MySQL和mybatis查询相关
0.mybatis的xml文件头
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="me.gacl.dao.UserMapper" >
</mapper>
1.mybatis 中 foreach collection的用法
<select id="dynamicForeachTest" parameterType="java.util.List" resultType="Blog"> select * from t_blog where id in <foreach collection="list" index="index" item="item" open="(" separator="," close=")"> #{item} </foreach> </select>
2.mybatis批量插入更新
方法一:
<update id="batchUpdate" parameterType="java.util.List">
<foreach separator=";" index="index" item="item" collection="list" close="" open="">
update sys_group set level = #{item.level,jdbcType=INTEGER}
where group_id = #{item.groupId,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</foreach>
</update>
方法二:
<update id="batchUpdate1" parameterType="java.util.List"> update sys_group set level = null where level in <foreach separator="," index="index" item="item" collection="list" close=")" open="("> #{item} </foreach> </update>
3.mybatis映射
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="me.gacl.domain.User" >
<id column="user_id" property="userId" jdbcType="CHAR" />
<result column="user_name" property="userName" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="user_birthday" property="userBirthday" jdbcType="DATE" />
<result column="user_salary" property="userSalary" jdbcType="DOUBLE" />
</resultMap>
<sql id="Base_Column_List" >
user_id, user_name, user_birthday, user_salary
</sql>
4.mybatis查询select
<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="java.lang.String" > select <include refid="Base_Column_List" /> from t_user where user_id = #{userId,jdbcType=CHAR} </select>
5.mybatis删除delete
<delete id="deleteByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.String" > delete from t_user where user_id = #{userId,jdbcType=CHAR} </delete>
6.mybatis插入insert
一:
<insert id="insert" parameterType="me.gacl.domain.User" > insert into t_user (user_id, user_name, user_birthday, user_salary) values (#{userId,jdbcType=CHAR}, #{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{userBirthday,jdbcType=DATE}, #{userSalary,jdbcType=DOUBLE}) </insert>
二:
<insert id="insertSelective" parameterType="me.gacl.domain.User" > insert into t_user <trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides="," > <if test="userId != null" > user_id, </if> <if test="userName != null" > user_name, </if> <if test="userBirthday != null" > user_birthday, </if> <if test="userSalary != null" > user_salary, </if> </trim> <trim prefix="values (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides="," > <if test="userId != null" > #{userId,jdbcType=CHAR}, </if> <if test="userName != null" > #{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, </if> <if test="userBirthday != null" > #{userBirthday,jdbcType=DATE}, </if> <if test="userSalary != null" > #{userSalary,jdbcType=DOUBLE}, </if> </trim> </insert>
7.mybatis更新update
一:
<update id="updateByPrimaryKey" parameterType="me.gacl.domain.User" > update t_user set user_name = #{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, user_birthday = #{userBirthday,jdbcType=DATE}, user_salary = #{userSalary,jdbcType=DOUBLE} where user_id = #{userId,jdbcType=CHAR} </update>
二:
<update id="updateByPrimaryKeySelective" parameterType="me.gacl.domain.User" > update t_user <set > <if test="userName != null" > user_name = #{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, </if> <if test="userBirthday != null" > user_birthday = #{userBirthday,jdbcType=DATE}, </if> <if test="userSalary != null" > user_salary = #{userSalary,jdbcType=DOUBLE}, </if> </set> where user_id = #{userId,jdbcType=CHAR} </update>
8.mybatis插入返回主键
<insert id="insert" parameterType="me.gacl.domain.User" >
<selectKey resultType="java.lang.Integer" order="AFTER" keyProperty="id">
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()
</selectKey>
insert into t_user (user_id, user_name, user_birthday,
user_salary)
values (#{userId,jdbcType=CHAR}, #{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{userBirthday,jdbcType=DATE},
#{userSalary,jdbcType=DOUBLE})
</insert>
主键值封装到User对象中了。
int count = user.getId()获取的就是主键值。
9.避免重复插入 insert into select from where not exists
CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` int(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `age` int(10) DEFAULT NULL, `name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `role` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `email` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `phone` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=25 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO user ( `age`, `name`, `role`, `email` ) SELECT 22, 'admin', 'admin', 'admin' FROM user WHERE NOT EXISTS ( SELECT `name` FROM user WHERE `name` = 'admin' ) LIMIT 1;
10. 插入或更新 ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE
create table daily_hit_counter ( day date not null, slot tinyint unsigned not null, cnt int unsigned not null, primary key(day, slot) ) engine = InnoDB;
insert into daily_hit_counter (day, slot, cnt) values ('2017-11-19', 1, 1) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE cnt = cnt + 1;
insert into daily_hit_counter (day, slot, cnt) values ('2017-11-19', 2, 1) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE cnt = cnt + 1;
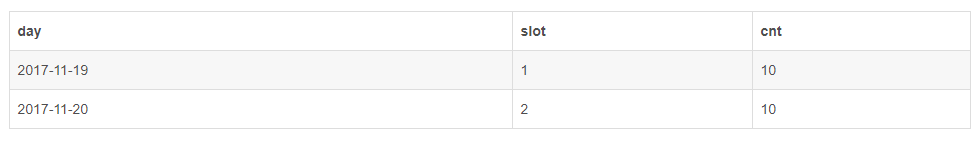
插入之前已有数据。
第一条执行更新,第二条执行插入。
11.INSERT INTO SELECT语句与SELECT INTO FROM语句区别
语句形式为:Insert into Table2(field1,field2,…) select value1,value2,… from Table1
或者:Insert into Table2 select * from Table1
注意:
(1)要求目标表Table2必须存在,并且字段field,field2…也必须存在
(2)注意Table2的主键约束,如果Table2有主键而且不为空,则 field1, field2…中必须包括主键
(3)注意语法,不要加values,和插入一条数据的sql混了,不要写成:
Insert into Table2(field1,field2,…) values (select value1,value2,… from Table1)
由于目标表Table2已经存在,所以我们除了插入源表Table1的字段外,还可以插入常量。
2.SELECT INTO FROM语句
语句形式为:SELECT vale1, value2 into Table2 from Table1
要求目标表Table2不存在,因为在插入时会自动创建表Table2,并将Table1中指定字段数据复制到Table2中。
注意:如果在sql/plus或者PL/SQL执行这条语句,会报”ORA-00905:缺失关键字”错误,原因是PL/Sql与T-SQL的区别。
T-SQL中该句正常,但PL/SQL中解释是:
select..into is part of PL/SQL language which means you have to use it inside a PL/SQL block. You can not use it in a SQL statement outside of PL/SQL.
即不能单独作为一条sql语句执行,一般在PL/SQL程序块(block)中使用。
如果想在PL/SQL中实现该功能,可使用Create table newTable as select * from …:
如: create table NewTable as select * from ATable;
NewTable 除了没有键,其他的和ATable一样
———SQL SELECT INTO语法介绍
SQL SELECT INTO 语句可用于创建表的备份复件。
SELECT INTO 语句
SELECT INTO 语句从一个表中选取数据,然后把数据插入另一个表中。
SELECT INTO 语句常用于创建表的备份复件或者用于对记录进行存档。
SQL SELECT INTO 语法
您可以把所有的列插入新表:
SELECT * INTO new_table_name [IN externaldatabase] FROM old_tablename
或者只把希望的列插入新表:
SELECT column_name(s) INTO new_table_name [IN externaldatabase] FROM old_tablename
SQL SELECT INTO 实例 - 制作备份复件
下面的例子会制作 “Persons” 表的备份复件:
SELECT * INTO Persons_backup FROM Persons
IN 子句可用于向另一个数据库中拷贝表:
SELECT * INTO Persons IN ‘Backup.mdb’ FROM Persons
如果我们希望拷贝某些域,可以在 SELECT 语句后列出这些域:
SELECT LastName,FirstName
INTO Persons_backup
FROM Persons
SQL SELECT INTO 实例 - 带有 WHERE 子句
我们也可以添加 WHERE 子句。
下面的例子通过从 “Persons” 表中提取居住在 “Beijing” 的人的信息,创建了一个带有两个列的名为 “Persons_backup” 的表:
SELECT LastName,Firstname INTO Persons_backup FROM Persons WHERE City=’Beijing’
SQL SELECT INTO 实例 - 被连接的表
从一个以上的表中选取数据也是可以做到的。
下面的例子会创建一个名为 “Persons_Order_Backup” 的新表,其中包含了从 Persons 和 Orders 两个表中取得的信息:
SELECT Persons.LastName,Orders.OrderNo
INTO Persons_Order_Backup
FROM Persons
INNER JOIN Orders
ON Persons.Id_P=Orders.Id_P
11来源于:这里





