1.4 C++的for,new
for,new等
遍历循环
取别名的方式最好
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int v[]{ 12,13,14,15 };
for (auto x : v) {
cout << x << endl;
}
cout << "-------------" << endl;
for (auto x : { 17,18,19 }) {
cout << x << endl;
}
cout << "-----取别名--------" << endl;
//取别名
for (auto& x : v) {
cout << x << endl;
}
}
动态内存分配
c++中我们一般把内存分为5个区域
栈:一般函数内的局部变量都会放在这里
堆:malloc/new分配,用free/delete来释放,忘记释放后,系统回收
全局/静态存储区:放全局变量和静态变量static
常量存储区:"I Love China"
程序diamante去
栈和堆
栈:空间有限。分配块
堆:不超过实际物理内存就用,分配比较慢
malloc和free:用来分配内存和释放内存
void *malloc(int NumBytes);分配的字节数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int* p = NULL;
p = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
if (p != NULL) {
*p = 5;
cout << p << endl;
cout << *p << endl;
free(p);
}
}
指针的++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int* p = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 100);
if (p != NULL) {
int* q = p;
*q++ = 1;//*q = 1;*q = *q +1
*q++ = 5;
cout << *p << endl; //1
cout << *(p + 1) << endl;//5
}
free(p);
}
new与delete
有malloc一定有free
有new一定有delte
new用[],delete用[]
C++中主要实用new和delete创建释放内存
不在使用malloc和free
new的一般格式
(1)指针变量名 = new 类型标识符;
(2)指针变量名 = new 类型标识符(初始值);
(3)指针变量名 = new 类型标识符【内存单元个数】;
//第一种创建方式
int* myint = new int;//int *p = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
if (myint != NULL) {
*myint = 8;
cout << *myint << endl;
delete myint;
}
给定初式值
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int* myint = new int(8);//int *p = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
if (myint != NULL) {
//*myint = 8;
cout << *myint << endl;
delete myint;
}
}
第三种方式给定空间
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int* pa = new int[100];
if (pa != NULL) {
int* q = pa;
*q++ = 12;
*q++ = 18;
cout << *pa << endl;//12
cout << *(pa + 1) << endl;//18
delete[] pa;
}
}
nullptr
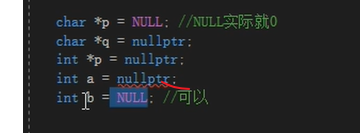
使用nullptr本质是为了防止混淆指与整型
nullptr代表空指针
不能给整型复制nullptr
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char* p = NULL;
char* q = nullptr;
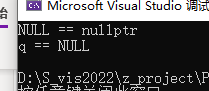
if (p == nullptr) {
cout << "NULL == nullptr" << endl;
}
if (q == NULL) {
cout << "q == NULL" << endl;
}
}
使用nullptr本质是为了防止混淆指与整型


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号