbios name = rhel
# logs split per machine
log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
# max 500KB per log file, then rotate
max log size = 500
security = user
passdb backend = tdbsam
load printers = no
共享目录
不需要密码的共享
需要将全局参数中的security设置成share(暂不清楚,在user工作模式下通过设置guest ok好像也可以,需要验证)
最小化配置:
[test]
comment = test
path = /tmp
read only = no
guest ok = yes
create mask = 644
其中:
read only默认为yes,表示只允许读,不允许写,所以需要修改
guest ok默认是no,表示不允许匿名访问
create mask默认是744,导致客户端创建的文件都是可执行文件,所以需要修改
注意:
writable和writeable是同义词
writeable和read only是反义同义词
writeable默认为no
read only默认为yes
完整配置需要配置available和browseable,不过这两个默认都是yes
用户名/密码方式的共享
需要将全局参数中的security设置成user
[win]
comment = win
path = /home/win
read only = yes
create mask = 644
valid users = win
这种方式首先需要使用root权限添加一个账户,然后使用smbpasswd -a xxx在samba数据库添加此用户的samba密码
输入smbpasswd -a xxx 时会直接让用户设置这个账户的samba密码
这个用户信息保存在tdb数据库里
修改密码:root权限下输入smbpasswd user_name即可修改user_name的samba密码
配置文件验证
使用testparm可以验证smb.conf文件的内容是否合法
[RHEL@localhost ~]$ testparm
Load smb config files from /etc/samba/smb.conf
rlimit_max: increasing rlimit_max (1024) to minimum Windows limit (16384)
Processing section "[test]"
Loaded services file OK.
Server role: ROLE_STANDALONE
Press enter to see a dump of your service definitions
[global]
workgroup = TEST
netbios name = TESTNET
server string = Samba Server Version %v
security = SHARE
log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
max log size = 50
load printers = No
[test]
comment = test
path = /tmp
read only = No
guest ok = Yes
客户端本地验证samba服务器共享的内容
smbclient -L //127.0.0.1
当samba服务器的工作模式被设置成share模式时,需要在上面的命令后面加-N选项表示不请求密码
[RHEL@localhost ~]$ smbclient -L //127.0.0.1 -N
Domain=[TEST] OS=[Unix] Server=[Samba 3.5.10-125.el6]
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
test Disk test
IPC$ IPC IPC Service (Samba Server Version 3.5.10-125.el6)
Domain=[TEST] OS=[Unix] Server=[Samba 3.5.10-125.el6]
Server Comment
--------- -------
TESTNET Samba Server Version 3.5.10-125.el6
Workgroup Master
--------- -------
TEST TESTNET
查看samba数据库里的用户信息
pdbedit -L
防火墙和SELinux
关闭防火墙:/etc/init.d/iptables stop
设置SELinux为宽容模式:setenforce 0
获取SELinux的状态: getenforce
排障
排障总共4种方式,
- nmap扫描是否有139和445端口被监听
- 映射网络驱动器
- net use命令查看当前有哪些连接
- 重启(对于修改了密码后登录不上非常有效)
常见问题场景:
1、windows访问时提示找不到网络路径,并带有错误码0x80070035,表示samba服务器未监听139和445端口(通过nmap可以看到)

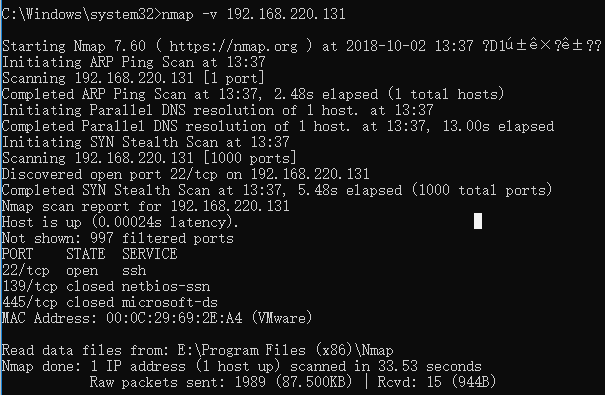
2、直接在windows的文件管理器里输入网络路径后提示"找不到xxxx,请检查拼写并重试",且无错误码,
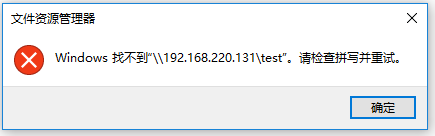
通过映射网络驱动器发现windows给出了详细的信息:SMB1协议不安全,需要使用SMB2以上的安全的协议,
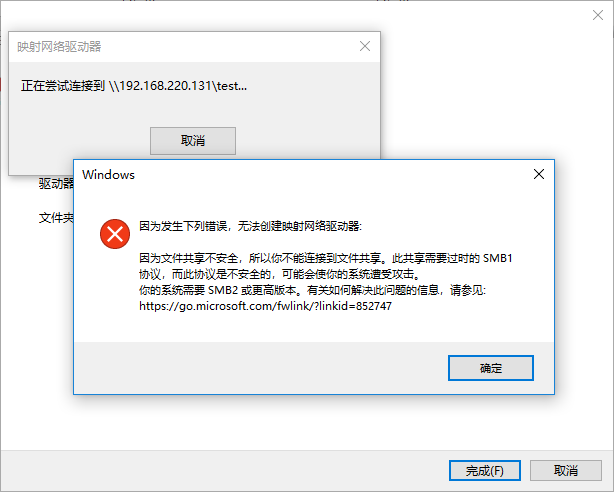
这种情况一般出现在win 10上,解决办法有两个,一是升级samba服务器,二是给win 10添加SMB1支持(在程序与功能里面可以启用)
3、windows访问时提示无权限

一般来说应该是和SELinux有关
解决办法也有两个:
- 如果共享的是家目录,使用setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs on命令即可,
如果是添加的目录,使用命令chcon -t samba_share_t /path给这个目录添加samba_share_t标签即可 - 关闭SELinux
原文:
#---------------
# SELINUX NOTES:
#
# If you want to use the useradd/groupadd family of binaries please run:
# setsebool -P samba_domain_controller on
#
# If you want to share home directories via samba please run:
# setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs on
#
# If you create a new directory you want to share you should mark it as
# "samba_share_t" so that selinux will let you write into it.
# Make sure not to do that on system directories as they may already have
# been marked with othe SELinux labels.
#
# Use ls -ldZ /path to see which context a directory has
#
# Set labels only on directories you created!
# To set a label use the following: chcon -t samba_share_t /path
#
# If you need to share a system created directory you can use one of the
# following (read-only/read-write):
# setsebool -P samba_export_all_ro on
# or
# setsebool -P samba_export_all_rw on
#
# If you want to run scripts (preexec/root prexec/print command/...) please
# put them into the /var/lib/samba/scripts directory so that smbd will be
# allowed to run them.
# Make sure you COPY them and not MOVE them so that the right SELinux context
# is applied, to check all is ok use restorecon -R -v /var/lib/samba/scripts
#
#--------------
版本
3.5.10里使用的是SMB1协议,被证明有漏洞,不推荐使用。
windows客户端访问符号链接失败
在/etc/samba/smb.conf里添加如下的内容即可正常
[global]
unix extensions = no
[share]
follow symlinks = yes
wide links = yes
其中:
- unix extensions是为了在samba里支持符号链接,硬链接等特性,主要给UNIX下的samba客户端使用,对windows客户端没有任何用处,所以在windows客户端访问时需要关掉这个选项,这个是选项是默认启用的。
- follow symlinks,这个参数控制samba服务器是否会跟随特定samba共享目录(非global选项)里的符号链接,默认是启用的。
- wide links,这个参数控制是否能够创建一个链接指向samba服务器未共享的目录(samba服务器默认允许创建指向已共享的目录的链接),可能会导致一个安全问题,所以这个参数默认不启用
man 5 smb.conf中的解释如下
unix extensions (G)
This boolean parameter controls whether Samba implements the CIFS UNIX
extensions, as defined by HP. These extensions enable Samba to better
serve UNIX CIFS clients by supporting features such as symbolic links,
hard links, etc... These extensions require a similarly enabled client,
and are of no current use to Windows clients.
Note if this parameter is turned on, the wide links parameter will
automatically be disabled.
Default: unix extensions = yes
follow symlinks (S)
This parameter allows the Samba administrator to stop smbd(8) from
following symbolic links in a particular share. Setting this parameter to
no prevents any file or directory that is a symbolic link from being
followed (the user will get an error). This option is very useful to stop
users from adding a symbolic link to /etc/passwd in their home directory
for instance. However it will slow filename lookups down slightly.
This option is enabled (i.e. smbd will follow symbolic links) by default.
Default: follow symlinks = yes
wide links (S)
This parameter controls whether or not links in the UNIX file system may
be followed by the server. Links that point to areas within the directory
tree exported by the server are always allowed; this parameter controls
access only to areas that are outside the directory tree being exported.
Note: Turning this parameter on when UNIX extensions are enabled will
allow UNIX clients to create symbolic links on the share that can point to
files or directories outside restricted path exported by the share
definition. This can cause access to areas outside of the share. Due to
this problem, this parameter will be automatically disabled (with a
message in the log file) if the unix extensions option is on.
Default: wide links = no
如何判断smb.conf里的某些字段的默认选项
比如follow symlinks字段默认是yes, 则当在smb.conf里配置了这个字段等于yes时在testparm里不会显示这个字段,如果配置成no则会显示



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号