一、标准输入、标准输出流
1、System.in 和 System.out 分别代表了系统标准的输入和输出设备。
2、默认输入设备是: 键盘, 输出设备是:显示器;
3、System.in的类型是InputStream;
4、System.out的类型是PrintStream,其是OutputStream的子类,FilterOutputStream 的子类;
5、重定向:通过System类的setIn, setOut方法对默认设备进行改变。
public static void setIn(InputStream in) 重新指定输入流
public static void setOut(PrintStream out) 重新指定输出流
二、Scanner
1、Scanner
Scanner 是作为一个扫描器,它能够以标准格式以及扫描器语言环境的格式的指定文件、流中读取数据。
2、构造方法
Scanner(File source):构造一个新的 Scanner,它生成的值是从指定文件扫描的
Scanner(InputStream source):构造一个新的 Scanner,它生成的值是从指定的输入流扫描的
Scanner(Readable source):构造一个新的 Scanner,它生成的值是从指定源扫描的
Scanner(String source):构造一个新的 Scanner,它生成的值是从指定字符串扫描的
而默认情况下是从键盘输入的数据中扫描,即 System.in 这其实 是 System类中的一个输入流。
3、继承结构与方法列表

4、案例
1 @Test
2 public void test01(){
3 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
4 System.out.print("请输入一个整数:"); //从键盘输入
5 int num = input.nextInt();
6 System.out.println("num = " + num);
7 input.close();
8 }
9
10 @Test
11 public void test02() throws FileNotFoundException{
12 Scanner input = new Scanner(new FileInputStream("1.txt"));//InputStream
13
14 while(input.hasNextLine()){
15 String line = input.nextLine();
16 System.out.println(line);
17 }
18
19 input.close();
20 }
21
22 @Test
23 public void test03() throws FileNotFoundException{
24 Scanner input = new Scanner(new File("1.txt")); //InputStream
25
26 while(input.hasNextLine()){
27 String line = input.nextLine();
28 System.out.println(line);
29 }
30
31 input.close();
32 }
33
34 @Test
35 public void test04() throws FileNotFoundException{
36 Scanner input = new Scanner("1.txt"); //InputStream
37
38 while(input.hasNextLine()){
39 String line = input.nextLine();
40 System.out.println(line);
41 }
42
43 input.close();
44 }
45
46
47 @Test
48 public void test05() throws FileNotFoundException{
49 Scanner input = new Scanner(new File("d:/1.txt"),"GBK");//使用InputStream,并指定字符集
50
51 while(input.hasNextLine()){
52 String line = input.nextLine();
53 System.out.println(line);
54 }
55
56 input.close();
57 }
5、
二、标准输入、标准输出流查看代码
在 System 类中可以看到这样的三个成员变量:

其中 in 代表了标准输入流, out 代表标准输出流,err 代表标准错误输出流。
再来看 setIn() 、setOut()和 setErr() 方法:
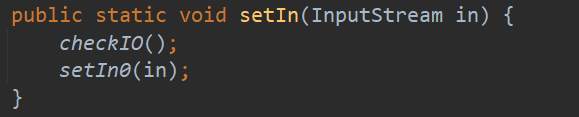
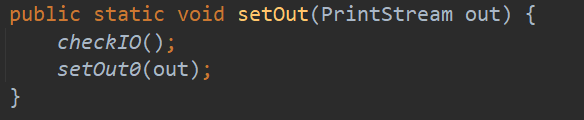
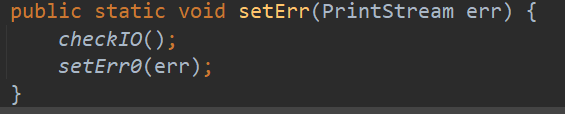
这三个静态方法首先会执行 checkIO(),然后执行一些列的 set 方法。
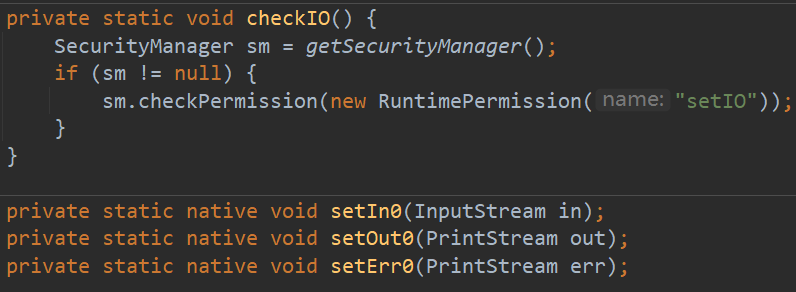
在这里可以看到调用最终的是本地方法,就是调用其他语言(调用C等底层语言)来获取使得键盘成为标准输入,使得屏幕成为标准输出。
所以我们可以调用 System 类的 setIn() 和 setOut() 方法来实现输入输出的重定向。
三、案例
1、案例一
从键盘输入字符串,要求将读取到的整行字符串转成大写输出。然后继续进行输入操作,直至当输入“e”或者“exit”时,退出程序。
方式一:使用Scanner实现,调用next()返回一个字符串
方式二:使用System.in实现。System.in ---> 转换流 ---> BufferedReader的readLine()
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 BufferedReader br = null;
3 try {
4 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
5 br = new BufferedReader(isr);
6
7 while (true) {
8 System.out.println("请输入字符串:");
9 String data = br.readLine();
10 if ("e".equalsIgnoreCase(data) || "exit".equalsIgnoreCase(data)) {
11 System.out.println("程序结束");
12 break;
13 }
14
15 String upperCase = data.toUpperCase();
16 System.out.println(upperCase);
17
18 }
19 } catch (IOException e) {
20 e.printStackTrace();
21 } finally {
22 if (br != null) {
23 try {
24 br.close();
25 } catch (IOException e) {
26 e.printStackTrace();
27 }
28
29 }
30 }
31 }
2、案例二
Create a program named MyInput.java: Contain the methods for reading int, double, float, boolean, short, byte and String values from the keyboard.
1 import java.io.*;
2
3 public class MyInput {
4 // Read a string from the keyboard
5 public static String readString() {
6 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
7
8 // Declare and initialize the string
9 String string = "";
10
11 // Get the string from the keyboard
12 try {
13 string = br.readLine();
14
15 } catch (IOException ex) {
16 System.out.println(ex);
17 }
18
19 // Return the string obtained from the keyboard
20 return string;
21 }
22
23 // Read an int value from the keyboard
24 public static int readInt() {
25 return Integer.parseInt(readString());
26 }
27
28 // Read a double value from the keyboard
29 public static double readDouble() {
30 return Double.parseDouble(readString());
31 }
32
33 // Read a byte value from the keyboard
34 public static double readByte() {
35 return Byte.parseByte(readString());
36 }
37
38 // Read a short value from the keyboard
39 public static double readShort() {
40 return Short.parseShort(readString());
41 }
42
43 // Read a long value from the keyboard
44 public static double readLong() {
45 return Long.parseLong(readString());
46 }
47
48 // Read a float value from the keyboard
49 public static double readFloat() {
50 return Float.parseFloat(readString());
51 }
52 }
3、输出重定向
1 @Test
2 public void test01(){
3 PrintStream out = System.out;
4 System.out.println(out);
5 }
6 @Test
7 public void test02() throws FileNotFoundException{
8 System.setOut(new PrintStream("1.txt")); //指定输出流,重定向
9
10 System.out.println("aaaa");
11 System.out.println("bbb");
12 System.out.println("ccc");
13 System.out.println("ddd");
14 }
4、重定向 System.in 和 System.out
1 import java.io.FileDescriptor;
2 import java.io.FileInputStream;
3 import java.util.Scanner;
4
5 public class TestSystemIn {
6 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
7 //重定向从文件输入
8 System.setIn(new FileInputStream("java\\info.txt"));
9 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
10 while(input.hasNext()){
11 String str = input.nextLine();
12 System.out.println(str);
13 }
14 input.close();
15
16 //重定向回键盘输入
17 System.setIn(new FileInputStream(FileDescriptor.in));
18 }
19 }
20
21
22 import java.io.FileDescriptor;
23 import java.io.FileOutputStream;
24 import java.io.PrintStream;
25
26 public class TestSystemOut {
27 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
28 System.out.println("hello");
29 //重定向输出到文件
30 System.setOut(new PrintStream("java\\print.txt"));
31 System.out.println("world");
32 //重定向回控制台
33 System.setOut(new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor.out)));
34 System.out.println("java");
35 }
36 }
四、


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号