排序算法
通常面试的时候先让你来个冒泡算法,背下来就行吧
// keshan.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
void bubble_sort(int a[],int n){
int i,j,tmp;
for(j = 0;j<n-1;j++){
for(int i=0;i<n-1-j;i++){
if(a[i]<a[i+1]){
tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[i+1];
a[i+1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int a[] = {3,4,5,2,14};
bubble_sort(a,5);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
printf("%d\n",a[i]);
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
还有直接插入排序算法
请参见郑莉老师的c++教程
[ ]看成一个被插对象,外面的依次插入
算法的程序为:
//9_11.h
#ifndef ARRAY_BASED_SORTING_FUNCTIONS
#define ARRAY_BASED_SORTING_FUNCTIONS
//用直接插入排序法对数组A中的元素进行升序排列
template <class T>
void InsertionSort(T A[], int n)
{
int i, j;
T temp;
// 将下标为1~n-1的元素逐个插入到已排序序列中适当的位置
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
//从A[i-1]开始向A[0]方向扫描各元素,寻找适当位置插入A[i]
j = i;
temp = A[i];
while (j > 0 && temp < A[j-1])
{ //逐个比较,直到temp>=A[j-1]时,j便是应插入的位置。
//若达到j==0,则0是应插入的位置。
A[j] = A[j-1]; //将元素逐个后移,以便找到插入位置时可立即插入。
j--;
}
// 插入位置已找到,立即插入。
A[j] = temp;
}
}
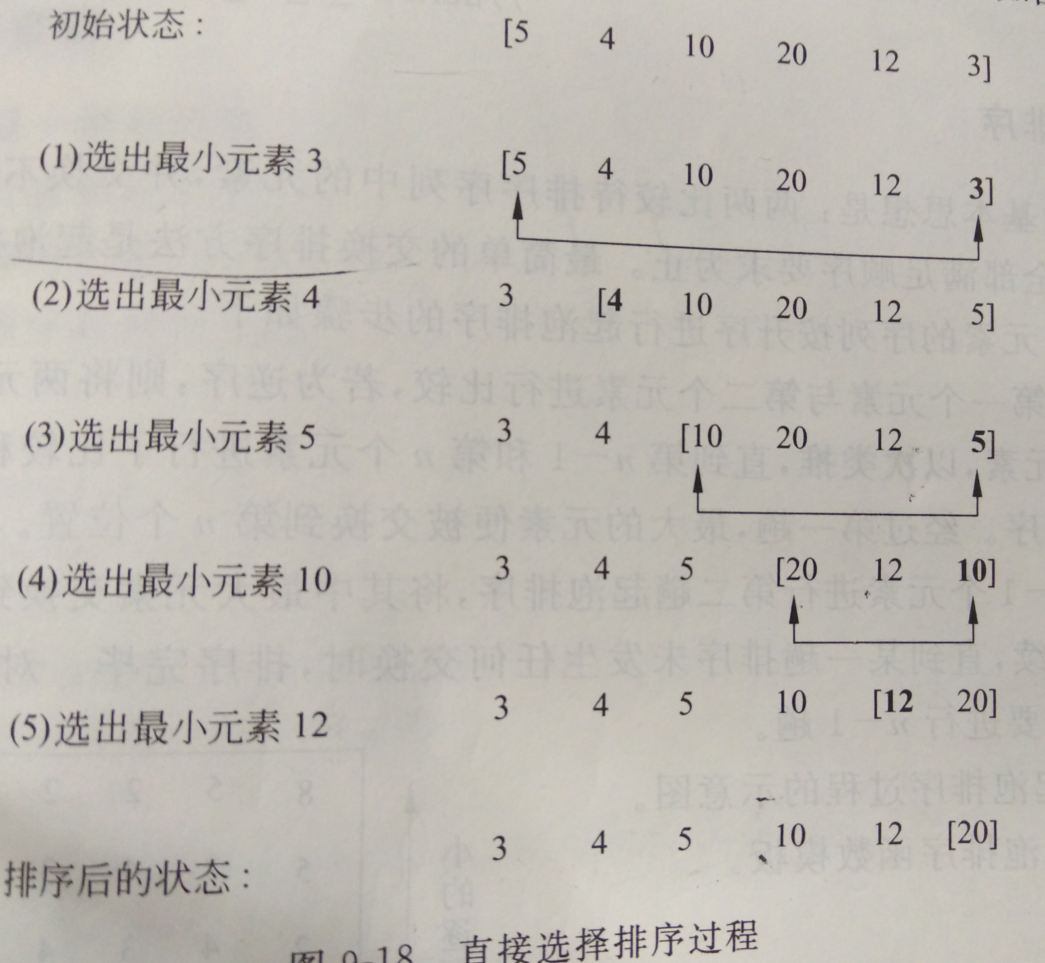
#endif选择排序的算法原理为:
笔算草稿为:
最终的代码为
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void select_sort(int a[],int n){
for(int j = 0;j<n;j++){
int min = a[j];
int index = j;
for(int i=j+1;i<n;i++){
if(min<a[i]){
min = a[i];
index = i;
}
}
int tmp = a[index];
a[index] = a[j];
a[j] = tmp;
}
}
int main(){
int a[6] ={5,4,10,20,12,3};
select_sort(a,6);
for(int i =0;i<6;i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
getchar();
return 0;
}郑莉老师的代码为:
//9_12.h
#ifndef ARRAY_BASED_SORTING_FUNCTIONS
#define ARRAY_BASED_SORTING_FUNCTIONS
// 辅助函数:交换x和y的值
template <class T>
void Swap (T &x, T &y)
{
T temp;
temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
// 用选择法对数组A的n个元素进行排序
template <class T>
void SelectionSort(T A[], int n)
{
int smallIndex; //每以趟中选出的最小元素之下标
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n-1; i++)
{
smallIndex = i; //最小元素之下标初值设为i
for (j = i+1; j < n; j++) //在元素A[i+1]..A[n-1]中逐个比较显出最小值
if (A[j] < A[smallIndex]) //smallIndex始终记录当前找到的最小值的下标
smallIndex = j;
Swap(A[i], A[smallIndex]); // 将这一趟找到的最小元素与A[i]交换
}
}
#endif
可以看出更简洁
算法实现的步骤为:
1.举个例子理解算法
2.草稿纸上列出算法
先列一次的迭代,再列n次的
4.电脑上代码实现
体现了从特殊到一般的思想。
做这些貌似没用题的意义在于训练自己解题的基本素养,方式。要不然直接默写出来没什么意思。
对于快速排序也是常考的考点,简称快排。听了网易公开课算法导论的笔记如下
对于公开课的一个例子
对应的一个代码如下
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int& m,int& n){//注意要加&
int temp = m;
m = n;
n = temp;
}
int one_fast_sort(int a[],int n){
int i=0,j=1;
int key = a[0];
while(j<n){ //注意不能等于n
if(key>a[j]){
swap(a[i+1],a[j]);
i++;
}
j++;
}
swap(a[0],a[i]);
return i;
}
int main(){
int a[]={6,10,13,5,8,3,2,11};
int temp = one_fast_sort(a,8);
//cout<<temp<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<8;i++){
cout<<a[i]<<endl;
}
getchar();
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号