C++设计模式:原型模式(详解+实现案例)
原型模式
原型模式:
用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象,简单理解就是“克隆指定对象”
使用场景
某些结构复杂的对象的创建工作中由于需求的变化,这些对象经常面临着剧烈的变化,但是他们却拥有比较稳定一致的接口。此时便可以使用原型模式。
实现步骤
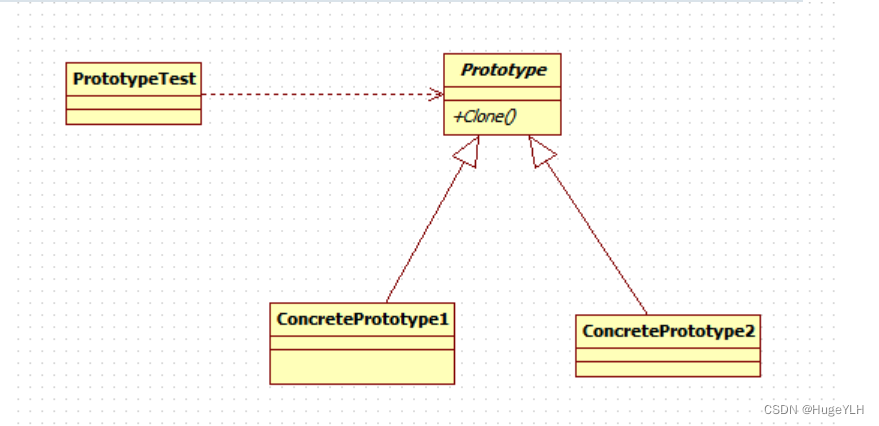
- 提供一个抽象原型类:规定了具体原型对象必须实现的接口。
- 提供多个具体原型类:实现抽象原型类的
clone()方法,它是可被复制的对象。 - 提供访问类:使用具体原型类中的
clone()方法来复制新的对象。
案例一
最简单的原型模式,其实就是调用抽象原型类中的clone,使得对象可以直接通过克隆来创建对象。
优点:
- 提高性能
- 避免使用构造函数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//抽象原型类
class Dog
{
public:
virtual ~Dog() {}
virtual Dog* clone() = 0; //克隆方法
virtual void play() = 0; //其他公共接口
};
//具体原型类
class Twoha :public Dog
{
public:
Twoha(string name)
:name{ name } {}
//拷贝构造函数(深拷贝)
Twoha(const Twoha& lhs)
{
//存在指针则必须使用深拷贝
name = lhs.name;
}
//实现抽象方法
Dog* clone()
{
return new Twoha{ *this };
}
void play()
{
cout << "我是一只" << name << endl;
}
private:
string name;
};
int main()
{
Dog* dog = new Twoha{ "二哈" };
Dog* Eha1 = dog->clone();
Dog* Eha2 = dog->clone();
Eha1->play();
Eha2->play();
delete dog;
delete Eha1;
delete Eha2;
return 0;
}
案例二
//1. 抽象原型类
class Shape
{
public:
virtual ~Shape() {}
virtual Shape* clone() = 0;
virtual int getid() = 0;
virtual string getType() = 0;
protected:
string Type;
private:
int id;
};
//2. 三个形状具体原型
class Circle :public Shape
{
public:
Circle(string Type, int id) :Type(Type), id(id) {}
~Circle() {}
//Circle(const Circle& lhs) { Type = lhs.Type, id = lhs.id; }
Shape* clone() { return new Circle{ *this }; }
int getid() { return id; }
string getType() { return Type; }
protected:
string Type;
private:
int id;
};
class Rectangle :public Shape
{
public:
Rectangle(string Type, int id) :Type(Type), id(id) {}
~Rectangle() {}
Rectangle(const Rectangle& lhs) { Type = lhs.Type, id = lhs.id; }
Shape* clone() { return new Rectangle{ *this }; }
int getid() { return id; }
string getType() { return Type; }
protected:
string Type;
private:
int id;
};
class Square :public Shape
{
public:
Square(string Type, int id) :Type(Type), id(id) {}
~Square() {}
Square(const Square& lhs) { Type = lhs.Type, id = lhs.id; }
Shape* clone() { return new Square{ *this }; }
int getid() { return id; }
string getType() { return Type; }
protected:
string Type;
private:
int id;
};
//3. 存储对象种类的数据库
class ShapeType
{
public:
~ShapeType()
{
for (auto& x : ShapeMap)
{
delete x.second;
x.second = nullptr;
}
}
//构造原始对象
ShapeType()
{
Circle* circle = new Circle{ "圆形",1 };
Square* square = new Square{"正方形",2};
Rectangle* rectangle = new Rectangle{"矩形",3};
ShapeMap.emplace(circle->getType(), circle);
ShapeMap.emplace(square->getType(), square);
ShapeMap.emplace(rectangle->getType(), rectangle);
}
//根据你所需要的种类来获得克隆对象
Shape* getShape(string Type)
{
return ShapeMap[Type]->clone();
}
private:
unordered_map<string, Shape*> ShapeMap;
};
int main()
{
//1. 创建对象种类库
ShapeType obj;
//2. 从对象库中获得对象的克隆体(getShape函数返回某个对象的克隆)
Shape* m_circle = obj.getShape("圆形");
Shape* m_Square = obj.getShape("正方形");
Shape* m_Rectangle = obj.getShape("矩形");
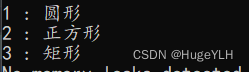
cout << m_circle->getid() << " : " << m_circle->getType() << endl;
cout << m_Square->getid() << " : " << m_Square->getType() << endl;
cout << m_Rectangle->getid() << " : " << m_Rectangle->getType() << endl;
delete m_circle;
delete m_Square;
delete m_Rectangle;
return 0;
}
优缺点
优点
- 如果创建新的对象比较复杂,可以利用原型模式简化对象的创建过程,同时也能够提高效率。
- 简化对象的创建,无需理会创建过程。
- 可以在程序运行时(对象属性发生了变化)获得一份内容相同的实例,他们之间不会相互干扰
缺点
- 每一个类都必须配备一个克隆方法,对于已有的没有克隆方法的类来说是致命的。
本文来自博客园,作者:hugeYlh,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/helloylh/p/17209627.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号