尚硅谷【SpringBoot】入门
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av20965295/?p=2


缺点: 基于springframe的封装 对framework api需要熟悉

2微服务
2014 martin fowler
微服务
传统架构模式单体应用
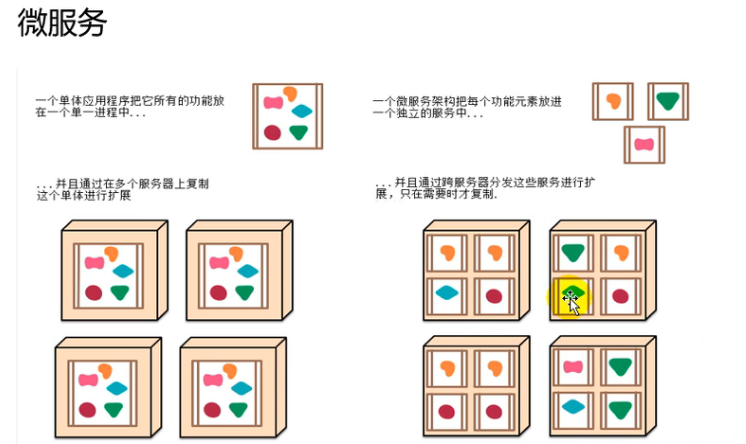
用springboot快速构建一个微服务单元
### 1、MAVEN设置;
给maven 的settings.xml配置文件的profiles标签添加
```xml
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
</profile>
```
### 2、IDEA设置
整合maven进来;
setting
### 1、创建一个maven工程;(jar)
### 2、导入spring boot相关的依赖
```xml
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.9.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
```
### 3、编写一个主程序;启动Spring Boot应用
``java
/**
* @SpringBootApplication 来标注一个主程序类,说明这是一个Spring Boot应用
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloWorldMainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Spring应用启动起来
SpringApplication.run(HelloWorldMainApplication.class,args);
}
}
```
### 4、编写相关的Controller、Service
```java
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "Hello World!";
}
}
```
### 5、运行主程序测试
### 6、简化部署
```xml
<!-- 这个插件,可以将应用打包成一个可执行的jar包;-->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
```
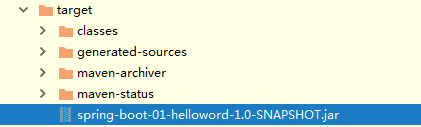
将这个应用打成jar包,直接使用java -jar的命令进行执行;
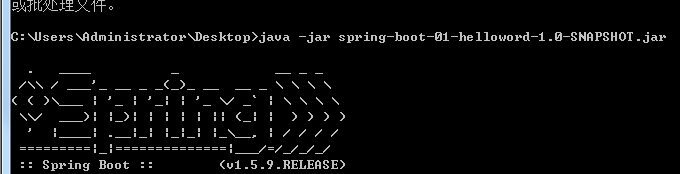
## 5、Hello World探究
### 1、POM文件
#### 1、父项目
```xml
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.9.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
他的父项目是
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>1.5.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependencies</relativePath>
</parent>
他来真正管理Spring Boot应用里面的所有依赖版本;
以后我们导入依赖默认是不需要写版本;(没有在dependencies里面管理的依赖自然需要声明版本号)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
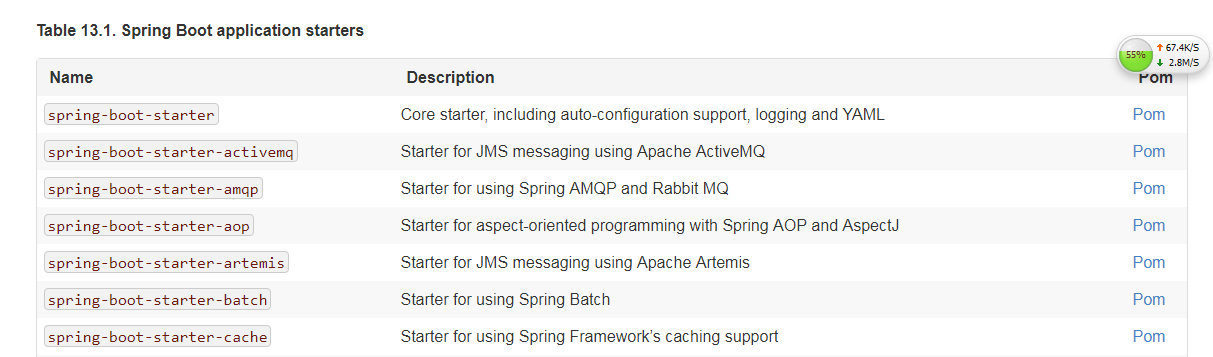
spring-boot-starter-==web==:
spring-boot-starter:spring-boot场景启动器;帮我们导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的组件;
Spring Boot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starters(启动器),只需要在项目里面引入这些starter相关场景的所有依赖都会导入进来。要用什么功能就导入什么场景的启动器https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.5.20.BUILD-SNAPSHOT/reference/htmlsingle/#using-boot-starter
/**
* @SpringBootApplication 来标注一个主程序类,说明这是一个Spring Boot应用
*/
@SpringBootApplication: Spring Boot应用标注在某个类上说明这个类是SpringBoot的主配置类,SpringBoot就应该运行这个类的main方法来启动SpringBoot应用;
该注解为组合注解
@SpringBootConfiguration:Spring Boot的配置类;
标注在某个类上,表示这是一个Spring Boot的配置类;
@Configuration:配置类上来标注这个注解;
配置类 ----- 配置文件;配置类也是容器中的一个组件;@Component
@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置功能;
以前我们需要配置的东西,Spring Boot帮我们自动配置;@EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自动配置功能;这样自动配置才能生效;
@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class):
Spring的底层注解@Import,给容器中导入一个组件;导入的组件由AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class;
==将主配置类(@SpringBootApplication标注的类)的所在包及下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器;==
@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class);给容器中导入组件?
EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector:导入哪些组件的选择器;
将所有需要导入的组件以全类名的方式返回;这些组件就会被添加到容器中;
会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration);就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件,并配置好这些组件;
1、IDEA:使用 Spring Initializer快速创建项目 (需要联网)
IDE都支持使用Spring的项目创建向导快速创建一个Spring Boot项目;
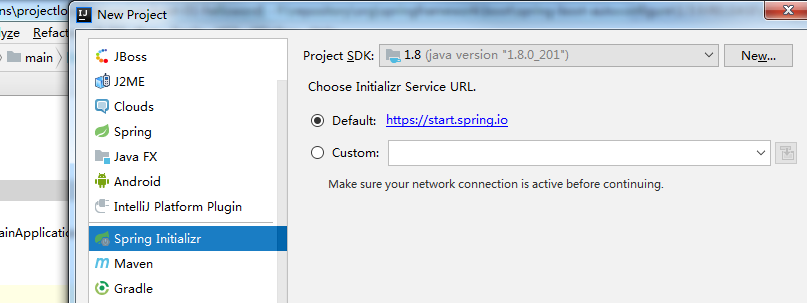
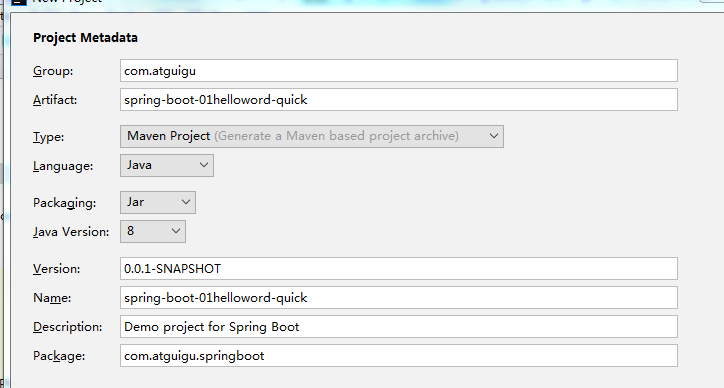
选择我们需要的模块;向导会联网创建Spring Boot项目;
默认生成的Spring Boot项目;
-
主程序已经生成好了,我们只需要我们自己的逻辑
-
resources文件夹中目录结构
-
static:保存所有的静态资源; js css images;
-
templates:保存所有的模板页面;(Spring Boot默认jar包使用嵌入式的Tomcat,默认不支持JSP页面);可以使用模板引擎(freemarker、thymeleaf);
-
application.properties:Spring Boot应用的配置文件;可以修改一些默认设置;
![]()
-
2、STS使用 Spring Starter Project快速创建项目
1、配置文件
SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件,配置文件名是固定的;
•application.properties
•application.yml
配置文件的作用:修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值;SpringBoot在底层都给我们自动配置好;
YAML(YAML Ain't Markup Language)
YAML A Markup Language:是一个标记语言
YAML isn't Markup Language:不是一个标记语言;
标记语言:
以前的配置文件;大多都使用的是 xxxx.xml文件;
YAML:以数据为中心,比json、xml等更适合做配置文件;
YAML:配置例子
server
XML:
<server>
<port>8081</port>
</server>
2、YAML语法:
1、基本语法
k:(空格)v:表示一对键值对(空格必须有);
以空格的缩进来控制层级关系;只要是左对齐的一列数据,都是同一个层级的
server
2、值的写法
字面量:普通的值(数字,字符串,布尔)
k: v:字面直接来写;
字符串默认不用加上单引号或者双引号;
"":双引号;特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思
name: "zhangsan \n lisi":输出;zhangsan 换行 lisi
'':单引号;特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据
name: ‘zhangsan \n lisi’:输出;zhangsan \n lisi
对象、Map(属性和值)(键值对):
k: v:在下一行来写对象的属性和值的关系;注意缩进
对象还是k: v的方式
friends
行内写法:
friends
数组(List、Set):
用- 值表示数组中的一个元素
pets
行内写法
pets
配置文件
person
javaBean:

/** * 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中 * @ConfigurationProperties:告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定; * prefix = "person":配置文件中哪个下面的所有属性进行一一映射 * * 只有这个组件是容器中的组件,才能容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties功能; * */ @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") public class Person { private String lastName; private Integer age; private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog;

server: port: 8081 person: lastName: zhangsan age: 18 boss: false birth: 2017/12/12 maps:{k1: v1,k2: v2} lists: - lisi - wangwu dog: name: xiaogou age: 2
<!--导入配置文件处理器,配置文件进行绑定就会有提示-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
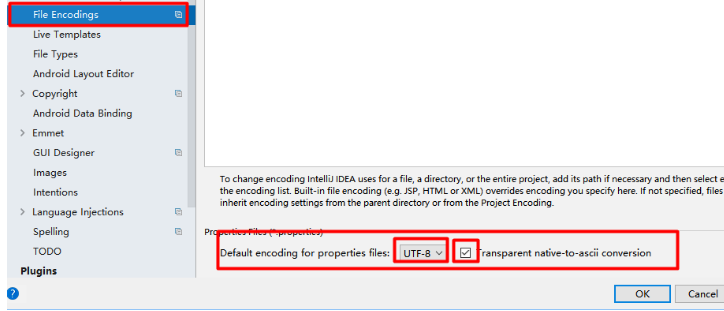
1、properties配置文件在idea中默认utf-8可能会乱码
调整
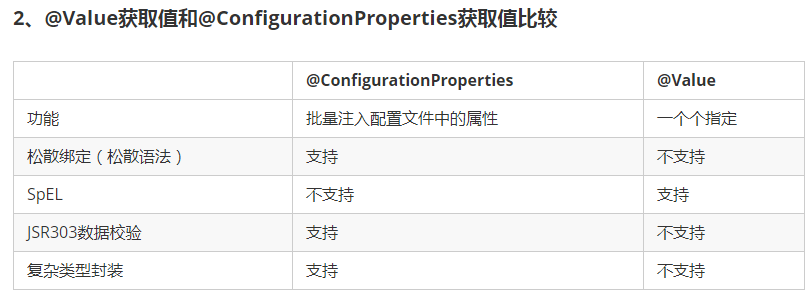
如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value;
如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties;
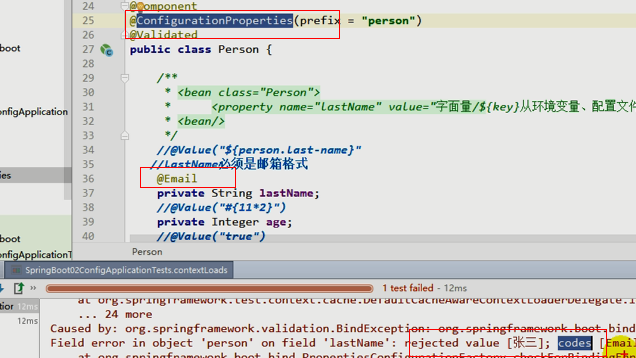
校验@ConfigurationProperties条件下 校验生效 email格式没通过
Spring Boot里面没有Spring的配置文件,我们自己编写的配置文件,也不能自动识别;
想让Spring的配置文件生效,加载进来;@ImportResource标注在一个配置类上
SpringBoot推荐给容器中添加组件的方式;推荐使用全注解的方式
1、配置类@Configuration------>Spring配置文件
2、使用@Bean给容器中添加组件
/**
* @Configuration:指明当前类是一个配置类;就是来替代之前的Spring配置文件
*
* 在配置文件中用<bean><bean/>标签添加组件
*
*/
${random.value}、${random.int}、${random.long}
${random.int(10)}、${random.int[1024,65536]}
2、占位符获取之前配置的值,如果没有可以是用:指定默认值
person.last-name=张三${random.uuid}
person.age=${random.int}
person.birth=2017/12/15
person.boss=false
person.maps.k1=v1
person.maps.k2=14
person.lists=a,b,c
person.dog.name=${person.hello:hello}_dog
person.dog.age=15
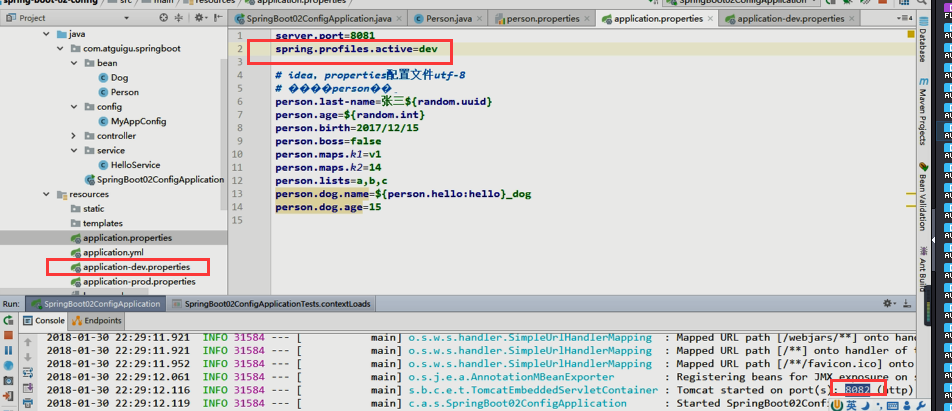
1、多Profile文件
我们在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml
默认使用application.properties文件里的配置;
application.properties里激活其他properties环境配置
2、yml支持多文档块方式
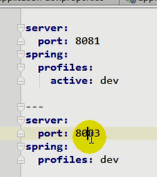
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles:
active: prod
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8084
spring:
profiles: prod #指定属于哪个环境
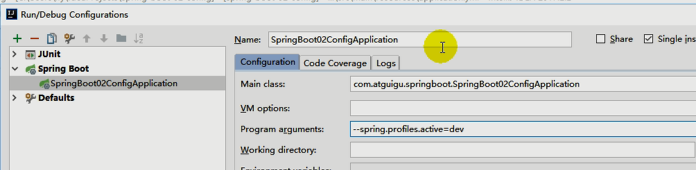
3、激活指定profile
2、命令行:
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev;
可以直接在测试的时候,配置传入命令行参数
3、虚拟机参数;
-Dspring.profiles.active=dev
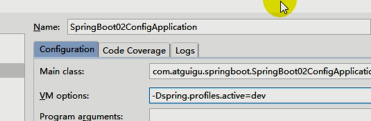
命令行参数
springboot 启动会扫描以下位置的application.properties或者application.yml文件作为Spring boot的默认配置文件
–file:./config/
–file:./
–classpath:/config/ classpath(resource路径)
–classpath:/
优先级由高到底,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置;
SpringBoot会从这四个位置全部加载主配置文件;互补配置;
==我们还可以通过spring.config.location来改变默认的配置文件位置==
项目打包好以后,我们可以使用命令行参数的形式,启动项目的时候来指定配置文件的新位置;指定配置文件和默认加载的这些配置文件共同起作用形成互补配置;
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.config.location=G:/application.properties
==SpringBoot也可以从以下位置加载配置; 优先级从高到低;高优先级的配置覆盖低优先级的配置,所有的配置会形成互补配置==
1.命令行参数
所有的配置都可以在命令行上进行指定
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8087 --server.context-path=/abc
多个配置用空格分开; --配置项=值
2.来自java:comp/env的JNDI属性
3.Java系统属性(System.getProperties())
4.操作系统环境变量
5.RandomValuePropertySource配置的random.*属性值
==由jar包外向jar包内进行寻找;==
==优先加载带profile==
6.jar包外部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
7.jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
==再来加载不带profile==
8.jar包外部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
9.jar包内部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
10.@Configuration注解类上的@PropertySource
11.通过SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties指定的默认属性
所有支持的配置加载来源;
配置文件到底能写什么?怎么写?自动配置原理;application.porterty
1、自动配置原理:
1)、SpringBoot启动的时候加载主配置类,开启了自动配置功能 ==@EnableAutoConfiguration==
2)、@EnableAutoConfiguration 作用:
-
利用EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector给容器中导入一些组件?
-
可以查看selectImports()方法的内容;
-
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);获取候选的配置
-
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()
扫描所有jar包类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories
把扫描到的这些文件的内容包装成properties对象
从properties中获取到EnableAutoConfiguration.class类(类名)对应的值,然后把他们添加在容器中
-
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.jest.JestAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceResolverAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceDelegatingViewResolverAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.SitePreferenceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.reactor.ReactorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.FallbackWebSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.OAuth2AutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.SocialWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.FacebookAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.LinkedInAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.TwitterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration
3)、每一个自动配置类进行自动配置功能;
4)、以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)为例解释自动配置原理;
根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效?
一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号