Spring Cloud(十一)声名式服务调用:Feign的使用 (上)
一、写在前边
最近开发任务比较忙,下班也开始锻炼了,这个系列的文章就放了很久,看github我提交的Feign的入门程序已经好久了,今天正好得空,这就更上一贴,准备分几部分写
注意:之前几个项目中,笔者忽略了一个问题,pom文件中如果parent节点下的是spring-cloud-starter-parent而不是spring-boot-starter-parent的话,这样就可以不用写如下代码了
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Camden.SR3</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
二、Feign简介
通过前面的学习对Ribbon和Hystrix来进行开发,通过这两个重磅武器学会了如何在微服务实现客户端的负载均衡、服务调用和断路保护,实践中我们发现这两个基础工具总是成对出现的,那么有没有更高层次的封装来简化开发呢?
Spring为我们提供了Spring Cloud Feign就是这样的一个工具,基于Netflix Feign实现,除了负载均衡、服务调用和断路保护的功能外,还提供了声明式Web服务客户端的定义方式以及兼容SpringMVC的注解支持。
三、快速入门
继续使用之前的整个项目,没有这个项目的同学请clone下来代码,地址:https://github.com/HellxZ/SpringCloudLearn.git
新建一个项目名为FeignCustomer,
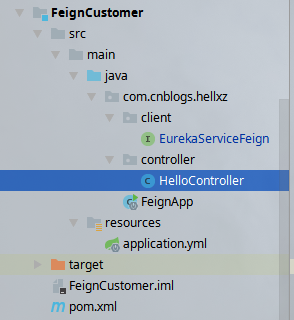
pom.xml如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.cnblogs.hellxz</groupId>
<artifactId>FeignCustomer</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>Dalston.SR5</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!-- Hystrix,Feign是基于Hystrix的-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Eureka依赖,连接注册中心的都需要有这个依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Feign依赖,声明式开发 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- SpringMVC依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
如同常规在resources包下创建application.yml
server:
port: 9001
spring:
application:
name: feign-customer
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://peer1:1111/eureka
创建主类,相较于其他只需添加@EnableFeignClients来开启Feign的支持
package com.cnblogs.hellxz;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.SpringCloudApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.feign.EnableFeignClients;
@EnableFeignClients //开启Feign
@SpringCloudApplication
public class FeignApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FeignApp.class, args);
}
}
除了以上的我们需要一个用来调用服务提供者的工具,在Ribbon那几章我们使用的是RestTemplate,Feign是一种声明式调用工具,下面就来探索一下
在com.cnblogs.hellxz.client创建EurekaServiceFeign,这个是用来当做Service一样的用法,代码如下:
package com.cnblogs.hellxz.client;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.feign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
/**
* 服务提供者的Feign
* 这个接口相当于把原来的服务提供者项目当成一个Service类,
* 我们只需在声明它的Feign-client的名字,会自动去调用注册中心的这个名字的服务
* 更简单的理解是value相当于MVC中的Controller类的父路径,通过"父路径+子路径和参数来调用服务"
*/
@FeignClient(value = "eureka-service") //其中的value的值为要调用服务的名称
public interface EurekaServiceFeign {
/**
* 第一个Feign代码
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello", method=RequestMethod.GET)
String helloFeign();
}
刚才说过我们可以使用这个Feign当做Service来使用服务提供者的方法,得出返回值,这里我们写一个Controller来示范一下使用
package com.cnblogs.hellxz.controller;
import com.cnblogs.hellxz.client.EurekaServiceFeign;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("feign")
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private EurekaServiceFeign eurekaServiceFeign; //注入Feign
@GetMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
public String sayHello(){
//在方法中调用feign的方法
return eurekaServiceFeign.helloFeign();
}
}
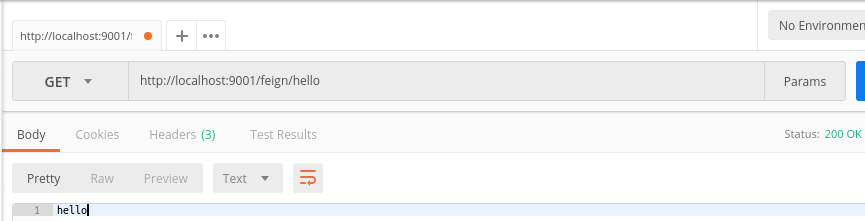
好了,我们分别启动注册中心、服务提供者、还有这个Feign项目
使用postman进行测试,使用Get请求访问http://localhost:9001/feign/hello
四、参数绑定
Spring官方在整合NetFlix Feign的时候,加入了SpringMVC的注解支持,这使得Feign让习惯了SpringMVC的程序员更好的过渡过来,下面我举几个例子,就举项目中最常用的吧。
1. @PathVariable
扩充EurekaServiceFeign,添加如下代码,注释很详细,不多说
/**
* 在服务提供者我们有一个方法是用直接写在链接,SpringMVC中用的@PathVariable
* 这里边和SpringMVC中有些有一点点出入,SpringMVC中只有一个参数而且参数名的话是不用额外指定参数名的,而feign中必须指定
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/greet/{dd}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
String greetFeign(@PathVariable("dd") String dd);
在HelloController中也添加对应的代码,用来调用上边的方法
/**
* 注意这里是SpringMVC,URL中的参数与方法中的参数名相同无需在注解中注明参数名
*/
@GetMapping("/greet/{test}")
@ResponseBody
public String greet(@PathVariable String test){
return eurekaServiceFeign.greetFeign(test);
}
测试这个方法
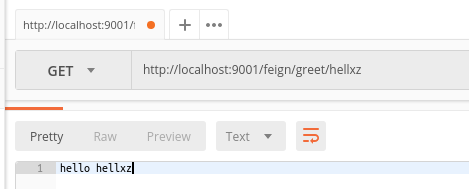
2. @RequestParam
为声名为Feign的类添加方法,调用服务提供者的方法
如下代码中使用的User类是从服务提供者模块中复制出来的
/**
* 这里说下@RequestParam 注解和SpringMVC中差别也是不大,我认为区别在于Feign中的是参数进入URL或请求体中,
* 而SpringMVC中是参数从请求体中到方法中
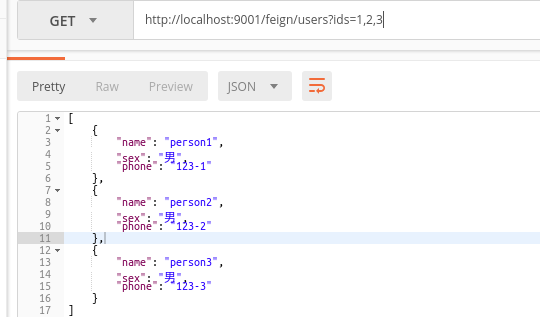
* @param ids id串,比如“1,2,3”
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<User> getUsersByIds(@RequestParam("ids") List<Long> ids);
调用这个方法的方法
/**
* 调用Feign中使用@RequestParam的方法
*/
@GetMapping("/users")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> getUserListByIds(@RequestParam("ids") List<Long> ids){
return eurekaServiceFeign.getUsersByIds(ids);
}
测试
3. @RequestHeader
这里是为请求的Header中加入参数的注解,但是之前我们的服务提供者并没有这个方法,这里为GetRequestController添加一个方法如下
@GetMapping("/headers")
public String getParamByRequestHeader(@RequestHeader("name") String name){
return name;
}
现在我们为Feign这个类添加一个调用上边方法的方法
/**
* 这里是将参数添加到Headers中
* @param name 参数
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/headers")
String getParamByHeaders(@RequestHeader("name") String name);
在Controller中,添加代码
@GetMapping("/headers")
@ResponseBody
public String getParamByHeaders(@RequestHeader("name") String name){
return eurekaServiceFeign.getParamByHeaders(name);
}
测试
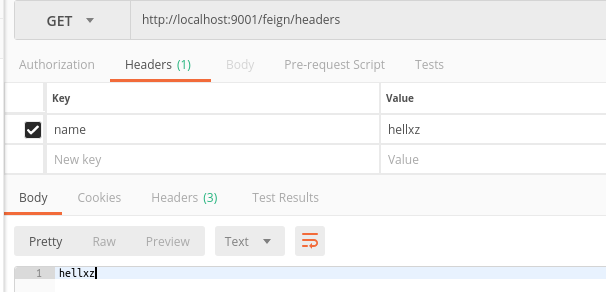
5. @RequestBody
使用这个注解需要使用Post请求,这里简单举例
Feign类中添加方法
/**
* 调用服务提供者的post方法,接收回来再被服务提供者丢回来
* @param user User对象
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.POST)
User getUserByRequestBody(@RequestBody User user);
Controller中添加
@PostMapping("/requestBody")
@ResponseBody
public User getParamByRequestBody(@RequestBody User user){
return eurekaServiceFeign.getUserByRequestBody(user);
}
测试
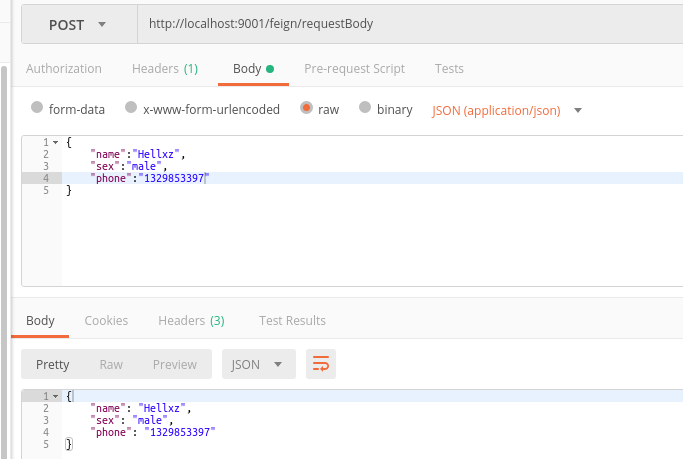
需要注意的是
@RequestParam和@RequestHeader,以及最先提到的@PathVariable这三个注解都需要写明参数名称,这点与SpringMVC中不同,否则会报IllegalStateException异常,所以一定要指明参数名!
时间不早了,明天继续更



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号