On Recognizing Texts of Arbitrary Shapes with 2D Self-Attention
和用LSTM的方法对比,
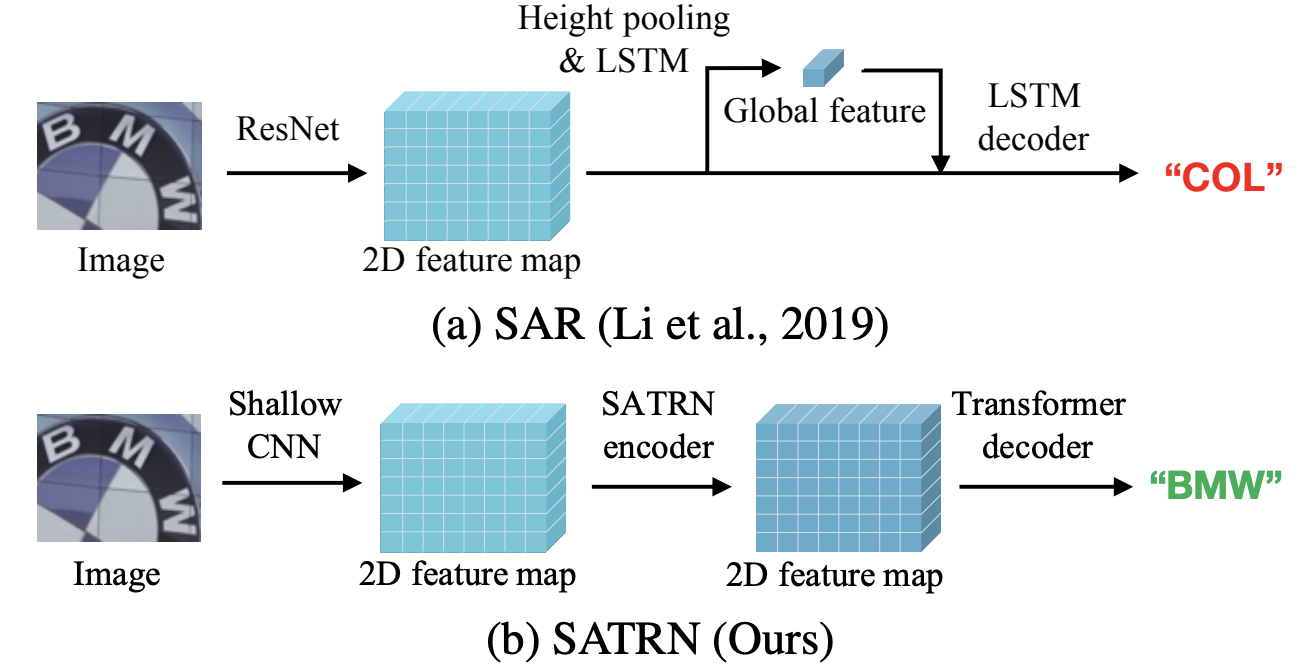
和transform相比主要区别在于编码器上,由3部分构成:
1、Shallow CNN,用于控制计算量

2、Adaptive 2D positional encoding
论文中说Transformer的Position Encoding模块可能在视觉作用中起不了作用,但是位置信息又很重要,尤其是论文致力于解决任意形状的文本识别问题,作者对位置编码进行了可学习的自适应,目的是
![]()
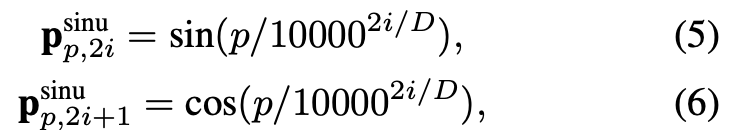
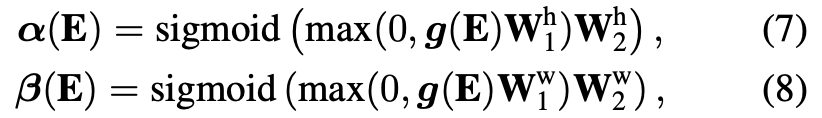
E是图像卷积特征,g是池化操作,然后经过线性层分别得到alpha和beta,再分别针对图像的h,w得到编码信息(按照Transformer位置编码方式)。
识别出的α和β直接影响高度和宽度位置编码,以控制水平轴和垂直轴之间的相对比率,以表达空间分集。通过学习从输入推断出α和β,A2DPE允许模型沿高度和宽度方向调整长度元素。
We visualize random input images from three groups with different predicted aspect ratios, as a by-product of A2DPE. Figure 7 shows the examples according to the ratios α/β. Low aspect ratio group, as expected, contains mostly horizontal samples, and high aspect ratio group contains mostly vertical samples. By dynamically adjusting the grid spacing, A2DPE reduces the representation burden for the other modules, leading to performance boost.
3、Locality-aware feedforward layer
For good STR performance, a model should not only utilize long-range dependencies but also local vicinity around single characters.
作者认为transformer的自监督长在长距离的关系处理,local关系处理的并不够好,所以在feedforward位置作者做了从a到c的替换,提升相近特征间的交互。
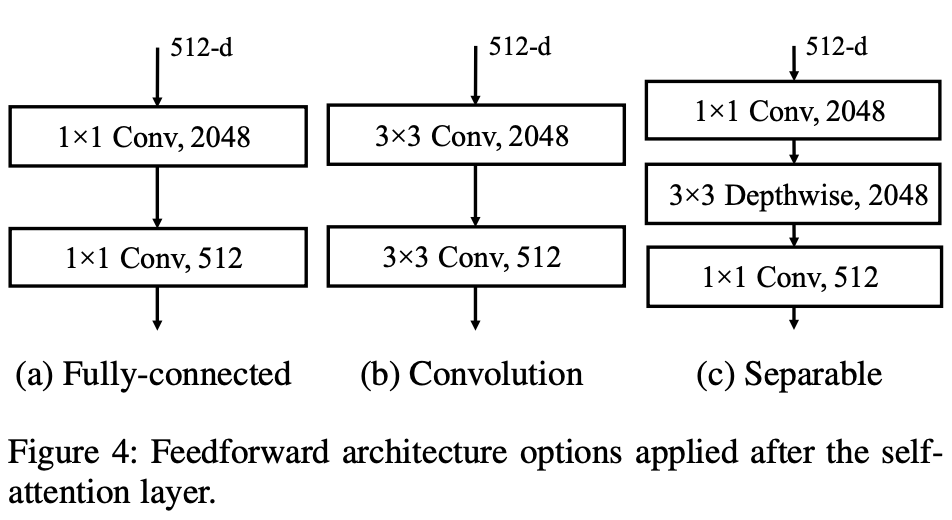
512-d的不同step的特征利用卷积进行特征交互,属于transformer对cv局部特征的一种融合,感觉应该有一定作用。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号