逻辑回归代码demo
程序所用文件:https://files.cnblogs.com/files/henuliulei/%E5%9B%9E%E5%BD%92%E5%88%86%E7%B1%BB%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE.zip
概念
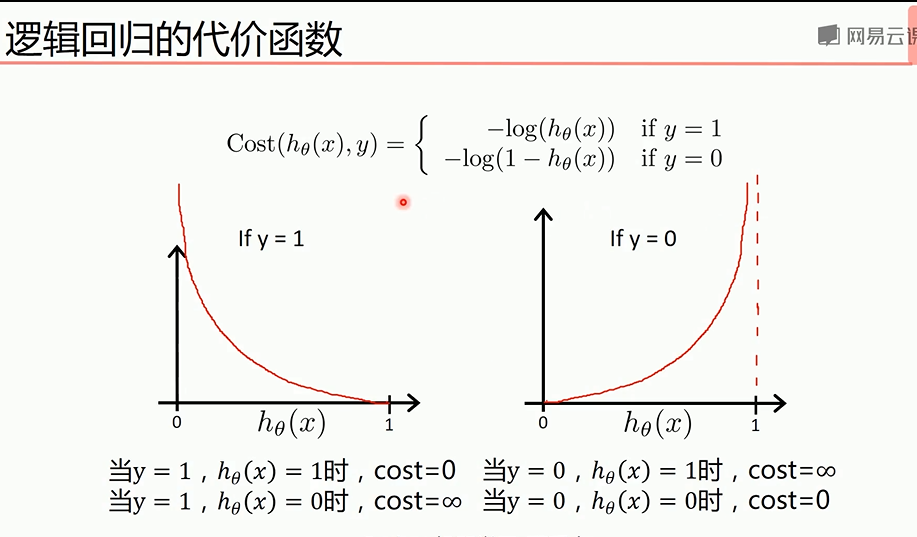
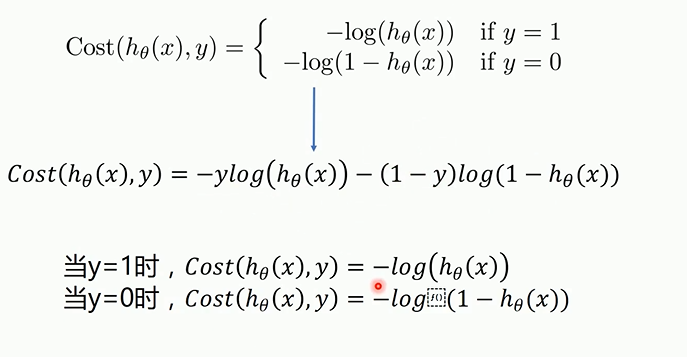

代价函数关于参数的偏导
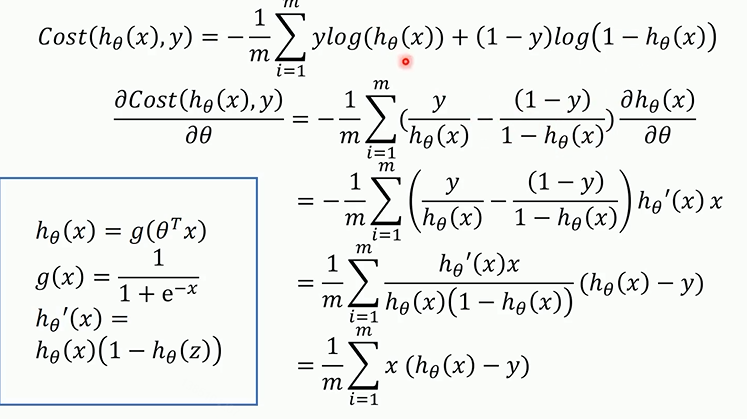
梯度下降法最终的推导公式如下

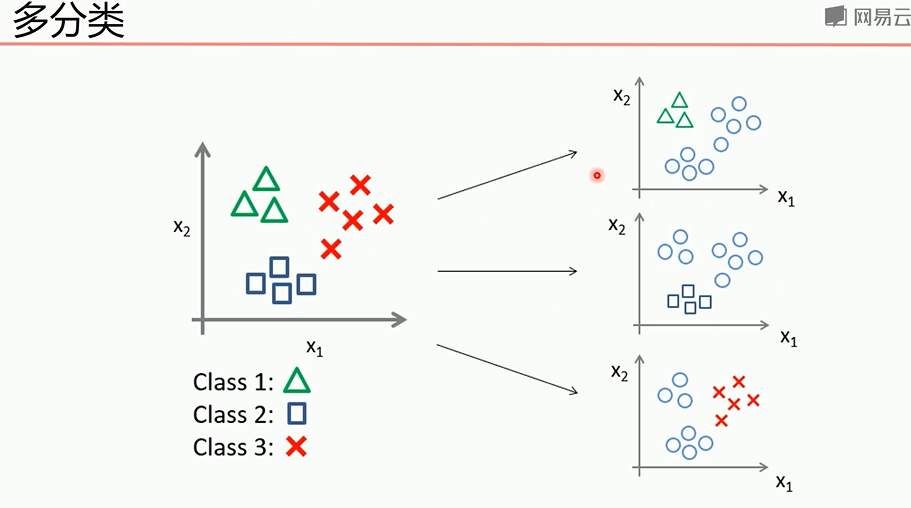
多分类问题可以转为2分类问题
正则化处理可以防止过拟合,下面是正则化后的代价函数和求导后的式子

正确率和召回率F1指标


我们希望自己预测的结果希望更准确那么查准率就更高,如果希望更获得更多数量的正确结果,那么查全率更重要,综合考虑可以用F1指标
梯度下降法实现线性逻辑回归
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 2 import numpy as np 3 from sklearn.metrics import classification_report#分类 4 from sklearn import preprocessing#预测 5 # 数据是否需要标准化 6 scale = True#True是需要,False是不需要,标准化后效果更好,标准化之前可以画图看出可视化结果 7 scale = False 8 # 载入数据 9 data = np.genfromtxt("LR-testSet.csv", delimiter=",") 10 x_data = data[:, :-1] 11 y_data = data[:, -1] 12 13 def plot(): 14 x0 = [] 15 x1 = [] 16 y0 = [] 17 y1 = [] 18 # 切分不同类别的数据 19 for i in range(len(x_data)): 20 if y_data[i] == 0: 21 x0.append(x_data[i, 0]) 22 y0.append(x_data[i, 1]) 23 else: 24 x1.append(x_data[i, 0]) 25 y1.append(x_data[i, 1]) 26 27 # 画图 28 scatter0 = plt.scatter(x0, y0, c='b', marker='o') 29 scatter1 = plt.scatter(x1, y1, c='r', marker='x') 30 # 画图例 31 plt.legend(handles=[scatter0, scatter1], labels=['label0', 'label1'], loc='best') 32 33 34 plot() 35 plt.show() 36 # 数据处理,添加偏置项 37 x_data = data[:,:-1] 38 y_data = data[:,-1,np.newaxis] 39 40 print(np.mat(x_data).shape) 41 print(np.mat(y_data).shape) 42 # 给样本添加偏置项 43 X_data = np.concatenate((np.ones((100,1)),x_data),axis=1) 44 print(X_data.shape) 45 46 def sigmoid(x): 47 return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-x)) 48 49 def cost(xMat, yMat, ws): 50 left = np.multiply(yMat, np.log(sigmoid(xMat * ws))) 51 right = np.multiply(1 - yMat, np.log(1 - sigmoid(xMat * ws))) 52 return np.sum(left + right) / -(len(xMat)) 53 54 def gradAscent(xArr, yArr): 55 if scale == True: 56 xArr = preprocessing.scale(xArr) 57 xMat = np.mat(xArr) 58 yMat = np.mat(yArr) 59 60 lr = 0.001 61 epochs = 10000 62 costList = [] 63 # 计算数据行列数 64 # 行代表数据个数,列代表权值个数 65 m, n = np.shape(xMat) 66 # 初始化权值 67 ws = np.mat(np.ones((n, 1))) 68 69 for i in range(epochs + 1): 70 # xMat和weights矩阵相乘 71 h = sigmoid(xMat * ws) 72 # 计算误差 73 ws_grad = xMat.T * (h - yMat) / m 74 ws = ws - lr * ws_grad 75 76 if i % 50 == 0: 77 costList.append(cost(xMat, yMat, ws)) 78 return ws, costList 79 # 训练模型,得到权值和cost值的变化 80 ws,costList = gradAscent(X_data, y_data) 81 print(ws) 82 if scale == False: 83 # 画图决策边界 84 plot() 85 x_test = [[-4],[3]] 86 y_test = (-ws[0] - x_test*ws[1])/ws[2] 87 plt.plot(x_test, y_test, 'k') 88 plt.show() 89 # 画图 loss值的变化 90 x = np.linspace(0, 10000, 201) 91 plt.plot(x, costList, c='r') 92 plt.title('Train') 93 plt.xlabel('Epochs') 94 plt.ylabel('Cost') 95 plt.show() 96 # 预测 97 def predict(x_data, ws): 98 if scale == True: 99 x_data = preprocessing.scale(x_data) 100 xMat = np.mat(x_data) 101 ws = np.mat(ws) 102 return [1 if x >= 0.5 else 0 for x in sigmoid(xMat*ws)] 103 104 predictions = predict(X_data, ws) 105 106 print(classification_report(y_data, predictions))#计算预测的分
sklearn实现线性逻辑回归
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 2 import numpy as np 3 from sklearn.metrics import classification_report 4 from sklearn import preprocessing 5 from sklearn import linear_model 6 # 数据是否需要标准化 7 scale = False 8 # 载入数据 9 data = np.genfromtxt("LR-testSet.csv", delimiter=",") 10 x_data = data[:, :-1] 11 y_data = data[:, -1] 12 13 def plot(): 14 x0 = [] 15 x1 = [] 16 y0 = [] 17 y1 = [] 18 # 切分不同类别的数据 19 for i in range(len(x_data)): 20 if y_data[i] == 0: 21 x0.append(x_data[i, 0]) 22 y0.append(x_data[i, 1]) 23 else: 24 x1.append(x_data[i, 0]) 25 y1.append(x_data[i, 1]) 26 27 # 画图 28 scatter0 = plt.scatter(x0, y0, c='b', marker='o') 29 scatter1 = plt.scatter(x1, y1, c='r', marker='x') 30 # 画图例 31 plt.legend(handles=[scatter0, scatter1], labels=['label0', 'label1'], loc='best') 32 33 plot() 34 plt.show() 35 logistic = linear_model.LogisticRegression() 36 logistic.fit(x_data, y_data) 37 if scale == False: 38 # 画图决策边界 39 plot() 40 x_test = np.array([[-4],[3]]) 41 y_test = (-logistic.intercept_ - x_test*logistic.coef_[0][0])/logistic.coef_[0][1] 42 plt.plot(x_test, y_test, 'k') 43 plt.show() 44 predictions = logistic.predict(x_data) 45 46 print(classification_report(y_data, predictions))
梯度下降法实现非线性逻辑回归
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 2 import numpy as np 3 from sklearn.metrics import classification_report 4 from sklearn import preprocessing 5 from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures 6 # 数据是否需要标准化 7 scale = False 8 # 载入数据 9 data = np.genfromtxt("LR-testSet2.txt", delimiter=",") 10 x_data = data[:, :-1] 11 y_data = data[:, -1, np.newaxis] 12 13 def plot(): 14 x0 = [] 15 x1 = [] 16 y0 = [] 17 y1 = [] 18 # 切分不同类别的数据 19 for i in range(len(x_data)): 20 if y_data[i] == 0: 21 x0.append(x_data[i, 0]) 22 y0.append(x_data[i, 1]) 23 else: 24 x1.append(x_data[i, 0]) 25 y1.append(x_data[i, 1]) 26 # 画图 27 scatter0 = plt.scatter(x0, y0, c='b', marker='o') 28 scatter1 = plt.scatter(x1, y1, c='r', marker='x') 29 # 画图例 30 plt.legend(handles=[scatter0, scatter1], labels=['label0', 'label1'], loc='best') 31 32 plot() 33 plt.show() 34 # 定义多项式回归,degree的值可以调节多项式的特征 35 poly_reg = PolynomialFeatures(degree=3) 36 # 特征处理 37 x_poly = poly_reg.fit_transform(x_data) 38 def sigmoid(x): 39 return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-x)) 40 41 42 def cost(xMat, yMat, ws): 43 left = np.multiply(yMat, np.log(sigmoid(xMat * ws))) 44 right = np.multiply(1 - yMat, np.log(1 - sigmoid(xMat * ws))) 45 return np.sum(left + right) / -(len(xMat)) 46 47 def gradAscent(xArr, yArr): 48 if scale == True: 49 xArr = preprocessing.scale(xArr) 50 xMat = np.mat(xArr) 51 yMat = np.mat(yArr) 52 53 lr = 0.03 54 epochs = 50000 55 costList = [] 56 # 计算数据列数,有几列就有几个权值 57 m, n = np.shape(xMat) 58 # 初始化权值 59 ws = np.mat(np.ones((n, 1))) 60 61 for i in range(epochs + 1): 62 # xMat和weights矩阵相乘 63 h = sigmoid(xMat * ws) 64 # 计算误差 65 ws_grad = xMat.T * (h - yMat) / m 66 ws = ws - lr * ws_grad 67 68 if i % 50 == 0: 69 costList.append(cost(xMat, yMat, ws)) 70 return ws, costList 71 # 训练模型,得到权值和cost值的变化 72 ws,costList = gradAscent(x_poly, y_data) 73 print(ws) 74 75 # 获取数据值所在的范围 76 x_min, x_max = x_data[:, 0].min() - 1, x_data[:, 0].max() + 1 77 y_min, y_max = x_data[:, 1].min() - 1, x_data[:, 1].max() + 1 78 79 # 生成网格矩阵 80 xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02), 81 np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02)) 82 #print(xx.shape)#xx和yy有相同shape,xx的每行相同,总行数取决于yy的范围 83 #print(yy.shape)#xx和yy有相同shape,yy的每列相同,总行数取决于xx的范围 84 # np.r_按row来组合array, 85 # np.c_按colunm来组合array 86 # >>> a = np.array([1,2,3]) 87 # >>> b = np.array([5,2,5]) 88 # >>> np.r_[a,b] 89 # array([1, 2, 3, 5, 2, 5]) 90 # >>> np.c_[a,b] 91 # array([[1, 5], 92 # [2, 2], 93 # [3, 5]]) 94 # >>> np.c_[a,[0,0,0],b] 95 # array([[1, 0, 5], 96 # [2, 0, 2], 97 # [3, 0, 5]]) 98 z = sigmoid(poly_reg.fit_transform(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]).dot(np.array(ws)))# ravel与flatten类似,多维数据转一维。flatten不会改变原始数据,ravel会改变原始数据 99 for i in range(len(z)): 100 if z[i] > 0.5: 101 z[i] = 1 102 else: 103 z[i] = 0 104 print(z) 105 z = z.reshape(xx.shape) 106 107 # 等高线图 108 cs = plt.contourf(xx, yy, z) 109 plot() 110 plt.show() 111 # 预测 112 def predict(x_data, ws): 113 # if scale == True: 114 # x_data = preprocessing.scale(x_data) 115 xMat = np.mat(x_data) 116 ws = np.mat(ws) 117 return [1 if x >= 0.5 else 0 for x in sigmoid(xMat*ws)] 118 119 predictions = predict(x_poly, ws) 120 121 print(classification_report(y_data, predictions))
sklearn实现非线性逻辑回归
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 from sklearn import linear_model 4 from sklearn.datasets import make_gaussian_quantiles 5 from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures 6 # 生成2维正态分布,生成的数据按分位数分为两类,500个样本,2个样本特征 7 # 可以生成两类或多类数据 8 x_data, y_data = make_gaussian_quantiles(n_samples=500, n_features=2,n_classes=2)#生成500个样本,2个特征,2个类别 9 plt.scatter(x_data[:, 0], x_data[:, 1], c=y_data) 10 plt.show() 11 logistic = linear_model.LogisticRegression() 12 logistic.fit(x_data, y_data) 13 # 获取数据值所在的范围 14 x_min, x_max = x_data[:, 0].min() - 1, x_data[:, 0].max() + 1 15 y_min, y_max = x_data[:, 1].min() - 1, x_data[:, 1].max() + 1 16 # 生成网格矩阵 17 xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02), 18 np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02)) 19 z = logistic.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])# ravel与flatten类似,多维数据转一维。flatten不会改变原始数据,ravel会改变原始数据 20 z = z.reshape(xx.shape) 21 # 等高线图 22 cs = plt.contourf(xx, yy, z) 23 # 样本散点图 24 plt.scatter(x_data[:, 0], x_data[:, 1], c=y_data) 25 plt.show() 26 print('score:',logistic.score(x_data,y_data))#使用线性逻辑回归,得分很低 27 28 # 定义多项式回归,degree的值可以调节多项式的特征 29 poly_reg = PolynomialFeatures(degree=5) 30 # 特征处理 31 x_poly = poly_reg.fit_transform(x_data) 32 # 定义逻辑回归模型 33 logistic = linear_model.LogisticRegression() 34 # 训练模型 35 logistic.fit(x_poly, y_data) 36 37 # 获取数据值所在的范围 38 x_min, x_max = x_data[:, 0].min() - 1, x_data[:, 0].max() + 1 39 y_min, y_max = x_data[:, 1].min() - 1, x_data[:, 1].max() + 1 40 41 # 生成网格矩阵 42 xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02), 43 np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02)) 44 z = logistic.predict(poly_reg.fit_transform(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]))# ravel与flatten类似,多维数据转一维。flatten不会改变原始数据,ravel会改变原始数据 45 z = z.reshape(xx.shape) 46 # 等高线图 47 cs = plt.contourf(xx, yy, z) 48 # 样本散点图 49 plt.scatter(x_data[:, 0], x_data[:, 1], c=y_data) 50 plt.show() 51 print('score:',logistic.score(x_poly,y_data))#得分很高
作者:你的雷哥
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须在文章页面给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!