Servlet路径跳转 重定向与内部跳转的区别
本篇博客中的url-pattern标签
<url-pattern>/hs</url-pattern>
一、前端界面中
1.使用相对路径访问
index.jsp:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>$Title$</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="hs">相对路径访问Servlet</a>
</body>
</html>
a标签的目标地址中的内容与web.xml中url-pattern标签中的映射地址一致,但最前面不加/
错误情况:最前面加上 /
若把目标地址前面加上/
<a href="/hs">访问Servlet</a>
点击链接之后会显示404
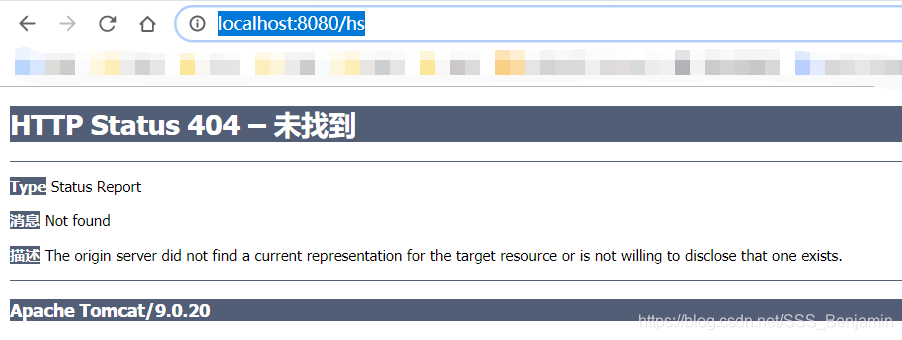
地址栏中的地址说明正在访问服务器下的hs,明显是错误的
此处,第一个/表示服务器的根目录
PS:url-pattern处必须以/开头,这里的/表示项目的跟目录
2.使用绝对路径访问
使用request.getContextPath(),表示项目的跟目录
index.jsp:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>$Title$</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="/hs">相对路径访问Servlet</a><br>
<a href= "<%=request.getContextPath()%>/hs">绝对路径访问Servlet</a>
</body>
</html>
表单中action的url地址写法与超链接方式完全相同
二、Servlet中的路径跳转
以httpServlet的doGet方法跳转到test.jsp为例
1.重定向方式
doGet:
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/test.jsp");
}
使用request.getContextPath()获得上下文对象
2.服务器内部跳转
doGet:
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
request.getRequestDispatcher("/test.jsp").forward(request,response);
}
}
这里的/表示项目的根目录
错误情况:路径直接"text.jsp"
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.sendRedirect("test.jsp");
}
或者
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
request.getRequestDispatcher("test.jsp").forward(request,response);
}
}
都无法正确跳转,因为相对路径中直接写test.jsp说明当前文件与test.jsp在同一目录下,显然是错误的
三、重定向与内部跳转的区别
| 重定向 | 内部跳转 |
|---|---|
| 也称外部跳转,是第一次请求后,服务器端向客户端发送了一个响应response告诉客户端一个新的请求地址,于是客户端以这个新地址为目标地址发出第二次request请求,此时的request对象已经不是第一次请求的request对象了,所以无法获取到第一次请求里的参数和属性。 | 通过服务器将请求转发到另外的页面或者servlet中,此时跳转到的目标页面或者servlet可以仍可获取到请求对象、请求中的属性、参数。 |
| 地址栏url会发生变化 | 地址栏url不会发生变化 |
| 可以跳转到工程以外的jsp或者servlet | 无法跳转到工程以外的jsp或者servlet |



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号