内联函数_引用_默认参数_模版_函数重载
1:内联函数

普通函数是直接到函数内存地址去执行,但是内联函数是把函数拷贝一份到main函数里面,不要再去指定位置查找了。
函数代码执行时间很短,调用时间相对长此时用内联。但当代码执行时间长,将函数调入到内存里面的成本大于函数调用的时间此时不建议使用内联函数。
内联函数一般要比普通函数效率高,缺点是内存消耗大。

但一般在函数定义上加内联
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 inline int S(int num) 4 { 5 return num * num; 6 } 7 #define S1(num) num * num//以后在所有使用S(num)的地方,被自动替换为 num * num 8 int main() 9 { 10 cout << S(5) << endl;//25 11 cout << S(5+10) << endl;//225 12 cout << S1(5) << endl;//25 13 cout << S1(5+10) << endl;//65 14 //很明显,最后一个宏定义的结果出错,他的计算思路是5+10*5+10,所以c++推荐使用内联,不推荐使用宏定义 15 return 0; 16 }
2:引用


const int& refValue = 12//可以跟常量

使用引用的时候习惯加上const(除非你明确要对引用变量进行修改),可以防止对变量的随意修改。
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 void Swap1(int num1, int num2)//传参 4 { 5 int temp; 6 temp = num1; 7 num1 = num2; 8 num2 = temp; 9 } 10 void Swap2(int* num1, int* num2)//传指针 11 { 12 int temp; 13 temp = *num1; 14 *num1 = *num2; 15 *num2 = temp; 16 } 17 void Swap3(int& num1, int& num2)//引用 18 { 19 int temp; 20 temp = num1; 21 num1 = num2; 22 num2 = temp; 23 } 24 int main() 25 { 26 int num1,num2; 27 cout << "输入要交换的两个参数" << endl; 28 cin >> num1 >> num2; 29 Swap1(num1, num2);//没有实现交换,因为传进的是副本 30 cout << "传参交换结果为:" << num1 << "\t" << num2 << endl; 31 Swap2(&num1, &num2);//实现了交换,因为是地址里面的内容被交换 32 cout << "传指针交换结果为:" << num1 << "\t" << num2 << endl; 33 Swap3(num1, num2);//实现了交换,引用其实就是变量的别名 34 cout << "引用换结果为:" << num1 << "\t" << num2 << endl; 35 return 0; 36 }

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int& sum()//返回值类型是引用类型的时候,不能返回局部变量 4 { 5 int num = 10; 6 int& rNum = num; 7 return rNum;//不能返回局部变量 8 } 9 void test() 10 { 11 int x = 1, y = 2, z = 3; 12 } 13 int main() 14 { 15 int& result = sum();//因为rNum是局部变量,函数结束后会被系统回收 16 test();//result所指的位置因为被回收,所以其他变量可以申请占用并修改数据 17 cout << "result = " << result << endl;//result = 2,说明空间数据被修改,因此引用类型不能返回局部变量 18 return 0; 19 }
返回类型是引用类型的只能返回传入的引用

上述代码返回值只能返回一个,切改返回值是传入的参数的一个,即可以为num1或者num2.

上述代码因为result和num所指空间相同,所以result被修改,num也被修改,所以为防止引用被误修改,一般加上const。

基本类型数组啊不鼓励使用引用传递,结构体对象啊多使用引用
3:默认参数
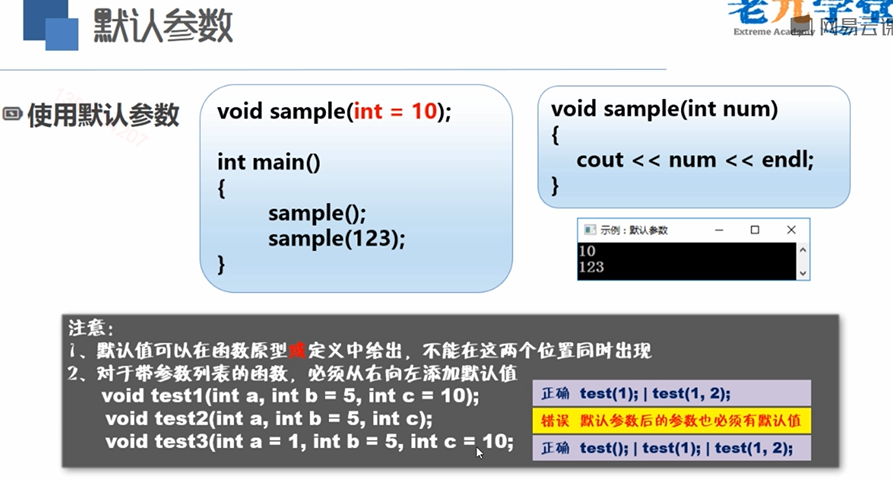
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 void test(int x = 10)//默认值是10 4 { 5 cout << x << endl; 6 } 7 void test1(int x, int y = 10)//从右到左按顺序声明 8 { 9 10 } 11 void test2(int x = 10, int y){//必须先默认右边的 12 13 } 14 int main() 15 { 16 test();//不写参数默认传10 17 test(100);//指明了参数 18 19 return 0; 20 }
4: 模版
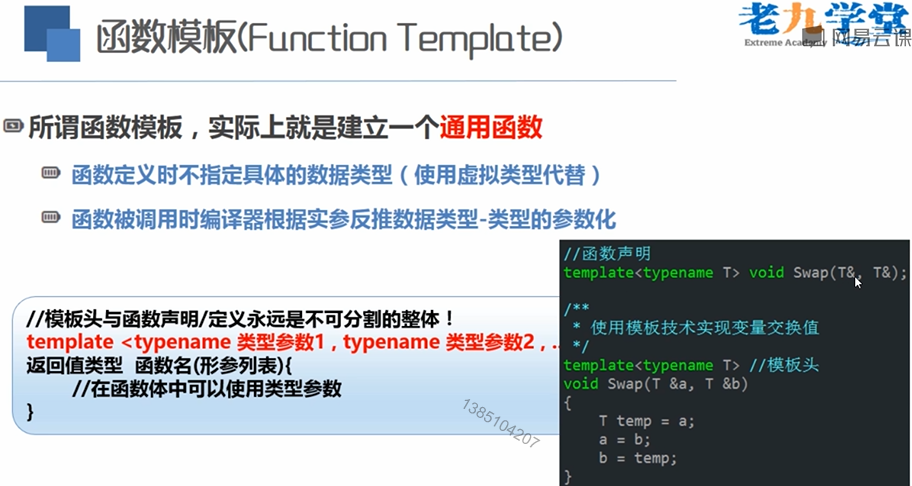
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 template<typename T> 4 void Swap(T& a,T& b)//可以传入任何类型,系统根绝传入的数据判别类型,大大提高代码的通用性 5 { 6 T temp; 7 temp = a; 8 a = b; 9 b = temp; 10 } 11 int main() 12 { 13 cout << "请输入两个整数:" <<endl; 14 int a,b; 15 cin >> a >> b; 16 Swap(a, b); 17 cout << "交换的结果为: "; 18 cout << a << "\t"<< b << endl; 19 cout << "请输入两个字符串:" <<endl; 20 string a1, b1; 21 cin >> a1 >> b1; 22 Swap(a1, b1); 23 cout << "交换的结果为: "; 24 cout <<a1 << "\t" << b1; 25 return 0; 26 }
5:函数重载


1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 void test(int x)//默认值是10 4 { 5 cout << x << endl; 6 } 7 void test() 8 { 9 cout << "test()" << endl; 10 } 11 int main() 12 { 13 //名字相同,参数列表不同,所以认为重载 14 test();//不带参数的 15 test(100);//带参数的, 16 17 return 0; 18 }
作者:你的雷哥
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须在文章页面给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!