优先队列的多向归并-java
多向归并是将多个分类的输入流合并为一个分类的输出流。
Input:
m1.txt:A B C F G I I Z
m2.txt:B D H P Q Q
m3.txt:A B E F J N
Output: A A B B B C D E F F G H I I J N P Q Q Z
分析:
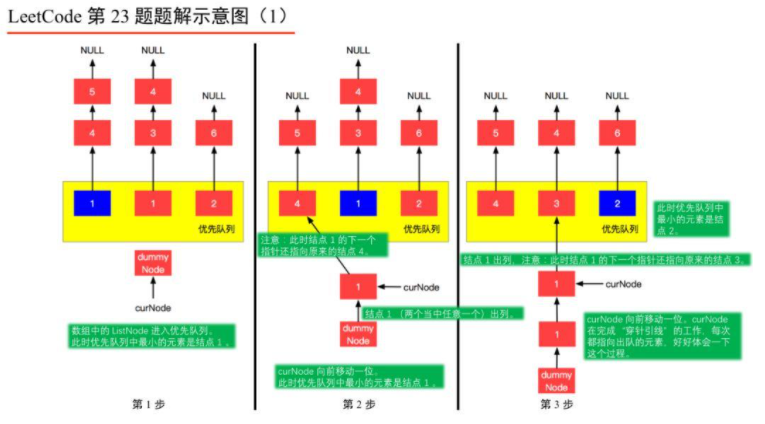
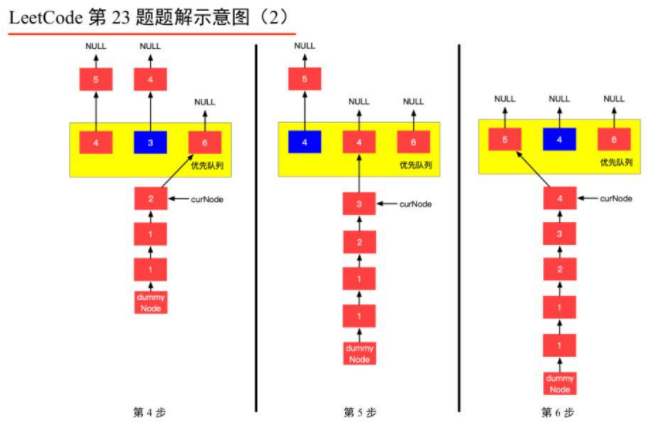
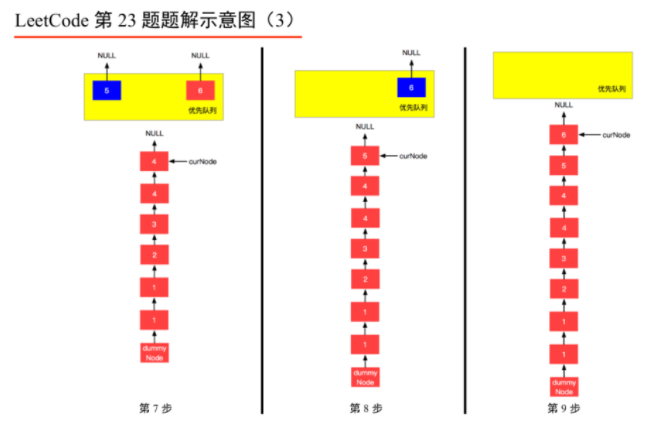
1、由于是 𝑘 个排序链表,那么这 𝑘 个排序的链表头结点中 val 最小的结点就是合并以后的链表中最小的结点;
2、最小结点所在的链表的头结点就要更新了,更新成最小结点的下一个结点(如果有的话),此时还是这 𝑘 个链表,这 𝑘k 个排序的链表头结点中 val 最小的结点就是合并以后的链表中第 2 小的结点。
我们每一次都从这 𝑘 个排序的链表头结点中拿出 val 最小的结点“穿针引线”成新的链表,这个链表就是题目要求的“合并后的排序链表”。
《算法》第四版提供的API如下所示:

实现代码如下:
public class Multiway { // This class should not be instantiated. private Multiway() { } // 将排序后的输入流合并在一起,并将排序后的结果写入标准输出 private static void merge(In[] streams) { int n = streams.length; IndexMinPQ<String> pq = new IndexMinPQ<String>(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) if (!streams[i].isEmpty()) pq.insert(i, streams[i].readString()); // 提取并打印最小值,然后从其流中读取下一个。 while (!pq.isEmpty()) { StdOut.print(pq.minKey() + " "); int i = pq.delMin(); if (!streams[i].isEmpty()) pq.insert(i, streams[i].readString()); } StdOut.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { int n = args.length; In[] streams = new In[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) streams[i] = new In(args[i]); merge(streams); } }
class Solution { public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) { int len = lists.length; if (len == 0) { return null; } PriorityQueue<ListNode> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(len, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a.val)); ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1); ListNode curNode = dummyNode; for (ListNode list : lists) { if (list != null) { // 这一步很关键,不能也没有必要将空对象添加到优先队列中 priorityQueue.add(list); } } while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) { // 优先队列非空才能出队 ListNode node = priorityQueue.poll(); // 当前节点的 next 指针指向出队元素 curNode.next = node; // 当前指针向前移动一个元素,指向了刚刚出队的那个元素 curNode = curNode.next; if (curNode.next != null) { // 只有非空节点才能加入到优先队列中 priorityQueue.add(curNode.next); } } return dummyNode.next; } }





