spring框架3:bean的装配1(spring的核心功能)
引言
Bean
大家把bean理解为就是Java类,类里面有属性和行为,既成员变量和成员方法等等,那如果我们想要使角该类中的这些东西,首先要做的就是创建该类的对象,然后调用对象中的客种东西。那bean其实就是这个类。
注意:大家不要把bean想的多么抽象,多么难理解,就把它当成一个类即可。
Spring中的Bean:
Spring中的Bean其实和上面的Bean是一样的,只不过有一点点小区别,比如
我们平时使用Bean的话,直接new个Bean的对象就可以了,.但是如果是使用Spring的Bean的话,我们得需要丢配置,把Bean配置好,才可以使用Bean对象中的东西,配置方式有两种,一种是基于XML的方式(setter属性注入和构造器注入),一种是基于注解的方式(实际开发更多用这种),因为xml配置显得比较臃肿。
Spring容器:
其实Spring容器是一个抽象的概念,不过大家可以把它形象化,把spring容器可以形象成一个大箱子,箱子是用来装东西的,那Spring容器这个大箱子用来装什么呢?答案很简单,用来装Bean的,就是装Java类的。
思考:为什么要让spring容器来装Bean呢?
因为只要把Bean装到Spring容器中,Spring容器就会帮助我们来new这个Bean的对象,而不需要我们自己去new对象了,大大的降低了程序的耦合性,这也正是我们学习spring框架的最大的好处。
spring框架有两种装配bean的方法:xml配置、通过注解实现。
1. 基于xml的bean装配
(1)Setter方法注入
什么是setter方式注入?
注入是指让Spring容器来给对象中的属性赋值,大家回忆一下当年咱们学过的知识点,如果我们定义一个Person类,该类中有一个私有的name属性,为了给name属性赋值,我们是不是提供了setName的方法。同理,在Spring的配置中,也可以通过setXXX的这种方式给属性赋值。
创建模块springBean1项目
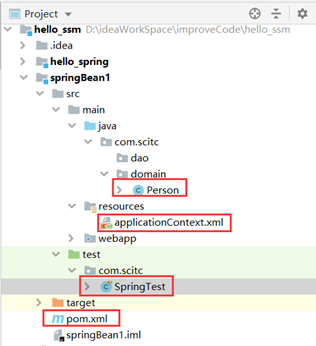
目录结构如上所示,创建一个实体对象person、修改applicationContext.xml、添加测试类SpringTest、pom.xml
编写pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.20</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
编写Person.java
package com.scitc.domain; import java.util.List; public class Person { private String name; private int age; private List list; //为所有属性提供Setter方法,未提供构造方法时,默认提供无参构造方法 public void setName(String name) { this.name= name; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age= age; } public void setList(List list) { this.list = list; } public void sayHello(){ String message = "Hello "+this.name+";your age is "+this.age; System.out.println(message); } } 说明:添加三个属性,为每个属性添加set方法。并提供一个sayHello()方法。
编写applicationContext.xml
<!--通过Setter属性注入的方式装配Person实例 --> <bean id="person" class="com.scitc.domain.Person"> <property name="name" value="Setter属性注入"/> <property name="age" value="16"/> <!-- list集合注入值--> <property name="list"> <list> <value>"为list集合注入值1"</value> <value>"为list集合注入值2"</value> </list> </property> </bean>
测试类SpringTest
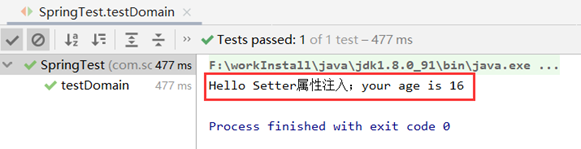
package com.scitc; import com.scitc.domain.Person; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class SpringTest { @Test public void testDomain(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Person person = (Person)context.getBean("person"); //输出Setter属性注入值 person.sayHello(); } }
运行:
(2)构造器方法注入
该方法与setter方法的区别:
person.java、SpringTest、applicationContext.xml三个文件不同。
Person.java
package com.scitc.domain; import java.util.List; public class Person { private String name; private int age; private List list; //无参构造方法 ,无属性值注入时采用无参构造函数的默认值。 public Person(){ this.name= "无参构造器注入"; this.age= 28; } //有参构造方法 public Person(String name,int age,List list){ this.name= name; this.age= age; this.list=list; } public void setName(String name) { this.name= name; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age= age; } public void setList(List list) { this.list = list; } public void sayHello(){ String message = "Hello "+this.name+";your age is "+this.age; System.out.println(message); } }
applicationContext.xml
<!--默认无参构造器注入方式装配Person实例--> <bean id="person" class="com.scitc.domain.Person"> </bean> <!--通过有参构造器注入方式装配Person实例--> <bean id="person1" name="person1" class="com.scitc.domain.Person"> <constructor-arg value="有参构造器注入" type="java.lang.String"/> <constructor-arg value="25" type="int"/> <constructor-arg> <list> <value>"构造方法为list集合注入值1"</value> <value>"构造方法为list集合注入值1"</value> </list> </constructor-arg> </bean>
SpringTest
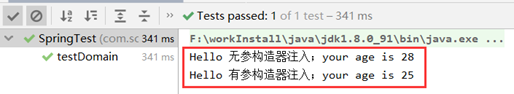
package com.scitc; import com.scitc.domain.Person; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class SpringTest { @Test public void testDomain(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Person person = (Person)context.getBean("person"); //输出Setter属性注入值 person.sayHello(); //输出有参构造方法注入值 Person person1 = (Person)context.getBean("person1"); person1.sayHello(); } }
运行:

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号