原型和原型链
JS 是一个基于原型继承的语言
class 和继承
- class 是一个面向对象语法的实现
- 通过 constructor 构建, 可以赋值属性和方法
class Student { constructor (name, age, num) { this.name = name this.age = age this.num = num } say () { console.log(`我是 ${this.name}, 我今年 ${this.age} 岁, 我的学号是 ${this.num}`) } } let liming = new Student('李明', 18, '0001') // 通过类 new 对象/实例 console.log(liming.name) // 李明 console.log(liming.age) // 18 liming.say() // 我是 李明, 我今年 18 岁, 我的学号是 0001
继承
- extends 继承的关键字
- super 使用父类构造函数, 必须放继承的类构造函数的首行
- 扩展或重写方法
// 父类 class People { constructor (name, age) { this.name = name this.age = age } eat () { console.log(`${this.name} 会吃饭`) } } // 子类 学生 class Student extends People { constructor (name, age, num) { super(name, age) this.num = num } say () { console.log(`我是 ${this.name}, 我今年 ${this.age} 岁, 我的学号是 ${this.num}`) } } // 子类 老师 class Teacher extends People { constructor (name, age, project) { super(name, age) this.project = project } teach () { console.log(`我是 ${this.name}, 我今年 ${this.age} 岁, 我教授 ${this.project}`) } } // 实例 const liming = new Student('李明', 18, '001') console.log(liming.name) // 李明 liming.eat() // 李明 会吃饭 liming.say() // 我是 李明, 我今年 18 岁, 我的学号是 001 // 实例 const wanglaoshi = new Teacher('王老师', 30, '语文') console.log(wanglaoshi.name) // 王老师 wanglaoshi.eat() // 王老师 会吃饭 wanglaoshi.teach() // 我是 王老师, 我今年 30 岁, 我教授 语文
类型判断 instanceof
instanceof 判断这个变量属于哪个 class 用于识别正在处理的对象的类型。与 typeof 方法不同的是,instanceof 方法要求开发者明确地确认对象为某特定类型。
- instanceof 可以判断所有的引用类型
- Object 是所有 class 的父类
console.log([] instanceof Array) // true console.log([] instanceof Object) // true console.log({} instanceof Object) // true console.log(liming instanceof Student) // true console.log(liming instanceof People) // true console.log(liming instanceof Object) // true
原型和原型链
隐式原型和显式原型
// class 实际是函数, 是ES6的语法糖 console.log(typeof People) // function console.log(typeof Student) // function // 隐式原型(__proto__)型和显式原型(prototype) console.log(liming.__proto__) // 实例对象的 隐式原型 console.log(Student.prototype) // 被实例类的 console.log(liming.__proto__ === Student.prototype)
图解关系

原型关系
- 每个 class 都有显式原型 prototype
- 每个实例都有隐式原型 __proto__
- 实例的 __proto__ 指向对应 class 的 prototype
基于原型的执行规则
- 获取属性 liming.name 或执行方法 liming.say() 时
- 先在自身寻找属性和方法
- 如果找不到则去 __proto__ 中查找
原型链图解
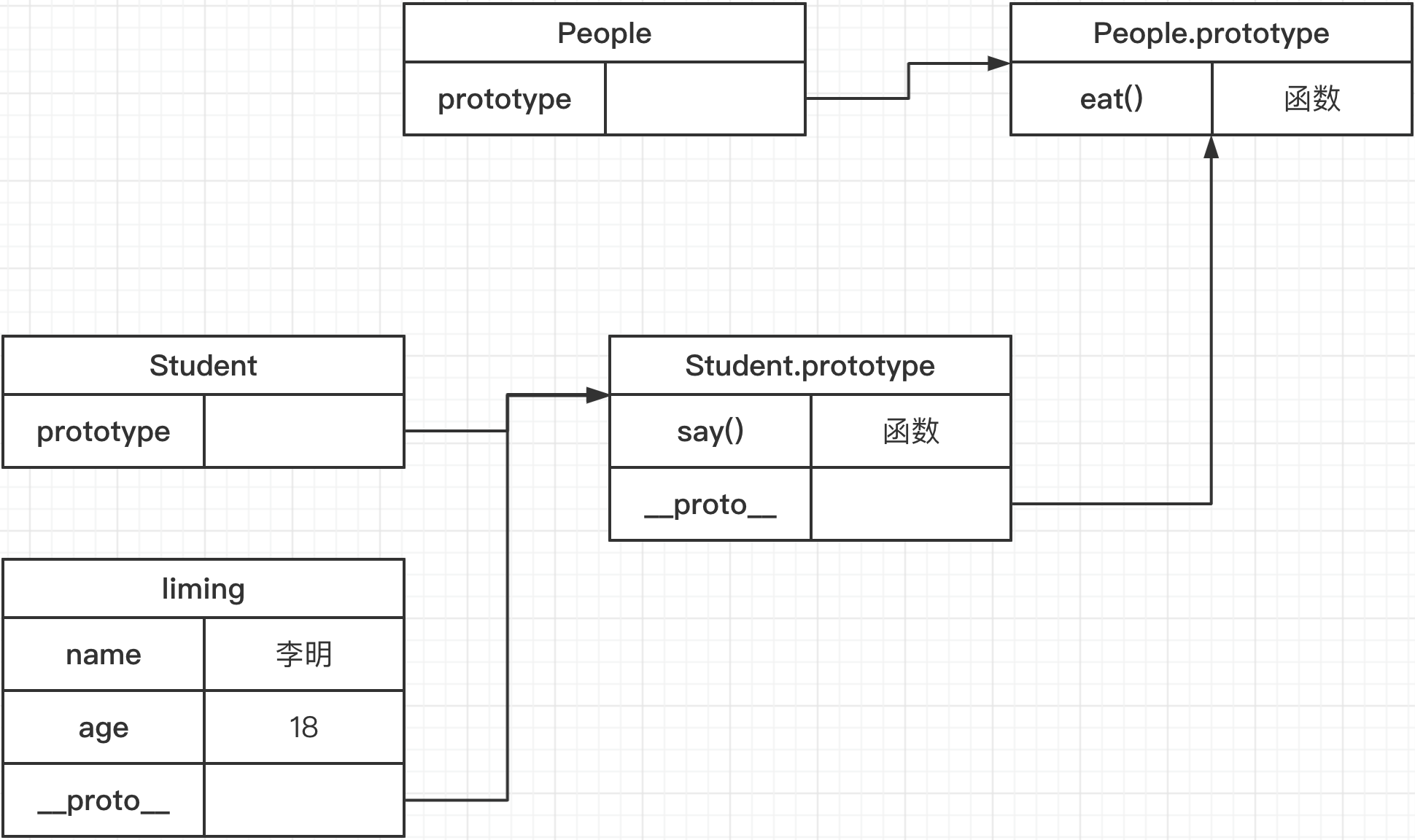
console.log(Student.prototype.__proto__) console.log(People.prototype) console.log(Student.prototype.__proto__ === People.prototype) // true // hasOwnProperty() 方法返回一个布尔值,判断对象是否包含特定的自身(非继承)属性。 // 这里来验证一下是不是通过原型链继承的属性 console.log(liming.hasOwnProperty('name')) // true console.log(liming.hasOwnProperty('eat')) // false
那么 hasOwnPropert() 方法很显然来自 Object
People.prototype.__proto__.hasOwnProperty('hasOwnProperty') // true
Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty('hasOwnProperty') // true
图解

如何判断一个变量是不是数组?
可以结合原型链的思维去理解 instanceof
a instanceof Array 准确判断一个变量是不是数组
手写一个简易的 jQuery 考虑插件和扩展性
class jQuery { constructor (selector) { const result = document.querySelectorAll(selector) const length = result.length for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) { this[i] = result[i] } this.length = length } get (index) { return this[index] } each (fn) { for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i ++) { const elem = this[i] fn(elem) } } on (type, fn) { return this.each(elem => { elem.addEventListener(type, fn, false) }) } // 扩展很多 API DOM 操作 } // 扩展性 - 插件机制 jQuery.prototype.dialog = function (info) { alert(info) } // 扩展性 - 复写机制(造轮子) class myJquery extends jQuery { constructor (selector) { super(selector) } // 扩展自己的方法 dialog2 (info) { alert(info) } }
class 的原型本质怎么理解
- 原型和原型链的图示
- 属性和方法的执行规则


