线程池详解_3
1: 同步方法


1 package Thread; 2 3 /** 4 * author liulei 5 * data 6 * since 1.8 7 * version 1.0 8 * Description 方法锁 9 */ 10 //不安全的买票 11 public class Test17 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) {//出现同一张票被多次购买 13 BuyTicket t = new BuyTicket(); 14 new Thread(t,"a").start(); 15 new Thread(t,"b").start(); 16 new Thread(t,"c").start(); 17 } 18 } 19 class BuyTicket implements Runnable{ 20 private int ticketNum = 10; 21 Boolean flag =true;//外部停止方式 22 @Override 23 public void run() { 24 try { 25 Thread.sleep(10); 26 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 while (flag){ 30 try { 31 buy(); 32 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 33 e.printStackTrace(); 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 private synchronized void buy() throws InterruptedException {//每个对象对应一把锁,这把锁就是this, 38 if(ticketNum <= 0){ 39 flag = false; 40 return; 41 } 42 Thread.sleep(100); 43 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "拿到" + ticketNum--); 44 45 } 46 47 48 }
2: 同步块

1 package Thread; 2 3 /** 4 * author liulei 5 * data 6 * since 1.8 7 * version 1.0 8 * Description 同步块 9 */ 10 public class Test18 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 Account account = new Account(100,"结婚基金"); 13 Drawing you = new Drawing(account, 50, "你"); 14 Drawing girl = new Drawing(account, 100, "她"); 15 you.start(); 16 girl.start();//可能导致多取钱 17 } 18 } 19 class Account{ 20 int money;//余额 21 String name;//卡名 22 23 public Account(int money, String name) { 24 this.money = money; 25 this.name = name; 26 } 27 } 28 //银行,模拟取款 29 class Drawing extends Thread{ 30 Account account;//账户 31 //取了多少钱 32 int drawingMoney; 33 //现在手里有多少钱 34 int nowmoney; 35 36 37 public Drawing(Account account, int drawingMoney, String name) { 38 super(name); 39 this.account = account; 40 this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney; 41 42 } 43 44 @Override 45 public void run() {//使用代码块加锁还不是在放上上是因为this是Drawing,而真正需要锁的对象是account 46 synchronized (account){ 47 if(account.money-drawingMoney<0){ 48 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "钱不够取不了"); 49 return; 50 } 51 account.money -=drawingMoney; 52 nowmoney += drawingMoney; 53 System.out.println(account.name + "余额为" + account.money); 54 System.out.println(this.getName()+"手里的钱" + nowmoney); 55 } 56 try { 57 Thread.sleep(100); 58 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 59 e.printStackTrace(); 60 } 61 } 62 }
1 package Thread; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 /** 7 * author liulei 8 * data 5.25 9 * since 1.8 10 * version 1.0 11 * Description 不安全线程3 12 */ 13 public class Test19 { 14 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 15 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 16 for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { 17 synchronized (list){//对多个线程共同处理的list进行加锁 18 new Thread(()->{ 19 list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 20 }).start(); 21 } 22 } 23 Thread.sleep(100); 24 System.out.println(list.size());//总数可能少于10000 25 } 26 27 }
package Thread; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList; /** * author liulei * data * since 1.8 * version 1.0 * Description 测试JUC安全类型的集合 */ public class Test20 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>();//本身是对list的升级,已经保证了线程安全性,不需要加锁 for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { new Thread(()->{ list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); }).start(); } Thread.sleep(100); System.out.println(list.size());//总数可能少于10000 } }
深入理解使用synchronized同步方法和同步代码块的区别
同步方法对于当前对象this是要多个线程工作操作的对象时可以用同步方法,当然可以用代码块替代。否则要用同步代码块,把进行增删改的对象作为锁。
方式一:同步代码块: synchronized(同步监视器){ //操作共享数据的代码 } 注:1.同步监视器:俗称锁,任何一个类的对象都可以才充当锁。要想保证线程的安全,必须要求所有的线程共用同一把锁! 2.使用实现Runnable接口的方式创建多线程的话,同步代码块中的锁,可以考虑是this。如果使用继承Thread类的方式,慎用this! 3.共享数据:多个线程需要共同操作的变量。 明确哪部分是操作共享数据的代码。 方式二:同步方法:将操作共享数据的方法声明为synchronized。 比如:public synchronized void show(){ //操作共享数据的代码} 注:1.对于非静态的方法而言,使用同步的话,默认锁为:this。如果使用在继承的方式实现多线程的话,慎用! 2.对于静态的方法,如果使用同步,默认的锁为:当前类本身。以单例的懒汉式为例。 Class clazz = Singleton.class 总结:释放锁:wait(); 不释放锁: sleep() yield() suspend() (过时,可能导致死锁)
对于锁属于类还是当前对象可以看看这篇博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/weibanggang/p/9470718.html (写的很好)
无论同步代码块还是同步方法都要保证不同对象处理的是同一把锁才可以保证同步。
下面的例子介绍了静态方法锁的是类本身,而非静态是对象
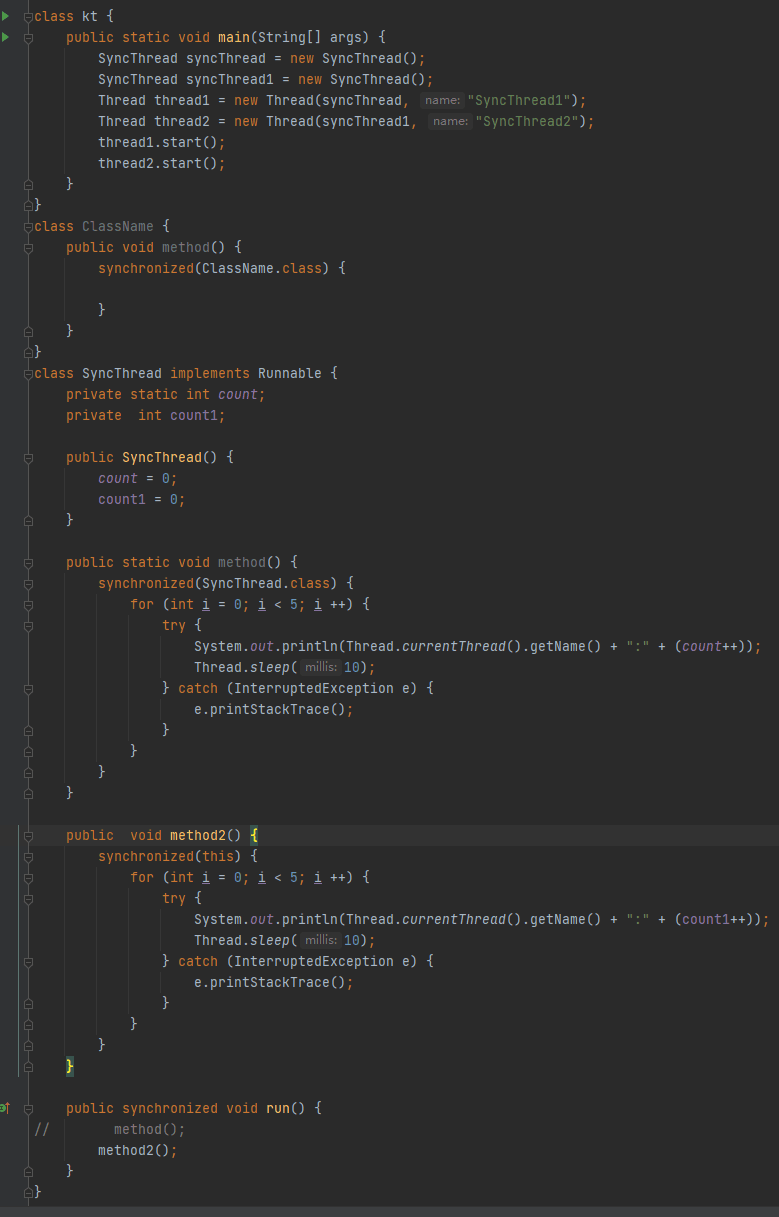
对于非静态方法只有所有的线程操作同一份对象才能保证锁的唯一性
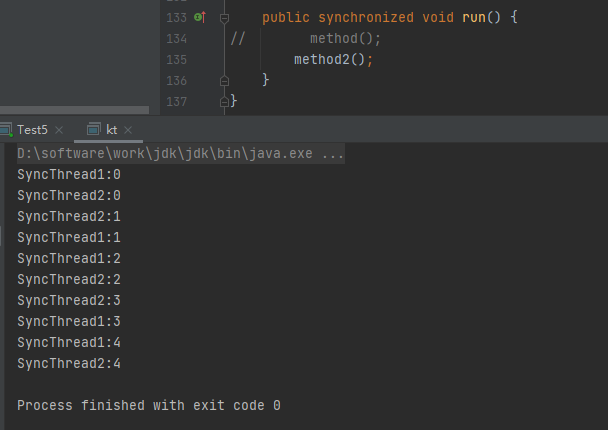
对于静态方法,因为锁的是当前类,所以锁对所有对象都有效,就保证了多对象的锁的唯一性,
3: 死锁

1 package Thread; 2 3 /** 4 * author liulei 5 * data 5.25 6 * since 1.8 7 * version 1.0 8 * Description 死锁:多个线程互相抱着对方需要的资源,形成僵持 9 */ 10 public class Test21 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 Makeup makeup = new Makeup(0,"李雷"); 13 Makeup makeup1 = new Makeup(1,"韩梅梅"); 14 makeup.start(); 15 makeup1.start(); 16 } 17 } 18 //口红 19 class Lipstick{ 20 21 } 22 //镜子 23 class Mirror{ 24 25 } 26 class Makeup extends Thread{ 27 //需要的资源只有一份,用static来保证只有一份 28 static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick(); 29 static Mirror mirror = new Mirror(); 30 int choice;//选择 31 String girlName;//使用 32 33 public Makeup(int choice, String girlName) { 34 this.choice = choice; 35 this.girlName = girlName; 36 } 37 38 @Override 39 public void run() { 40 try { 41 makeup(); 42 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 } 46 private void makeup() throws InterruptedException { 47 if(choice == 0){//李雷获得口红的锁,韩梅梅获得镜子的锁,但李雷韩梅梅希望获取对方的锁,但又不愿意释放自己的锁,形成死锁 48 synchronized (lipstick){ 49 System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红的锁"); 50 Thread.sleep(100); 51 synchronized (mirror){ 52 System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子的锁"); 53 } 54 } 55 56 } 57 if(choice == 1){ 58 synchronized (mirror){ 59 System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子的锁"); 60 Thread.sleep(100); 61 synchronized (lipstick){ 62 System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红的锁"); 63 } 64 } 65 66 } 67 } 68 }
解决死锁
package Thread; /** * author liulei * data 5.25 * since 1.8 * version 1.0 * Description 解决死锁的一个方法就是用完自己的锁后释放 */ public class Test22 { public static void main(String[] args) { Makeup1 makeup = new Makeup1(0,"李雷"); Makeup1 makeup1 = new Makeup1(1,"韩梅梅"); makeup.start(); makeup1.start(); } } //口红 class Lipstick1{ } //镜子 class Mirror1{ } class Makeup1 extends Thread{ //需要的资源只有一份,用static来保证只有一份 static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick(); static Mirror mirror = new Mirror(); int choice;//选择 String girlName;//使用 public Makeup1(int choice, String girlName) { this.choice = choice; this.girlName = girlName; } @Override public void run() { try { makeup(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void makeup() throws InterruptedException { if(choice == 0){//李雷获得口红的锁,韩梅梅获得镜子的锁,但李雷韩梅梅希望获取对方的锁,但又不愿意释放自己的锁,形成死锁 synchronized (lipstick){ System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红的锁"); Thread.sleep(100); } synchronized (mirror){ System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子的锁"); } } if(choice == 1){ synchronized (mirror){ System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子的锁"); Thread.sleep(100); } synchronized (lipstick){ System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红的锁"); } } } }
4: Lock

1 package Thread; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 4 5 /** 6 * author liulei 7 * data 5.25 8 * since 1.8 9 * version 1.0 10 * Description lock锁 11 */ 12 public class Test23 { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 TestLock testLock = new TestLock(); 15 new Thread(testLock).start(); 16 } 17 } 18 class TestLock implements Runnable{ 19 int ticketNum = 10; 20 private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 21 @Override 22 public void run() { 23 while (true){ 24 try{ 25 lock.lock();//加锁 26 if(ticketNum > 0){ 27 try { 28 Thread.sleep(1000); 29 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 System.out.println(ticketNum--); 33 }else{ 34 break; 35 } 36 }finally { 37 lock.unlock();//解锁 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 }

5: 线程通信


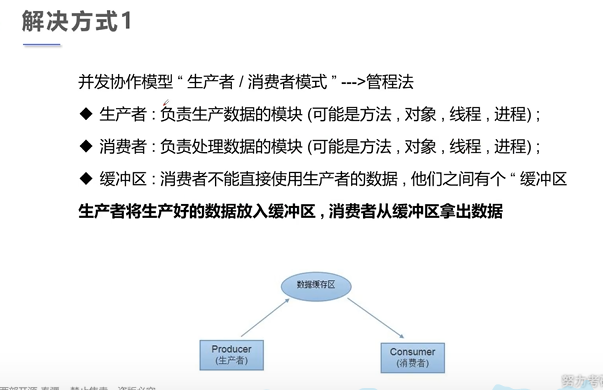
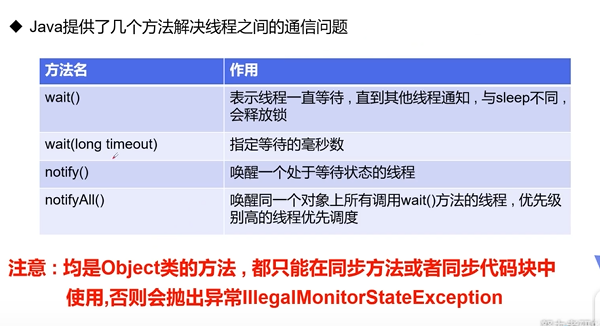

1 package Thread; 2 3 /** 4 * author liulei 5 * data 5.25 6 * since 1.8 7 * version 1.0 8 * Description 线程通信,生产者消费者(管程) 9 */ 10 public class Test24 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 SynContainer synContainer = new SynContainer(); 13 new consumer(synContainer).start(); 14 new product(synContainer).start(); 15 16 } 17 } 18 class product extends Thread{ 19 SynContainer synContainer; 20 21 public product(SynContainer synContainer) { 22 this.synContainer = synContainer; 23 } 24 25 @Override 26 public void run() { 27 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 28 29 try { 30 synContainer.push(new Chicken(i)); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 System.out.println("生产者生产第" + (i+1) + "只鸡"); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 class consumer extends Thread{ 39 SynContainer synContainer; 40 41 public consumer(SynContainer synContainer) { 42 this.synContainer = synContainer; 43 } 44 45 @Override 46 public void run() { 47 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 48 try { 49 System.out.println("消费者消费了第" + (synContainer.pop().id+1) + "只鸡"); 50 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 } 53 } 54 try { 55 synContainer.pop(); 56 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 57 e.printStackTrace(); 58 } 59 } 60 } 61 class Chicken{ 62 int id; 63 64 public Chicken(int id) { 65 this.id = id; 66 } 67 } 68 class SynContainer{ 69 Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[10];//容器大小 70 int count = 0;//容器计数器 71 //生产者放入产品 72 public synchronized void push(Chicken chicken) throws InterruptedException { 73 if(count == chickens.length){ 74 //通知消费者消费,生产等待 75 wait(); 76 } 77 chickens[count] = chicken; 78 count++; 79 //可以通知消费者消费了 80 notify(); 81 } 82 //消费者消费产品 83 public synchronized Chicken pop() throws InterruptedException { 84 //判断能否消费 85 if(count == 0){ 86 //等待生产者生产,消费者等待 87 wait(); 88 } 89 //可以消费了 90 count--; 91 Chicken chicken = chickens[count]; 92 //吃完了,通知生产者生产 93 notify(); 94 return chicken; 95 } 96 }
1 package Thread; 2 3 /** 4 * author liulei 5 * data 5.25 6 * since 1.8 7 * version 1.0 8 * Description 演员和观众(信号量) 9 */ 10 public class Test25 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 TV tv = new TV(); 13 new Player(tv).start(); 14 new Watcher(tv).start(); 15 } 16 } 17 //生产者-->演员 18 class Player extends Thread{ 19 TV tv; 20 21 public Player(TV tv) { 22 this.tv = tv; 23 } 24 25 @Override 26 public void run() { 27 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 28 if(i%2 == 0){ 29 try { 30 this.tv.play("梦想中国节目"); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 }else{ 35 try { 36 this.tv.play("天天向上节目"); 37 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 //消费者-->观众 45 class Watcher extends Thread{ 46 TV tv; 47 48 public Watcher(TV tv) { 49 this.tv = tv; 50 } 51 52 @Override 53 public void run() { 54 try { 55 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 56 tv.watch(); 57 } 58 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 59 e.printStackTrace(); 60 }; 61 } 62 } 63 //产品-->节目 64 class TV{ 65 //演员表演,观众等待 66 //观众观看,演员等待 67 String voice; 68 boolean flag = true;//没有节目了 69 //表演 70 public synchronized void play(String voice) throws InterruptedException { 71 if(!flag){ 72 wait(); 73 } 74 System.out.println("演员表演了" + voice); 75 //通知观众观看 76 this.notifyAll();//通知观看 77 this.voice = voice; 78 this.flag = false; 79 } 80 //观看 81 public synchronized void watch() throws InterruptedException { 82 if(flag){ 83 wait(); 84 } 85 System.out.println("观众观看了" + voice); 86 //通知演员表演 87 this.notifyAll(); 88 this.flag = true; 89 } 90 91 }
6: 线程池


1 package Thread; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 4 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 5 6 /** 7 * author liulei 8 * data 9 * since 1.8 10 * version 1.0 11 * Description 12 */ 13 public class Test26 { 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 //创建服务,创建线程池 16 ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); 17 service.execute(new MyThread());//执行 18 service.execute(new MyThread()); 19 service.execute(new MyThread()); 20 service.execute(new MyThread()); 21 service.shutdown();//关闭链接 22 } 23 } 24 class MyThread implements Runnable{ 25 @Override 26 public void run() { 27 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 28 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 29 } 30 } 31 }
线程池狂神说的比较简单,推荐自己再多看一些内容
https://www.cnblogs.com/jxxblogs/p/11655670.html
import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class TestPool { public static void main(String[] args) { // MyThread myThread = new MyThread(); // new Thread(myThread,"a").start(); // new Thread(myThread,"b").start(); // new Thread(myThread,"c").start(); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); executorService.execute(new MyThread()); executorService.execute(new MyThread()); executorService.execute(new MyThread()); executorService.submit(new MyThreads()); executorService.submit(new MyThreads()); } } class MyThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } } } class MyThreads implements Callable{ @Override public Object call() throws Exception { for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } return null; } }
作者:你的雷哥
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须在文章页面给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号