Java问题解读系列之String相关---String类的常用方法?
今天的题目是:String类的常用方法?
首先,我们在eclipse中定义一个字符串,然后使用alt+/就会出现String类的所有方法,如下图所示:
下面我就挑选一些常用的方法进行介绍:
首先定义两个字符串
String path1 = "C:\\Windows\\Web\\Wallpaper\\Windows\\img0.jpg";
String path2= " C:\\Windows\\Web\\Wallpaper\\Windows\\img0.jpg ";
1、charAt()方法,获取指定索引位置的字符
/**
* charAt()方法,获取指定索引位置的字符
*/
char c2 = path1.charAt(2);
System.out.println("path1的第2个字符是:"+c2+"\n");
char c3 = path1.charAt(3);
System.out.println("path1的第3个字符是:"+c3+"\n");
char c10 = path1.charAt(10);
System.out.println("path1的第10个字符是:"+c10+"\n");
上面的三个方法都是获取指定索引位置的字符,但是我用了三次输出,看着是没什么区别,其实大有学问,下面看一下他们的输出结果:
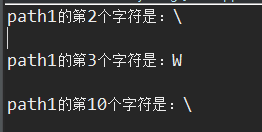
可以看出第2个字符是“\”;第3个字符是"W",而不是“\”;第10个字符也是“\”,而不是”s“,由此得出一个结论:
即字符串中的转义字符”\“将不会被视为字符串的一部分,也可以看做转义字符和被转义字符其实是占用同一个索引位置。
2、length()方法,用来获取字符串的长度
int l1 = path1.length();
System.out.println("path1的长度是:"+l1); //结果是41
3、substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex)方法:截取子串
String name1 = path1.substring(0, l1);
System.out.println("从0到"+l1+"截取的字符串是:"+name1);//C:\Windows\Web\Wallpaper\Windows\img0.jpg
String name2 = path1.substring(1, 5);
System.out.println("从1到5截取的字符串是:"+name2);// \Wi
java中对此方法的定义是:
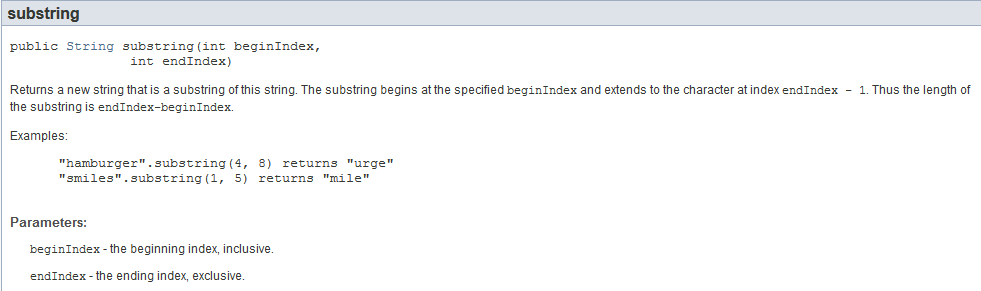
该方法中的两个参数分别指:
开始索引和结束索引,但是截取的时候不包含结束索引位置所在的字符,可以有以下两种理解:
(1)截取的是[beginIndex,endIndex-1]区间的字符串,两边都是闭区间,即包含该索引所在的字符;
(2)截取从beginIndex位置开始,长度为endIndex-beginIndex的字符串;
4、trim()方法:去掉字符串中的空格
int l2 = path2.length();
System.out.println("path2的长度是:"+l2);//45
String trim = path2.trim();
System.out.println("path2去掉空格后的长度是:"+trim.length())//41
5、equals(str)方法:比较两个字符串是否相等
boolean isequal = path1.equals(path2);
System.out.println(path1+(isequal?"等于":"不等于")+path2);//不相等,因为path2中有空格
6、contains()方法:判断字符串中是否包含某字符
boolean iscontain = path1.contains("jpg");
System.out.println(path1+"中"+(iscontain?"包含":"不包含")+"jpg");//C:\Windows\Web\Wallpaper\Windows\img0.jpg中包含jpg
7、endWith(String suffix)方法:判断字符串是否以suffix结尾,可用此方法获取文件后缀名来判断文件类型
boolean ends = path1.endsWith("jpg");//true
8、indexOf()方法:从前遍历,返回指定字符串所在的位置,有两种方法:
(1)indexOf(str):返回str在整个字符串中的位置,索引从0开始,向后查找;
(2)indexOf(str,fromIndex):返回str在整个字符串中的位置,索引从fromIndex开始,向后查找;
System.out.println("www.baidu.com".indexOf("com"));//10
System.out.println("www.baidu.com".indexOf("com",6));//10
9、lastIndexOf()方法:从后遍历,返回指定字符串所在的位置,有两种方法:
(1)lastIndexOf(str):返回str在整个字符串中的位置,索引从字符串结尾开始,向前查找;
(2)indexOf(str,fromIndex):返回str在整个字符串中的位置,索引从fromIndex开始,向前查找;
System.out.println("www.baidu.com".lastIndexOf("com"));//10
System.out.println("www.baidu.com".lastIndexOf("com",6));//-1
如果返回值是-1,则说明找不到指定的字符串。
10、split()方法:用来按照指定的字符分割字符串,返回一个字符串类型的数组
String all = "1,2,3,4,5";
String[] own = all.split(",");
System.out.println(own);//[Ljava.lang.String;@15db9742
System.out.println(own.getClass().isArray());//true,判断own是否为数组类型
System.out.println(own.length);//5
11、大小写转换方法
toLowerCase();大写转小写
toUpperCase();小写转大写
System.out.println("HELLO".toLowerCase());//hello
System.out.println("hello".toUpperCase());//HELLO
12、String.valueOf():将其他数据类型转成字符串类型
System.out.println(String.valueOf(true));//"true"
System.out.println(String.valueOf(false));//"false"
System.out.println(String.valueOf("1"));"1"
System.out.println(String.valueOf(1));"1"
13、getBytes():返回字节数组
String str = "hello,world!";
byte[] bstr = str.getBytes();
System.out.println(bstr.getClass().isArray());/true
System.out.println(bstr.getClass().isEnum());//false
System.out.println(bstr.length);//12
可以看到返回的是一个字节数组,长度为字符个数,即12
以上就是常用的字符串方法,其他可以参考jdk官方文档查询
以上是今天的问题解答,如有错误之处,望发现错误的你能够指出......
本文来自博客园,作者:bug改了我,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hellowhy/p/6537521.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号