C++ allocator设计内存管理器
前情回顾:
allocator内存管理类
allocator内存管理器
某些类需要在运行时分配可变大小的内存空间,一般来说我们使用容器如vector来管理我们的数据,但是对于某些类,在有些时候我们需要自己进行内存的分配。这些类必须定义自己的拷贝控制成员来管理所分配的内存。
我们将实现一个vector,这个vector保存的是sring类型的数据,而且使用我们自己创建的内存分配的方式。我们的这个类叫做 vecStr
基本属性
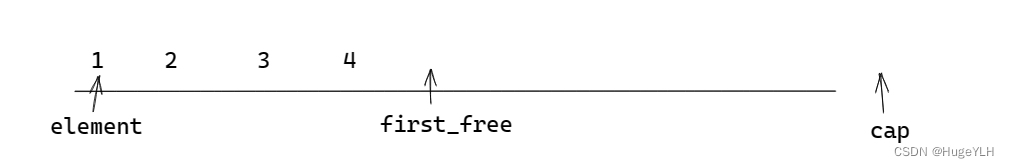
我们在自己创建的vecStr中需要有三个属性,分别是:
- element: 指向分配的内存的起始位置。
- first_free:指向已经构造完成的对象的下一个位置,即未构造的内存的起始位置。
- cap:总的内存空间的尾后位置。
如图所示:
类的设计
基本构造函数:
strVec();
strVec(std::initializer_list<std::string> initList);
~strVec();
strVec(const strVec& other); //拷贝构造函数
strVec& operator=(const strVec& other); //拷贝赋值运算符
以下几个具有关键功能的函数:
- alloc_n_copy:分配内存,并且拷贝给定范围的元素到一个新的内存中。
std::pair<std::string*, std::string*> alloc_n_copy(const std::string* beg, const std::string* end);
- reallocate: 当内存不够时,重新分配一块新的内存,并且拷贝原始内容,释放旧的内存
void reallocate();
- free:释放内存空间
//释放内存
void free();
- check_n_alloc:检查当前内存空间是否足够,不够的话调用reallocate重新分配一块内存。
//检查内存是否足够,不够的话就重新分配
void check_n_alloc();
其他功能性函数:
//获取总容量
size_t capacity()const { return cap - element; }
//获取已分配的容量大小
size_t size()const { return first_free - element; }
void push_back(const std::string& str);
关键功能的实现
- alloc_n_copy:接受一个开始位置和结束的位置的指针,开辟一块新的内存空间,并且把开始位置到结束位置中的内容拷贝到这块新的内存空间,并且返回这块内存空间的初始位置和尾后位置。
我们使用pair来保存这两个位置。
std::pair<std::string*, std::string*> strVec::alloc_n_copy(const std::string* beg, const std::string* end)
{
auto p = allocStr.allocate(end - beg); //分配end - beg个大小的内存空间,返回未构造的初始的位置
//拷贝内存到新的内存空间,uninitialized_copy返回拷贝结束后的位置,这个位置就是first_free的位置,p就是element的位置
return { p,std::uninitialized_copy(beg, end, p) };
}
使用uninitialized_copy来拷贝beg到end的内存空间的内容到新的内存空间p中。
- reallocate:旧内存空间不够时,我们重新开辟一块内存,并且把原始内容拷贝到新内存中,注意我们的新内存一般是原始内存的两倍大小。
- 使用move的进行移动构造,从而避免拷贝构造(拷贝后销毁)的繁琐操作,直接进行指针所有权的转移即可,这就是移动构造函数。
- 使用construct构造对象。
- 注意属性的更新,element first_free cap此时都指向了新的内存空间的对应位置。
void strVec::reallocate()
{
/*
在重新分配空间的时候,移动而不是拷贝构造
*/
//申请两倍的空间
auto NewSpace = (size() == 0) ? 1 : 2 * size();
//分配新内存
auto pNew = allocStr.allocate(NewSpace);
auto dest = pNew;
auto old = element;
for (size_t i = 0; i != size(); i++)
{
//移动构造旧的内存里的数据,移动到新的内存空间里
allocStr.construct(dest++, std::move(*old++));
}
free(); //释放旧内存
//更新数据
element = pNew;
first_free = dest;
cap = element + NewSpace;
}
- free:释放旧的内存空间,我们使用三种方法来释放旧的内存空间,for_each函数式,正序销毁和逆序销毁,注意,销毁只是调用了他们的析构函数,我们一定最后使用deallocate来彻底释放这块内存。
void strVec::free()
{
if (element)
{
#if 0
//for_each销毁
std::for_each(begin(), end(), [&](std::string& str)
{
allocStr.destroy(&str);
});
#elif 0
//逆序销毁旧元素
/*for (auto eleBeg = first_free; eleBeg != element;)
{
allocStr.destroy(--eleBeg);
}*/
#else
//正序销毁旧元素
for (auto elebeg = element; elebeg != first_free;)
{
allocStr.destroy(elebeg++);
}
#endif
allocStr.deallocate(element, cap - element);
}
}
完整的内存管理器
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <vld.h>
#include <algorithm>
/*
内存管理器
*/
class strVec
{
public:
strVec();
strVec(std::initializer_list<std::string> initList);
~strVec();
strVec(const strVec& other); //拷贝构造函数
strVec& operator=(const strVec& other); //拷贝赋值运算符
//总容量
size_t capacity()const { return cap - element; }
//已分配的容量
size_t size()const { return first_free - element; }
void push_back(const std::string& str);
//分配至少能容纳n个元素的内存空间
void reserve(const int& n);
//重新调整大小
void resize(const int& n, const std::string& str = "None");
public:
std::string* begin()const { return element; }
std::string* end()const { return first_free; }
private:
//分配内存,并且拷贝元素到这个范围里
std::pair<std::string*, std::string*> alloc_n_copy(const std::string* beg, const std::string* end);
//释放内存
void free();
//检查内存是否足够,不够的话就重新分配
void check_n_alloc();
//内存不够,分配新的内存空间:需要拷贝原来的元素并且释放原来的内存
void reallocate();
void reallocate(int n);
private:
std::allocator<std::string> allocStr; //内存分配器
std::string* element; //内存空间的起始元素
std::string* first_free; //已分配的实际元素之后的位置
std::string* cap; //总的分配空间之后的位置
};
strVec::strVec()
:element(nullptr), first_free(nullptr), cap(nullptr)
{
}
strVec::strVec(std::initializer_list<std::string> initList)
{
//分配合适的内存大小
int n = initList.size();
auto p = allocStr.allocate(n);
element = first_free = p;
cap = p + n;
for (auto& xStr : initList)
{
allocStr.construct(first_free++, xStr);
}
}
strVec::~strVec()
{
free();
}
strVec::strVec(const strVec& other)
{
//拷贝构造,other的内存拷贝到新的对象中
auto pPair = alloc_n_copy(other.element, other.first_free);
element = pPair.first;
first_free = pPair.second;
cap = pPair.second; //alloc_n_copy分配的空间恰好容纳给定的元素
}
strVec& strVec::operator=(const strVec& other)
{
//赋值运算符,直接对自身操作,返回自身,记得销毁原来的内存
auto pPair = alloc_n_copy(other.element, other.first_free);
free();
element = pPair.first;
first_free = cap = pPair.second;
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
return *this;
}
void strVec::push_back(const std::string& str)
{
//插入元素
check_n_alloc(); //检查空间大小
//构造对象
allocStr.construct(first_free++, str);
}
void strVec::reserve(const int& n)
{
//如果n小于等于当前容量,则什么也不做
if (n > capacity())
{
//重新分配
reallocate(n);
}
}
void strVec::resize(const int& n, const std::string& str)
{
if (n < capacity())
{
//如果说缩小容量,则删除后面的元素
int m = capacity() - n; //容量差值 15-10=5 则删除后五个元素
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
allocStr.destroy(--first_free);
}
cap = first_free;
}
else
{
//否则增大容量,末尾填充str
reallocate(n);
while (first_free != cap)
{
allocStr.construct(first_free++, str);
}
}
}
std::pair<std::string*, std::string*> strVec::alloc_n_copy(const std::string* beg, const std::string* end)
{
auto p = allocStr.allocate(end - beg); //分配end - beg个大小的内存空间,返回未构造的初始的位置
//拷贝内存到新的内存空间,uninitialized_copy返回拷贝结束后的位置,这个位置就是first_free的位置,p就是element的位置
return { p,std::uninitialized_copy(beg, end, p) };
}
void strVec::free()
{
if (element)
{
#if 0
//for_each销毁
std::for_each(begin(), end(), [&](std::string& str)
{
allocStr.destroy(&str);
});
#elif 0
//逆序销毁旧元素
/*for (auto eleBeg = first_free; eleBeg != element;)
{
allocStr.destroy(--eleBeg);
}*/
#else
//正序销毁旧元素
for (auto elebeg = element; elebeg != first_free;)
{
allocStr.destroy(elebeg++);
}
#endif
allocStr.deallocate(element, cap - element);
}
}
void strVec::check_n_alloc()
{
//内存不够
if (size() == capacity())
{
reallocate();
}
}
void strVec::reallocate()
{
/*
在重新分配空间的时候,移动而不是拷贝构造
*/
//申请两倍的空间
auto NewSpace = (size() == 0) ? 1 : 2 * size();
//分配新内存
auto pNew = allocStr.allocate(NewSpace);
auto dest = pNew;
auto old = element;
for (size_t i = 0; i != size(); i++)
{
//移动构造旧的内存里的数据,移动到新的内存空间里
allocStr.construct(dest++, std::move(*old++));
}
free(); //释放旧内存
//更新数据
element = pNew;
first_free = dest;
cap = element + NewSpace;
}
void strVec::reallocate(int n)
{
auto NewSpace = n;
//分配新内存
auto pNew = allocStr.allocate(NewSpace);
auto dest = pNew;
auto old = element;
for (size_t i = 0; i != size(); i++)
{
//移动构造旧的内存里的数据,移动到新的内存空间里
allocStr.construct(dest++, std::move(*old++));
}
free(); //释放旧内存
//更新数据
element = pNew;
first_free = dest;
cap = element + NewSpace;
}
内存管理器的测试:设计自定义的String类。
/*
char* 类型的内存分配器
*/
class String
{
public:
String();
String(const char* str);
String(const String& other);
String& operator=(const String& other);
~String();
size_t size() const { return end - element; }
//重新分配内存
public:
private:
void free();
std::pair<char*, char*> alloc_n_copy(const char* beg,const char* end);
//void reallocapacity();
char* element;
char* end;
std::allocator<char> alloCh; //内存分配器
};
int main()
{
String s{"woaini"};
String s1{ s };
String s2;
s2 = s1;
return 0;
}
String::String()
:element(nullptr),end(nullptr)
{
}
String::String(const char* str)
{
//分配内存
int len = strlen(str);
auto pStr = alloc_n_copy(str, str + len);
element = pStr.first;
end = pStr.second;
}
String::String(const String& other)
{
auto pNew = alloc_n_copy(other.element, other.end);
element = pNew.first;
end = pNew.second;
}
String& String::operator=(const String& other)
{
auto pNew = alloc_n_copy(other.element, other.end);
free();
element = pNew.first;
end = pNew.second;
return *this;
}
String::~String()
{
free();
}
void String::free()
{
if (element)
{
std::for_each(element, end, [&](char& str)
{
alloCh.destroy(&str);
});
alloCh.deallocate(element, end - element);
}
}
std::pair<char*, char*> String::alloc_n_copy(const char* beg, const char* end)
{
auto p = alloCh.allocate(end - beg);
return { p,std::uninitialized_copy(beg,end,p) };
}
本文来自博客园,作者:hugeYlh,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/helloylh/p/17209641.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号